NB-IoT (CoAP) Codec Example
This section uses a smoke detector as an example to describe how to develop a FunctionGraph codec in JavaScript for reporting properties and delivering commands over CoAP. The codec converts binary data into JSON data and provides a method for debugging.
Defining a Smoke Detector
Scenario
A smoke detector provides the following functions:
- Reporting smoke alarms (fire severity) and temperature.
- Receiving and running remote control commands, which can be used to enable the alarm function remotely. For example, the smoke detector can report the temperature on the fire scene and remotely trigger a smoke alarm for evacuation.
- The smoke detector has weak capabilities and cannot report data in JSON format defined by the device APIs, but can only report simple binary data.
Product Model
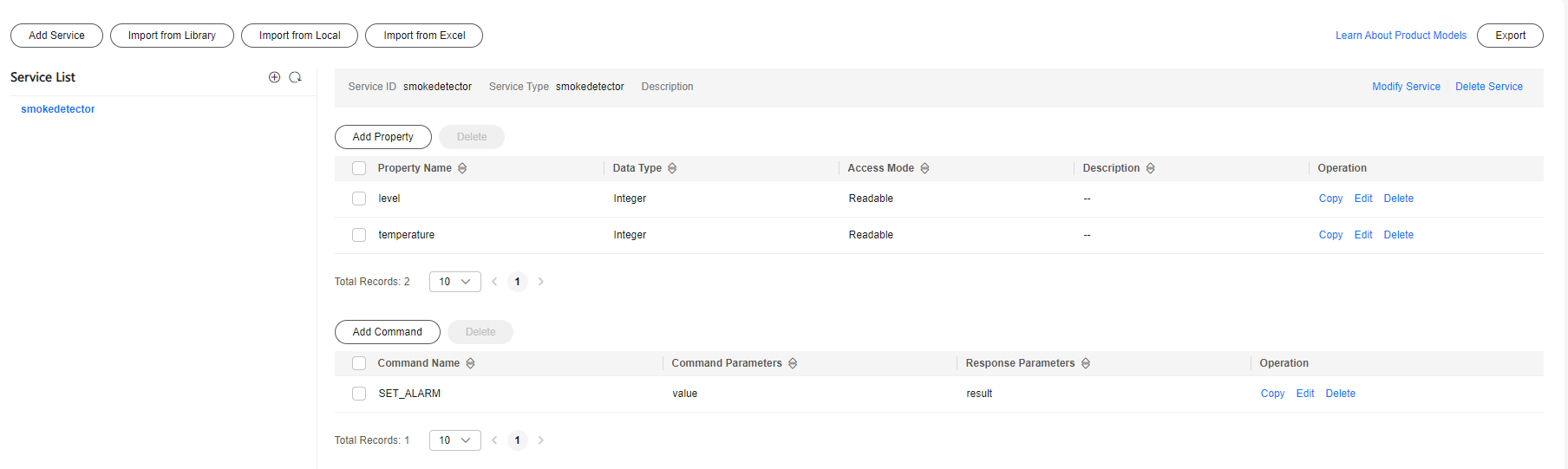
- level: indicates the fire severity.
- temperature: indicates the temperature at the fire scene.
- SET_ALARM: indicates whether to enable or disable the alarm function. The value 0 indicates that the alarm function is disabled, and 1 indicates that the alarm function is enabled. The response command result is used to report the modified alarm value.
