Using ODBC to Connect to a Cluster
DWS allows you to use an ODBC driver to connect to the database through an ECS on the Huawei Cloud platform or over the Internet.
For details about how to use the ODBC API, see the official document.
Prerequisites
- You have downloaded ODBC driver packages dws_x.x.x_odbc_driver_for_xxx.zip (for Linux) and dws_odbc_driver_for_windows.zip (for Windows). For details, see Downloading the JDBC or ODBC Driver.
DWS also supports open source ODBC driver: PostgreSQL ODBC 09.01.0200 or later.
- You have downloaded the open-source unixODBC code file 2.3.0 from https://sourceforge.net/projects/unixodbc/files/unixODBC/2.3.0/unixODBC-2.3.0.tar.gz/download.
- You have downloaded the SSL certificate file. For details, see Downloading an SSL Certificate.
Using an ODBC Driver to Connect to a Database (Linux)
- Upload the ODBC package and code file to the Linux environment and decompress them to the specified directory.
- Log in to the Linux environment.
- Prepare unixODBC.
- Decompress the unixODBC code file.
tar -xvf unixODBC-2.3.0.tar.gz
- Compile the code file and install the driver.
1 2 3 4
cd unixODBC-2.3.0 ./configure --enable-gui=no --prefix=[your_path] make make install

- In the command, [your_path] indicates the installation path, which can be specified as required. The path must be an absolute path.
- After the unixODBC is compiled and installed, the *.so.2 library file will be in the installation directory. To create the *.so.1 library file, change LIB_VERSION in the configure file to 1:0:0.
1LIB_VERSION="1:0:0"
- This driver dynamically loads the libodbcinst.so.* library files. If one of the library files is successfully loaded, the library file is loaded. The loading priority is libodbcinst.so > libodbcinst.so.1 > libodbcinst.so.1.0.0 > libodbcinst.so.2 > libodbcinst.so.2.0.0.
For example, a directory can be dynamically linked to libodbcinst.so.1, libodbcinst.so.1.0.0, and libodbcinst.so.2. The driver file loads libodbcinst.so first. If libodbcinst.so cannot be found in the current environment, the driver file searches for libodbcinst.so.1, which has a lower priority. After libodbcinst.so.1 is loaded, the loading is complete.
- Decompress the unixODBC code file.
- Replace the driver file. (This document uses the dws_8.1.x_odbc_driver_for_x86_redhat.zip package of Red Hat as an example.)
- Decompress the dws_8.1.x_odbc_driver_for_x86_redhat.zip package.
unzip dws_8.1.x_odbc_driver_for_x86_redhat.zip
- Copy all files in the lib directory extracted from the dws_8.1.x_odbc_driver_for_x86_redhat.zip package to the [your_path]/lib directory.
- Copy psqlodbcw.la and psqlodbcw.so in the odbc/lib directory to [your_path]/lib/odbc.
- Decompress the dws_8.1.x_odbc_driver_for_x86_redhat.zip package.
- Run the following command to modify the configuration of the driver file:
vi [your_path]/etc/odbcinst.ini
Copy the following content to the file:
[DWS] Driver64=[your_path]/lib/odbc/psqlodbcw.so
The parameters are as follows:
- [DWS]: indicates the driver name. You can customize the name.
- Driver64 or Driver: indicates the path where the dynamic library of the driver resides. For a 64-bit operating system, search for Driver64 first. If Driver64 is not configured, search for Driver.
- Run the following command to modify the data source file:
vi [your_path]/etc/odbc.ini
Copy the following content to the configuration file, save the modification, and exit.
[DWSODBC] Driver=DWS Servername=10.10.0.13 Database=gaussdb Username=dbadmin Password=password Port=8000 Sslmode=allowParameter
Description
Example Value
[DSN]
Data source name.
[DWSODBC]
Driver
Driver name, corresponding to DriverName in odbcinst.ini.
Driver=DWS
Servername
IP address of the server. When the cluster is bound to an ELB, set this parameter to the IP address of the ELB.
Servername=10.10.0.13
Database
Name of the database to be connected to.
Database=gaussdb
Username
Database username.
Username=dbadmin
Password
Database user password.
Password=password
Port
Port number of the server.
Port=8000
Sslmode
SSL certification mode. This parameter is enabled for the cluster by default.
Values and meanings:
- disable: only tries to establish a non-SSL connection.
- allow: tries establishing a non-SSL connection first, and then an SSL connection if the attempt fails.
- prefer: tries establishing an SSL connection first, and then a non-SSL connection if the attempt fails.
- require: only tries establishing an SSL connection. If there is a CA file, perform the verification according to the scenario in which the parameter is set to verify-ca.
- verify-ca: tries establishing an SSL connection and checks whether the server certificate is issued by a trusted CA.
- verify-full: not supported by DWS
NOTE:The SSL mode delivers higher security than the common mode. By default, the SSL function is enabled in a cluster to allow SSL or non-SSL connections from the client. You are advised to use the SSL mode when using ODBC to connect to a DWS cluster.
Sslmode=allow

