Restoring a DWS Table Snapshot
You can restore one or multiple tables in a specified snapshot backup set using a cluster or schema snapshot. You can restore a table snapshot using the following methods:
- Restoring a Table to the Original Cluster: Restore a table in a specified snapshot backup set to the original cluster if the table was modified or deleted by mistake.
- Restoring a Table or Multiple Tables to a New Cluster: Restore one or multiple tables in a specified snapshot backup set to a new cluster. In case of accidental deletion or operation on data in a table during service operations, you can use this function to find the latest snapshot that contains the table data and restore it to a new cluster. Compare the data between the old and new clusters without affecting the original table data, and then restore the data as needed.
Notes and Constraints
- One or multiple tables can be restored to a new cluster only if the cluster version is 9.1.0 or later.
- If the backup device is NFS, a table snapshot can be restored to the original cluster but not to a new cluster.
- Restoration can be performed only if the snapshot and the cluster are both in the Available state.
- A table in a read-only cluster cannot be restored.
- Fine-grained restoration does not support tables in an absolute or relative tablespace.
- You can restore fine-grained snapshots of clusters from an earlier version to a new cluster of version 9.1.0, even if the versions are different.
- You can restore the fine-grained snapshot of the 9.1.0 cluster to a new heterogeneous cluster of version 9.1.0, even if the number of nodes and specifications of the old and new clusters are different.
- Only fine-grained single-table or multi-table snapshots can be restored to a new cluster.
Prerequisites for Creating a Schema Snapshot
Manually enable the fine-grained snapshot.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Dedicated Clusters > Management > Snapshots. Alternatively, in the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster to switch to the Cluster Information page, and then choose Snapshots from the navigation pane.
- Click Create Snapshot in the upper right corner. Alternatively, choose More > Create Snapshot in the Operation column.
- Click
 next to Snapshot Level and click Configure.
next to Snapshot Level and click Configure.
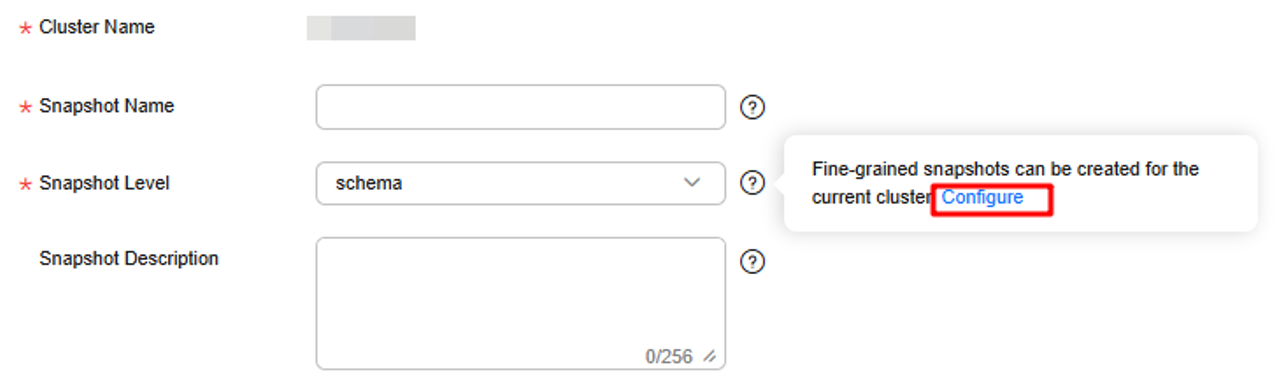
- On the Snapshots page, enable Fine-grained Snapshot. After enabling fine-grained snapshot, you can restore tables from automatic or manual snapshots.