Figure 1 Model definition - smokedetector
Developing a Codec
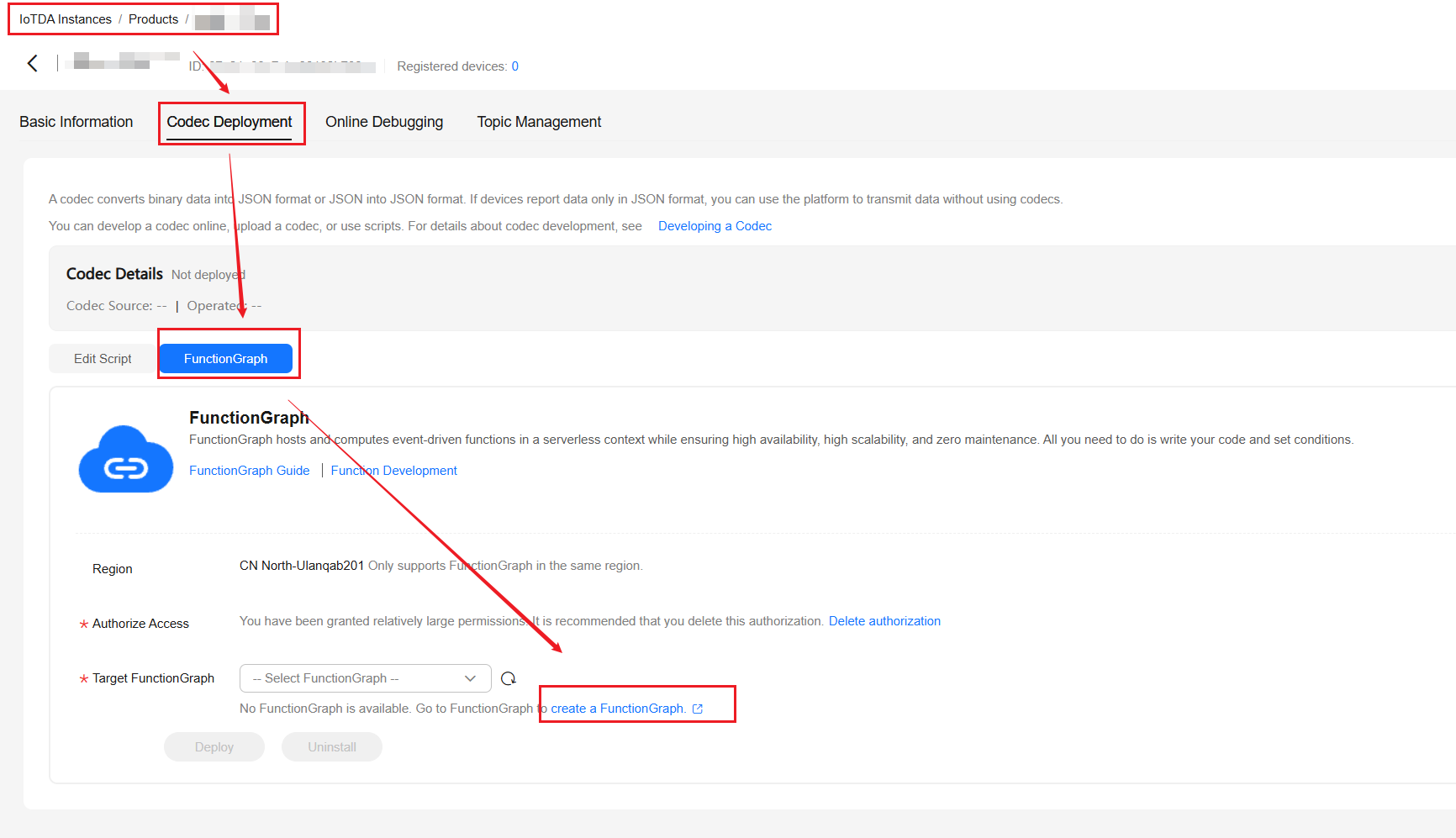
- On the smoke detector product page, click the Codec Development tab, select FunctionGraph, and click Create Function. If you use the tool for the first time, perform access authorization.
Figure 2 FunctionGraph-based Development - Function creation
- On the FunctionGraph console, click Create Function. On the displayed page, click Create from scratch, enter a function name, and select Node.js 16.17 as the runtime.