- You can view the values of Servername and Port on the DWS console. Log in to the DWS console and choose Client Connections from the navigation pane on the left. In the Data Warehouse Connection Information area, select a cluster and obtain its Private Network IP Address or Public Network IP Address. For details, see Obtaining the Connection Address of a DWS Cluster.
- Configure environment variables.
vi ~/.bashrc
Add the following information to the configuration file:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=[your_path]/lib/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH export ODBCSYSINI=[your_path]/etc export ODBCINI=[your_path]/etc/odbc.ini

It is not recommended to add LD_LIBRARY_PATH in the Kylin OS, as it may cause conflicts with the libssl.so library. The latest cluster versions 8.2.1 and 9.1.0 now include the rpath mechanism, which allows the dependency to be located without using LD_LIBRARY_PATH.
- Import environment variables.
source ~/.bashrc
- Run the following commands to connect to the database:
[your_path]/bin/isql -v DWSODBC
If the following information is displayed, the connection is successful:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
+---------------------------------------+ | Connected! | | | | sql-statement | | help [tablename] | | quit | | | +---------------------------------------+ SQL>
Using an ODBC Driver to Connect to a Database (Windows)
- Decompress ODBC driver package dws_odbc_driver_for_windows.zip (for Windows) and install psqlodbc.msi.
- Decompress the SSL certificate package to obtain the certificate file.
You have the option to deploy the certificate either automatically or manually, depending on your requirements.
- Automatic deployment:
Double-click the sslcert_env.bat file to trigger automatic deployment of the certificate to a default location.

The sslcert_env.bat file ensures the purity of the certificate environment. When the %APPDATA%\postgresql directory exists, a message will be prompted asking you whether you want to remove related directories. If you want to remove related directories, back up files in the directory.
- Manual deployment:
- Create a new folder named postgresql in the %APPDATA%\ directory.
- Copy files client.crt, client.key, client.key.cipher, and client.key.rand to the %APPDATA%\postgresql directory and change client in the file name to postgres. For example, change the name of client.key to postgres.key.
- Copy cacert.pem to %APPDATA%\postgresql and change the name of cacert.pem to root.crt.
- Automatic deployment:
- Open Driver Manager.
DWS provides 32-bit and 64-bit ODBC drivers. Choose the version suitable for your system when configuring the data source. (Assume the Windows system drive is drive C. If another disk drive is used, modify the path accordingly.)
- If you want to develop 32-bit programs in the 64-bit OS and have installed the 32-bit driver, open the 32-bit Driver Manager at C:\Windows\SysWOW64\odbcad32.exe.
Do not choose Control Panel > System and Security > Administrative Tools > Data Sources (ODBC) directly.

WOW64 is the acronym for Windows 32-bit on Windows 64-bit. C:\Windows\SysWOW64\ stores the 32-bit environment on a 64-bit system.
- If you want to develop 64-bit programs in the 64-bit OS and have installed the 64-bit driver, open the 64-bit Driver Manager at C:\Windows\System32\odbcad32.exe.
Do not choose Control Panel > System and Security > Administrative Tools > Data Sources (ODBC) directly.