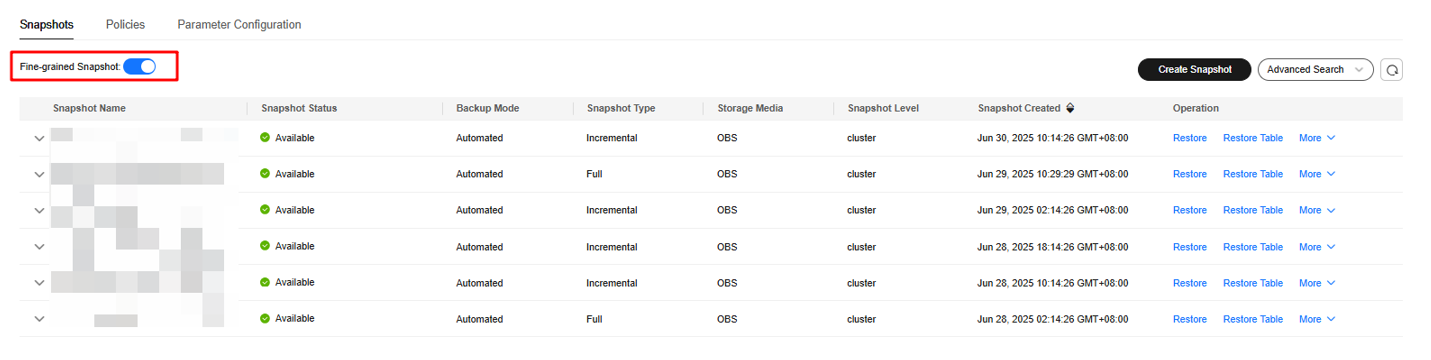
Restoring a Table to the Original Cluster
- Log in to the DWS console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Dedicated Clusters > Management > Snapshots.
- In the Operation column of a snapshot, click Restore Table.
- On the Restore Table page, set the parameters based on Table 1.
Table 1 Parameters for restoring one table Parameter
Description
Example Value
Database Name
Select a database from the drop-down list.
- Select a specified database for cluster snapshots.
- Select the database selected during backup for schema snapshots.
gaussdb
Schema
Select the schema where the table to be restored is located.
public
Source Table
Select the name of the table to be restored from the drop-down list.
Ensure that the table to be restored exists in the backup set. Otherwise, the restoration will fail.
-
Target Schema
Select the schema where the new table to be restored is located from the drop-down list.
The system creates a schema named Original schema name_dws_backup in the original database.
public_dws_backup
Target Table
Select the name of the new table to be restored from the drop-down list.
The name of the table to be restored follows this format: source-table-name+backupKey. You can choose to overwrite the original table by selecting its schema and name. Make sure the table name does not already exist. If it does, the existing table will be deleted.
The table name is case sensitive can contain up to 63 characters. It must start with a letter or underscore (_). Letters, digits underscores (_) are allowed.
-
Figure 1 Table-level restoration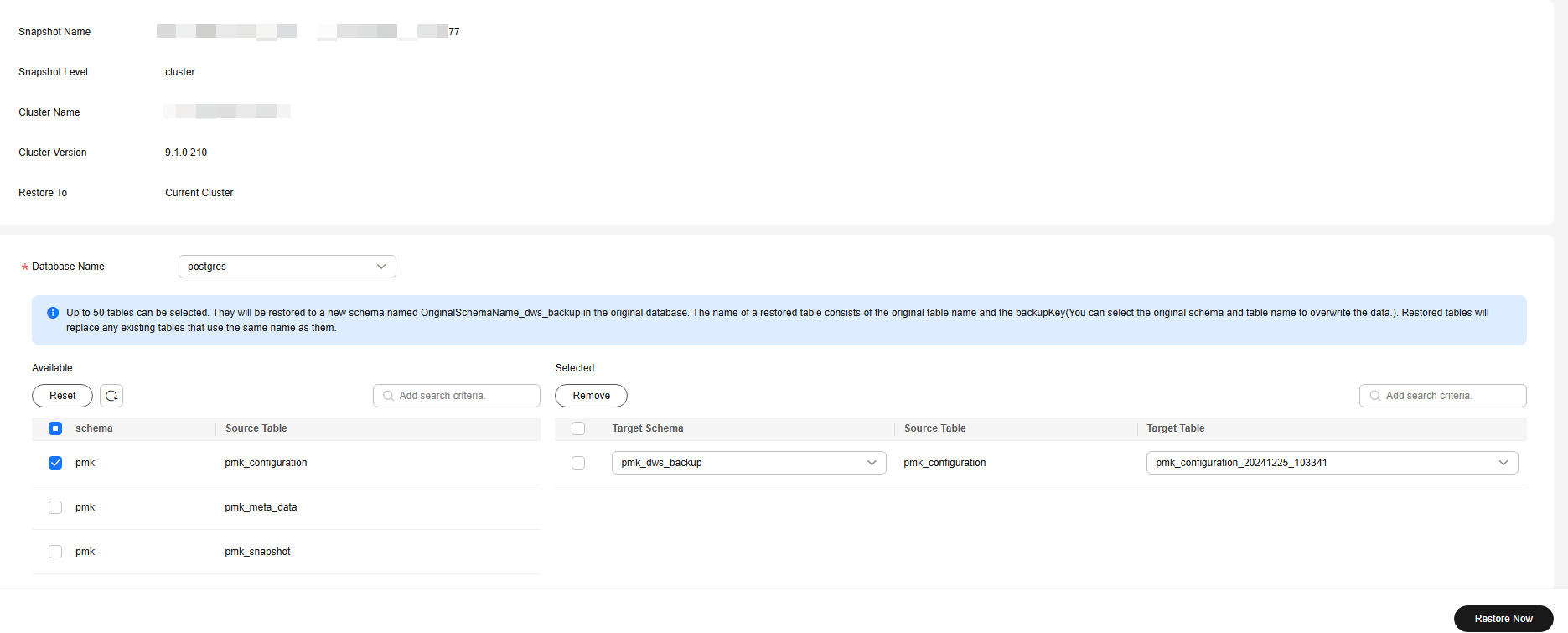
- Confirm the information and click Restore.
