Usage
Introduction
In addition to the default authentication mode, you can also use the internal functions provided by the platform to flexibly orchestrate authentication modes for devices connecting to the platform.
Scenarios
- Device migration from third-party IoT platforms to IoTDA: You can configure a custom template to be compatible with the original authentication mode. No modification is required on the device side.
- Native access: Custom templates can support more devices.
Process
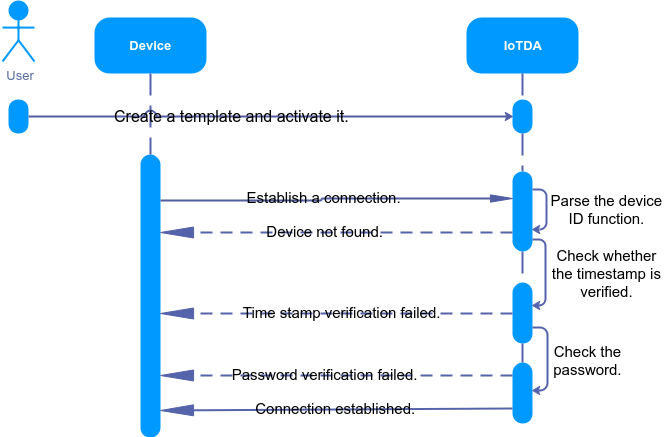
Constraints
- The device must use TLS and support Server Name Indication (SNI). The SNI must carry the domain name allocated by the platform.
- Max. templates: five for a user. Only one template can be enabled at a time.
- Max. functions nested: five layers.
- Max. content length: 4,000 characters. Chinese characters are not allowed.
- When the device uses secret authentication, the template password function must contain the original secret parameter (iotda::device:secret).
- The format of the template authentication parameter username cannot be the same as that of the custom function authentication parameter username. Otherwise, the custom function authentication is used. For example:
{deviceId}|authorizer-name={authorizer-name}|xxx - As custom authentication templates have higher priority, once you activate a custom authentication template, the platform uses the template instead of the default mode.
Our custom authentication mode enables device access without requiring reconstruction on the device side. It is important to avoid weak or verification-free modes. If the security level of your custom template is too low, it may lead to security issues. The platform does not assume any security responsibilities in such cases.
Procedure
- Create an authentication template. Specifically, log in to the IoTDA console, in the navigation pane, choose Devices > Custom Authentication, click Custom Template, and click Create Template. The authentication template used in this example is the same as that used in the default authentication.
Figure 2 Custom authentication - Creating a template

The overall content of the template is as follows:
{ "template_name": "system-default-auth", "description": "Example of the default authentication template of Huawei Cloud IoTDA", "status": "ACTIVE", "template_body": { "parameters": { "iotda::mqtt::client_id": { "type": "String" }, "iotda::mqtt::username": { "type": "String" }, "iotda::device::secret": { "type": "String" } }, "resources": { "device_id": { "Ref": "iotda::mqtt::username" }, "timestamp": { "type": "FORMAT", "pattern": "yyyyMMddHH", "value": { "Fn::SubStringAfter": [ "${iotda::mqtt::client_id}", "_0_1_" ] } }, "password": { "Fn::HmacSHA256": [ "${iotda::device::secret}", { "Fn::SubStringAfter": [ "${iotda::mqtt::client_id}", "_0_1_" ] } ] } } } }Table 1 Authentication template parameters Parameter
Item
Mandatory
Description
template_name
Template name
Yes
Template name. The name must be unique for a single user. Max. length: 128 characters. Use only letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-).
description
Description
No
Template description. Max. length: 2,048 characters. Use only letters, digits, and special characters (_?'#().,&%@!-).
status
Status
No
Template status. By default, a template is not enabled. A user can only have one enabled template at a time.
parameters
Parameter
Yes
MQTT connection parameters predefined by the platform. When a device uses password authentication, the template must contain the original secret parameter (iotda::device:secret).