Figure 3 Function list - Creating a function
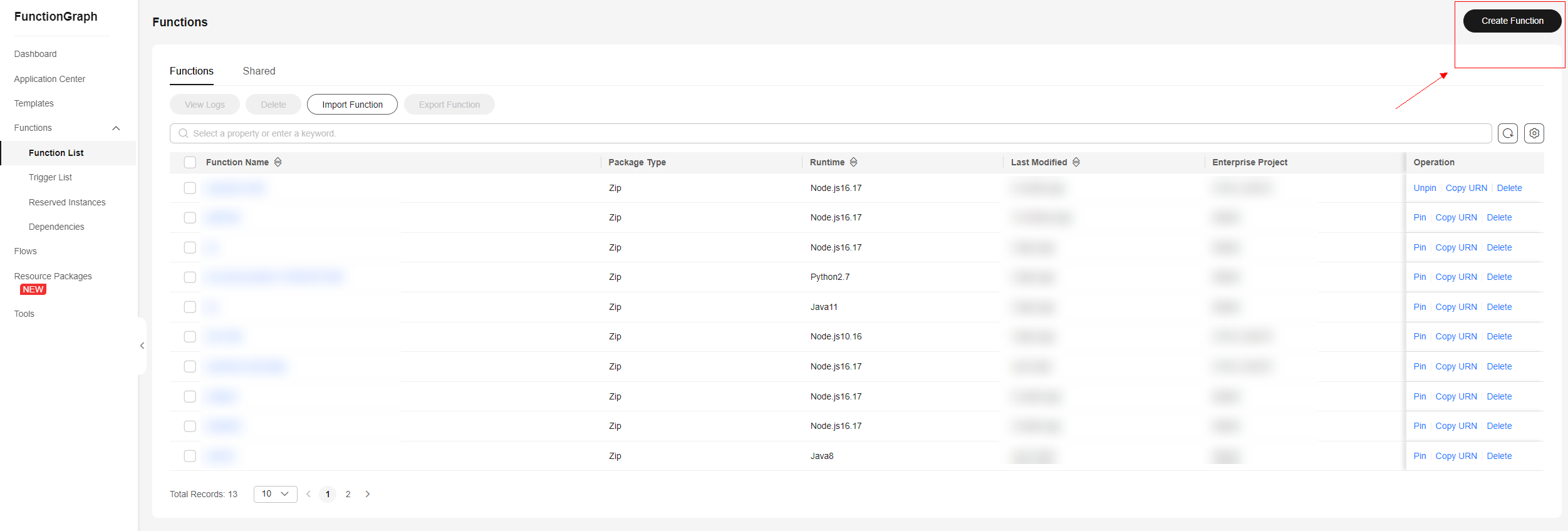 Figure 4 Creating a function - Parameters
Figure 4 Creating a function - Parameters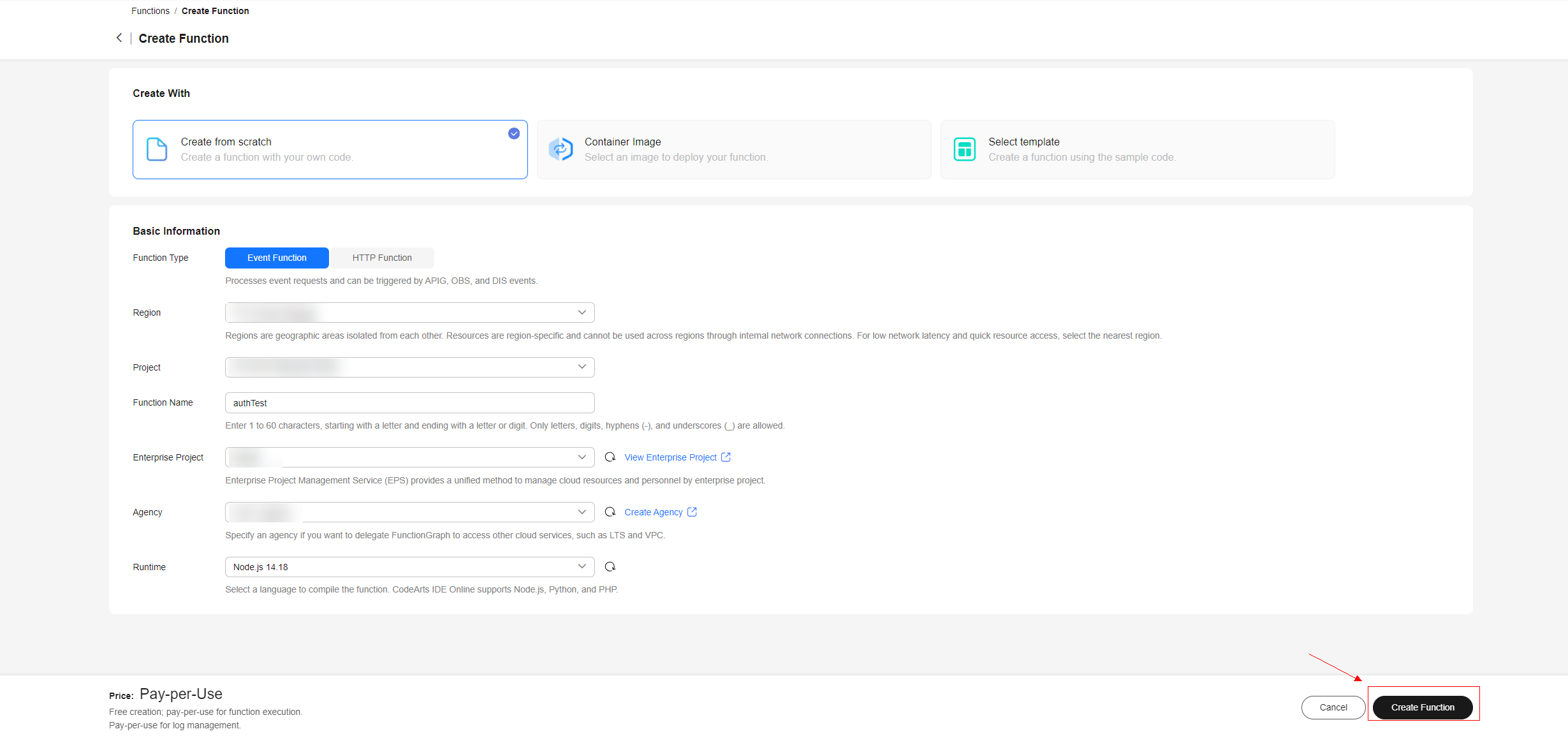
- Write a script to convert binary data into JSON data. The script must implement the following methods:
- Decode: Converts the binary data reported by a device into the JSON format defined in the product model. For details about the JSON format requirements, see Data Decoding Format Definition.
- Encode: Converts JSON data into binary data supported by the device when the platform sends downstream data to the device. For details about the JSON format requirements, see Data Encoding Format Definition.
The following is an example of the JavaScript implemented for the smoke detector. Copy the code to the project.// Upstream message types var MSG_TYPE_PROPERTIES_REPORT = 'properties_report'; // Device property reporting var MSG_TYPE_COMMAND_RSP = 'command_response'; // Command response // Downstream message types var MSG_TYPE_COMMANDS = 'commands'; // Command delivery var MSG_TYPE_PROPERTIES_REPORT_REPLY = 'properties_report_reply'; // Property reporting response // Message types var MSG_TYPE_LIST = { 0: MSG_TYPE_PROPERTIES_REPORT, // In the code stream, 0 indicates device property reporting. 1: MSG_TYPE_PROPERTIES_REPORT_REPLY, // In the code stream, 1 indicates a property reporting response. 2: MSG_TYPE_COMMANDS, // In the code stream, 2 indicates platform command delivery. 3: MSG_TYPE_COMMAND_RSP // In the code stream, 3 indicates a command response from the device. }; // FunctionGraph entry function exports.handler = async (event, context) => { const codecType = event.codecType; const message = JSON.parse(event.message); console.log("input Data:", event); if (codecType === "decode") { // Decoding operation return decode(message.payload); } else if (codecType === "encode") { // Encoding operation return encode(message); } } /* Example: When a smoke detector reports properties and returns a command response, it uses binary code streams. The JavaScript script will decode the binary code streams into JSON data that complies with the product model definition. Input parameters: payload:[0x00, 0x00, 0x50, 0x00, 0x5a] payload[0] indicates the data type. 0x00 