Configuring DWS Exception Rules
Feature Description
Some complex statements may consume a large number of resources for computing, leading to performance deterioration of the entire DWS database. To maintain system stability, DWS allows you to customize exception rules, and terminate/downgrade the tasks that hit the rules.
You can use SQL syntax to configure exception rules based on your resource and workload conditions, and associate the rules with resource pools. The system has a default exception rule to maintain stability when resources are insufficient, in case no user-defined rule is set up.
Notes and Constraints
- Clusters version 8.2.0 or later can handle exception rules. For setting exception rules on a single DN's maximum bandwidth, you need cluster version 8.2.1 or later.
- Cluster version 8.2.1 supports downgrading of exception rules (note that Decoupled storage and compute clusters do not). All exception rules are compatible with downgrading behavior. After downgrading, only network resource preemption is affected, lowering its priority. Downgraded network queries will only be scheduled when there are no normal queries in the system.
- The default exception rules are supported only by clusters of version 8.2.0 or later. After a cluster of an earlier version is upgraded to version 8.2.0 or later, the default exception rules do not take effect. You can create exception rules as needed.
- The default exception rule default_memsize is added to the cluster version 9.1.0.100, but it takes effect only in the newly installed cluster version 9.1.0.100 or later. When the cluster is upgraded to 9.1.0.100 or later, the default exception rules do not take effect. You can create rules as required.
- A resource pool links to several sets of exception rules that operate on an OR basis. Each set activates only when every condition within it is satisfied. A resource pool has two rule sets. The first set ends jobs after 1,200 seconds if they also use 2,000 MB of memory (setting elapsedtime to 1200 and memsize to 2000). The second set stops jobs that run for 2,400 seconds, regardless of memory usage (setting elapsedtime to 2400). Jobs terminate when either condition is met.
- Exception rules within the same group work together using an AND condition. For instance, if the execution time is set to 1,000 seconds (setting elapsedtime to 1000) and the memory limit is set to 500 MB (setting memsize to 500), the system terminates a job only when both conditions are met. Reaching just one threshold does not stop the job.
- The default exception rule applies when a user has no linked resource pool or when their resource pool lacks specific rules. If a user's resource pool has a defined rule, that rule overrides the default one.
Adding an Exception Rule
- Log in to the DWS console.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster to go to the Cluster Information page.
- In the navigation pane, choose Resource Management.
- Click the Exception Rule tab and click Add. Set the parameters listed in Table 2. An exception rule does not take effect immediately after being created. You need to bind it to a resource pool. For details, see 7.
Figure 1 Adding an exception rule
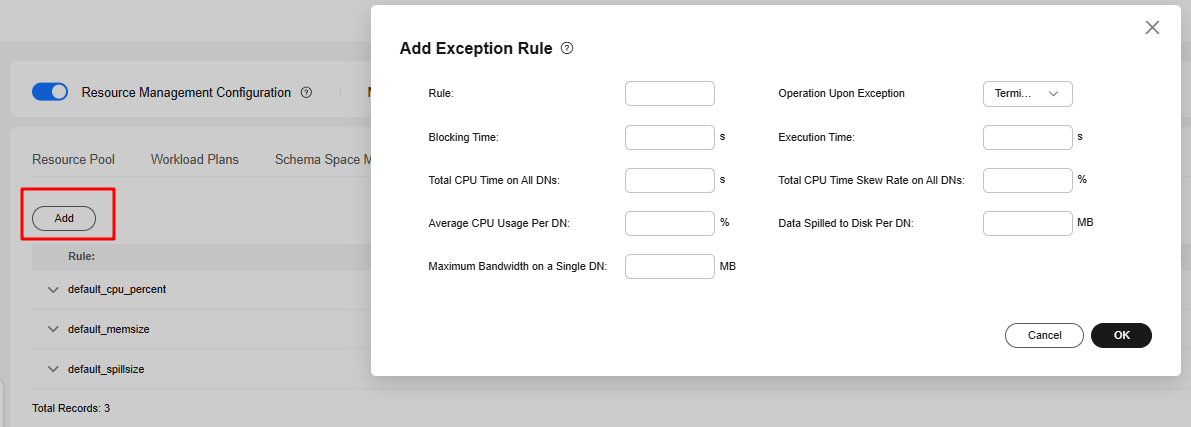
- Click OK.
Exception Rule Management Operations
- Log in to the DWS console.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster to go to the Cluster Information page.
- In the navigation pane, choose Resource Management.
- Click the Exception Rule tab, and edit or delete exception rules. Table 3 Exception rule management operations lists the operations.
Table 1 Exception rule management operations Operation
Description
Edit
Locate an exception rule and click Edit in the Operation column. In the displayed dialog box, modify the exception rule. For details, see Table 2.
To modify an exception rule, remove or set its threshold value to -1 if you wish to delete it.
Delete
Locate an exception rule and click Delete in the Operation column.
If an exception rule has been bound to an existing resource pool, the exception rule cannot be deleted. You need to unbind the exception rule from the resource pool before deleting it.
- Click OK.
User-defined Exception Rules and Default Exception Rules
The following table describes the user-defined exception rules and default exception rules supported by the current DWS version.
|
Exception Threshold Type |
Description |
Value Range (-1 disables a parameter. 0 is not supported.) |
Operation upon Exception |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Blocking Time |
Job blocking duration, in seconds. The time includes the total time spent in global and local concurrent queuing. The queuing time of each substatement (if any) in a statement is also counted. |
-1 or 1 to INT64_MAX-1 |
Terminate/Downgrade |
|
Execution Time |
Execution duration of a job, in seconds. The time indicates the duration from the start point of execution to the current time point. The execution time of each substatement (if any) in a statement is also counted. |
-1 or 1 to INT64_MAX-1 |
Terminate/Downgrade |
|
Total CPU time on all DNs. |
Total CPU time spent in executing a job on all DNs, in seconds. |
-1 or 1 to INT64_MAX-1 |
Terminate/Downgrade |
|
Total CPU Time Skew Rate on All DNs |
CPU time skew of a job executed on DNs. The value depends on the setting of elapsedtime. The system starts to check the CPU time skew of a job every 5 seconds after the job execution time reaches elapsedtime. |
-1, or 1 to 100 |
Terminate/Downgrade |
|
Average CPU Usage Per DN |
Average CPU usage of a job executed across all DNs. |
-1, or 1 to 100 |
Terminate/Downgrade |
|
Data Spilled to Disk Per DN |
Allowed maximum job data spilled to disks on a DN. The unit is MB. |
-1 or 1 to INT64_MAX-1 |
Terminate/Downgrade |
|
Maximum Bandwidth on a Single DN |
Maximum network bandwidth (MB) for a job on a single DN. |
-1 or 1 to INT64_MAX-1 |
Terminate/Downgrade |
|
Rule Name |
Description |
Operation upon Exception |
|---|---|---|
|
default_cpu_percent |
This rule is triggered if multiple jobs are running in a cluster, and the CPU usage of a resource pool reaches 90%. (If no resource pools are configured, the total CPU usage of the cluster is checked). This rule terminates the job whose execution time reached 15 minutes and average CPU usage exceeded 50%. |
Terminate |
|
default_spillsize |
This rule is triggered if the size of data spilled to disk on a single DN reaches 1/10 of the instance space during job execution in the cluster. |
Terminate |
|
default_memsize |
This event is triggered when the memory used by a job on a single DN reaches 80% or more of the minimum available memory of all DNs in the default cluster. This rule is supported only by clusters of version 9.1.0.100 or later. |
Terminate |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