C:\Windows\System32\ stores the environment consistent with the current OS. For technical details, see Windows technical documents.
- In a 32-bit OS, open C:\Windows\System32\odbcad32.exe.
Alternatively, click Computer, and choose Control Panel. Click Administrative Tools and click Data Sources (ODBC).
- If you want to develop 32-bit programs in the 64-bit OS and have installed the 32-bit driver, open the 32-bit Driver Manager at C:\Windows\SysWOW64\odbcad32.exe.
- Configure a data source to be connected to.
- On the User DSN tab, click Add and choose PostgreSQL Unicode for setup.
Figure 1 Configuring a data source to be connected to
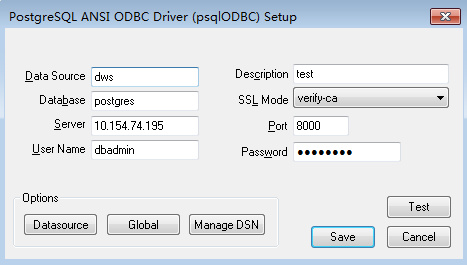
You can view the values of Server and Port on the DWS console. Log in to the DWS console and choose Client Connections from the navigation pane on the left. In the Data Warehouse Connection Information area, select a cluster and obtain its Private Network IP Address or Public Network IP Address. For details, see Obtaining the Connection Address of a DWS Cluster.
- Click Test to verify that the connection is correct. If Connection successful is displayed, the connection is correct.
- On the User DSN tab, click Add and choose PostgreSQL Unicode for setup.
- Compile an ODBC sample program to connect to the data source.
The ODBC API does not provide the database connection retry capability. You need to implement the connection retry processing in the service code.
The sample code is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83
// This example shows how to obtain DWS data through the ODBC driver. // DBtest.c (compile with: libodbc.so) #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <sqlext.h> #ifdef WIN32 #include <windows.h> #endif SQLHENV V_OD_Env; // Handle ODBC environment SQLHSTMT V_OD_hstmt; // Handle statement SQLHDBC V_OD_hdbc; // Handle connection char typename[100]; SQLINTEGER value = 100; SQLINTEGER V_OD_erg,V_OD_buffer,V_OD_err,V_OD_id; int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { // 1. Apply for an environment handle. V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV,SQL_NULL_HANDLE,&V_OD_Env); if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO)) { printf("Error AllocHandle\n"); exit(0); } // 2. Set environment attributes (version information). SQLSetEnvAttr(V_OD_Env, SQL_ATTR_ODBC_VERSION, (void*)SQL_OV_ODBC3, 0); // 3. Apply for a connection handle. V_OD_erg = SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC, V_OD_Env, &V_OD_hdbc); if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO)) { SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env); exit(0); } // 4. Set connection attributes. SQLSetConnectAttr(V_OD_hdbc, SQL_ATTR_AUTOCOMMIT, SQL_AUTOCOMMIT_ON, 0); // 5. Connect to a data source. You do not need to enter the username and password if you have configured them in the odbc.ini file. If you have not configured them, specify the name and password of the user who wants to connect to the database in the SQLConnect function. V_OD_erg = SQLConnect(V_OD_hdbc, (SQLCHAR*) "gaussdb", SQL_NTS, (SQLCHAR*) "", SQL_NTS, (SQLCHAR*) "", SQL_NTS); if ((V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS) && (V_OD_erg != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO)) { printf("Error SQLConnect %d\n",V_OD_erg); SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env); exit(0); } printf("Connected !\n"); // 6. Set statement attributes. SQLSetStmtAttr(V_OD_hstmt,SQL_ATTR_QUERY_TIMEOUT,(SQLPOINTER *)3,0); // 7. Apply for a statement handle. SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT, V_OD_hdbc, &V_OD_hstmt); // 8. Executes an SQL statement directly. SQLExecDirect(V_OD_hstmt,"drop table IF EXISTS testtable",SQL_NTS); SQLExecDirect(V_OD_hstmt,"create table testtable(id int)",SQL_NTS); SQLExecDirect(V_OD_hstmt,"insert into testtable values(25)",SQL_NTS); // 9. Prepare for execution. SQLPrepare(V_OD_hstmt,"insert into testtable values(?)",SQL_NTS); // 10. Bind parameters. SQLBindParameter(V_OD_hstmt,1,SQL_PARAM_INPUT,SQL_C_SLONG,SQL_INTEGER,0,0, &value,0,NULL); // 11. Execute the ready statement. SQLExecute(V_OD_hstmt); SQLExecDirect(V_OD_hstmt,"select id from testtable",SQL_NTS); // 12. Obtain the attributes of a certain column in the result set. SQLColAttribute(V_OD_hstmt,1,SQL_DESC_TYPE,typename,100,NULL,NULL); printf("SQLColAtrribute %s\n",typename); // 13. Bind the result set. SQLBindCol(V_OD_hstmt,1,SQL_C_SLONG, (SQLPOINTER)&V_OD_buffer,150, (SQLLEN *)&V_OD_err); // 14. Collect data using SQLFetch. V_OD_erg=SQLFetch(V_OD_hstmt); // 15. Obtain and return data using SQLGetData. while(V_OD_erg != SQL_NO_DATA) { SQLGetData(V_OD_hstmt,1,SQL_C_SLONG,(SQLPOINTER)&V_OD_id,0,NULL); printf("SQLGetData ----ID = %d\n",V_OD_id); V_OD_erg=SQLFetch(V_OD_hstmt); }; printf("Done !\n"); // 16. Disconnect from the data source and release handles. SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT,V_OD_hstmt); SQLDisconnect(V_OD_hdbc); SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC,V_OD_hdbc); SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, V_OD_Env); return(0); }
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