The platform predefines the following parameters:
iotda::mqtt::client_id: Client Id in the MQTT connection parameter triplet
iotda::mqtt::username: User Name in the MQTT connection parameter triplet
iotda::certificate::country: device certificate (country/region, C)
iotda::certificate::organization: device certificate (organization, O)
iotda::certificate::organizational_unit: device certificate (organization unit, OU)
iotda::certificate::distinguished_name_qualifier: device certificate (distinguished name qualifier, dnQualifier)
iotda::certificate::state_name: device_certificate (province/city, ST)
iotda::certificate::common_name: device certificate (common name, CN)
iotda::certificate::serial_number: device certificate (serial number, serialNumber)
iotda::device::secret: original secret of the device
device_id
Device ID function
Yes
Function for obtaining the device ID, in JSON format. The platform parses this function to obtain the corresponding device information.
timestamp
Timestamp verification
No
Whether to verify the timestamp in the device connection information. Recommended: Enable this function if the device connection parameters (clientId and username) contain the timestamp. Verification process: The platform compares the timestamp carried by the device with the platform system time. If the timestamp plus 1 hour is less than the platform system time, the verification fails.
type
Timestamp type
No
UNIX: Unix timestamp. Long integer, in seconds.
FORMAT: formatted timestamp, for example, 2024-03-28 11:47:39 or 2024/03/28 03:49:13.
pattern
Timestamp format
No
Time format template. Mandatory when the timestamp type is FORMAT.
y: year
M: month
d: day
H: hour
m: minute
s: second
S: millisecond
Example: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss and yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss
value
Timestamp function
No
Function for obtaining the timestamp when the device establishes a connection. Mandatory when timestamp verification is enabled.
password
MQTT password function
No
Password function. Mandatory when the device authentication type is secret authentication. The template parameters must contain the original device secret parameter (iotda::device:secret). For details about the device authentication type, see Registering an Individual Device. Verification process: The platform uses parameters, such as the device's original secret, in the function to perform a calculation. If the result is the same as the password carried in the connection establishment request, the authentication is successful. Otherwise, the authentication fails.
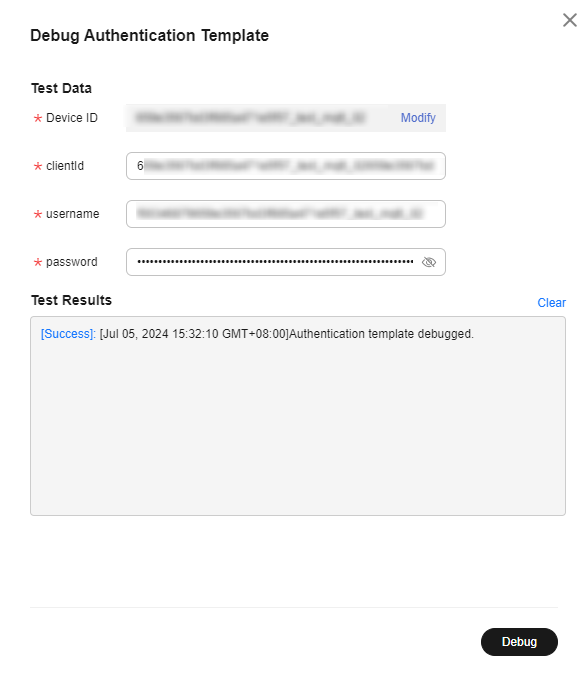
- Select a device debugging template. Click Debug, select a device for debugging, enter MQTT connection parameters, and click Debug to check the result. Note: If clientId in the standard format is used, the platform verifies whether the value of username is the same as the prefix of clientId.
Figure 3 Custom template - Debugging
After the device debugging is successful, click Enable to enable the template. Once the template is enabled, it will be used for authentication of all devices, and the enabled template cannot be modified. You are advised to modify the copy of the target template and debug it. Switch to the modified template only after the debugging is successful.
- Use MQTT.fx to simulate device connection setup. Set Broker Address to the platform access address, choose , and set port to 8883.
Figure 4 Device connection establishment
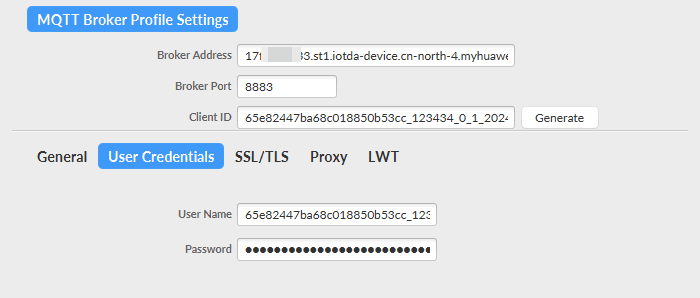 Figure 5 Device list - Device online status
Figure 5 Device list - Device online status
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