Restoring a Table or Multiple Tables to a New Cluster
- Log in to the DWS console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Dedicated Clusters > Management > Snapshots. Alternatively, in the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster to switch to the Cluster Information page, and then choose Snapshots from the navigation pane. All snapshots are displayed by default.
- In the Operation column of a snapshot, click Restore.
- Set the recovery level to the table level.
Figure 2 Table-level restoration
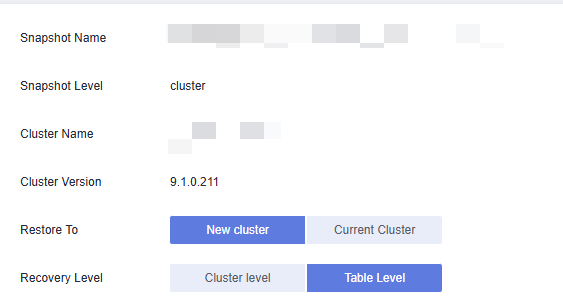
- Select the basic information about the new cluster to be restored. For details, see Creating a DWS Storage-Compute Coupled Cluster.
- If fine-grained heterogeneous recovery is available, you can select different node specifications and quantities for the new cluster, regardless of whether they match those of the original cluster.
- You need a cluster version of 9.1.0 or later to restore one or more tables to a new cluster.
- Select a single table or multiple tables. Select a database name from the drop-down list. If you select custom database configuration, you can adjust the following configuration parameters. If you select the default configuration, the parameters will use their default values. Once you've finished configuring, choose one or more tables in the table list to restore.
When you restore data to a new cluster, a new database is created. If the configuration of the new database is not the same as the snapshot database, the restoration process may fail. Before restoring, make sure to review the configuration of the original database. If it differs from the default configuration, adjust it accordingly.Figure 3 Custom database configuration

Table 2 Custom database parameters Parameter
Description
Value Range
Default Value
Template Name
Name of the template from which the database is created. DWS creates a database by copying a database template. DWS has two initial template databases template0 and template1 and a default user database gaussdb.
Names of existing databases, template0, and template1
template0
Character Encoding
- Encoding format used by the new database. The value can be a string (for example, SQL_ASCII) or an integer.
- By default, the encoding format of the template database is used. The encoding formats of the template databases template0 and template1 vary based on OS environments by default.
- The template1 database does not allow encoding customization. To specify encoding for a database when creating it, use template0.
- To specify encoding, set template to template0.
Value range: GBK, UTF8, Latin1, and SQL_ASCII
SQL_ASCII
Character Set Support
Character set used by the new database. For example, this parameter can be set using lc_collate = 'zh_CN.gbk'. The use of this parameter affects the sort order applied to strings, for example, in queries with ORDER BY, as well as the order used in indexes on text columns. The default is to use the collation order of the template database.
Valid collation order
C
Character Classification
Character classification to use in the new database. For example, this parameter can be set using lc_ctype = 'zh_CN.gbk'. The use of this parameter affects the categorization of characters, for example, lower, upper and digit. The default is to use the character classification of the template database.
Valid character classification
C
Type
Compatible database type
ORA, TD, and MySQL
ORA
- Click Next: Confirm.
- Confirm the information and click Restore.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





