DWS_2000000032 Number of Database Deadlocks in a DWS Cluster Exceeds the Threshold
Alarm Description
If the number of deadlocks in the cluster database exceeds the threshold within a specific time frame and the suppression conditions are not met, the DMS alarm module will generate an alarm. The alarm will be cleared once the DMS alarm module detects that the number of deadlocks in the cluster database is below the threshold.
Alarm Attributes
|
Alarm ID |
Alarm Category |
Alarm Severity |
Alarm Type |
Service Type |
Auto Cleared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
DWS_2000000032 |
Tenant plane |
> 10 (Critical); > 1 (Major) |
Service alarm |
DWS |
Yes |
Alarm Changes
|
Change Type |
Change Version |
Description |
Reason for Change |
|---|---|---|---|
|
New |
8.2.1.230 |
New alarm |
New alarm |
Alarm Parameters
|
Type |
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Fault Location |
Cluster name |
Cluster for which the alarm is generated. |
|
Tenant name |
Name of the tenant to which the cluster belongs. |
|
|
Alarm level |
Severity of the alarm. |
|
|
Additional Information |
Resource ID |
ID of the cluster for which the alarm is generated. |
|
Resource name |
Cluster for which the alarm is generated. |
|
|
Database name |
Name of the database for which the alarm is generated. |
|
|
First_alarm_time |
First occurrence event of an alarm, including the alarm threshold and current value. |
Impact on the System
The connection pool is unable to allocate more connections to service requests because a large number of lock requests are causing connections to be unresponsive.
Possible Causes
Resource contention and lock actions are mutually exclusive.
Procedure
- Log in to the DWS console.
- On the Alarm page, view the alarms generated in the last seven days.
- Use gsql to connect to the cluster based on the alarm information. For details, see Using the CLI to Connect to a DWS Cluster.
- Connect to the cluster and run the SQL statement to query the current lock conflict statement.
select * from pgxc_lock_conflicts;

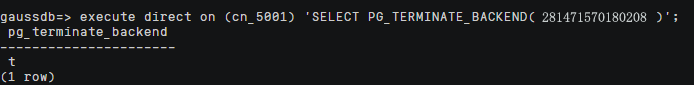
- Decide whether to terminate the lock based on the statement content. To terminate the lock, run the following statement. pid and nodename are obtained from the previous step.
execute direct on (nodename) 'SELECT PG_TERMINATE_BACKEND(pid)';
Alarm Clearance
This alarm is automatically cleared after the fault is rectified.
Related Information
None
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