indicates property reporting. payload[1] and payload[2] indicate the value of the level property. payload[3] and payload[4] indicate the value of the temperature property. payload[3] is the value before the decimal point, and payload[4] is the value after the decimal point. Output: {"msg_type":"properties_report","services":[{"service_id":"smokedetector","properties":{"level":80,"temperature":90}}]} Input parameters: payload: [0x03, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01] payload[0] indicates the data type. 0x03 indicates that the device returns a command response. payload[1] indicates the value of request_id used to identify the command. payload[2] indicates whether the command is successfully set. If the value is 0, the command is successfully set. payload[3] and payload[4] indicate the values of "value" in the command response. Output: {"msg_type":"command_response","request_id":1,"result_code":0,"paras":{"value":1}} */ function decode(payload) { // Decoding logic var binaryString = atob(payload); const byteArray = new Uint8Array(binaryString.length); for (let i = 0; i < binaryString.length; i++) { byteArray[i] = binaryString.charCodeAt(i); } /* byteArray is the binary data reported by the device after decoding. You can check whether the reported data is correctly parsed.*/ var returnData; var messageId = byteArray[0]; if (MSG_TYPE_LIST[messageId] == MSG_TYPE_PROPERTIES_REPORT) { returnData = decodePropertiesReport(byteArray); } else if (MSG_TYPE_LIST[messageId] == MSG_TYPE_COMMAND_RSP) { returnData = decodeCommandRsp(byteArray); } return returnData; } /* Example data: When a command is delivered, data in JSON format on IoTDA is encoded into a binary code stream using the encode method of JavaScript. Input parameters -> {"msg_type":"commands","request_id":1,"command_name":"SET_ALARM","service_id":"smokedetector","paras":{"value":1}} Output -> [0x02, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01] payload[0] indicates the data type, 0x02 indicates the platform command delivery. payload[1] indicates the command ID. payload[2] indicates the command name (when command_name is SET_ALARM, payload[2] = 0x00). payload[3] and payload[4] indicate the values of the delivered command. Sample data: When a response is returned for property reporting, data in JSON format on the platform is encoded into a binary code stream using the encode method of JavaScript. Input parameters -> {"msg_type":"properties_report_reply","request":"000050005a","result_code":0} Output -> [0x01, 0x00] payload[0] indicates the data type. 0x01 indicates the response message for reporting device properties. payload[1] indicates the device response result. 0x00 indicates success. */ function encode(data) { var msgType = data.msg_type; let payload = []; var status = 200; // Command delivery if (msgType == MSG_TYPE_COMMANDS) { payload[0] = 0x02; // Command delivery type payload[1] = data.request_id & 0xFF; // Command ID if (data.command_name == 'SET_ALARM') { payload[2] = 0x00; // Command name } // Set the command property value. payload[3] = (data.paras.value >> 8) & 0xFF; payload[4] = data.paras.value & 0xFF; } else if (msgType == MSG_TYPE_PROPERTIES_REPORT_REPLY) { // Response to device property reporting payload[0] = 0x01; // Response to the device property reporting type if (0 == data.result_code) { payload[1] = 0x00; // Property reporting processed } else { payload[1] = 0x01; status = 401; } } return outputData(status, { "payload": payload }); } // Property reporting (upstream) function decodePropertiesReport(byteArray) { // Set the value of serviceId, which corresponds to smokedetector in the product model. var serviceId = 'smokedetector'; var level = byteArray[1] * Math.pow(2, 8) + byteArray[2]; var status = 200; var jsonObj; if (byteArray.length < 4) { jsonObj = { "msg_type": "ERR", "message":"decodePropertiesReport byte length < 5." }; status = 402; } // Obtain the values of the fourth and fifth values. const integerPart = byteArray[3]; // Fourth value const decimalPart = byteArray[4]; // Fifth value // Combine the values into decimals. const temperature = parseFloat(integerPart + '.' + decimalPart); jsonObj = { "msg_type": MSG_TYPE_PROPERTIES_REPORT, "services": [{ "service_id": serviceId, "properties": { "level": level, "temperature": temperature } }] }; return outputData(status, jsonObj); } // Command response (upstream) function decodeCommandRsp(byteArray) { var requestId = byteArray[1]; var result_code = byteArray[2]; // Obtain the command execution result from the binary code stream. var value = byteArray[3] * Math.pow(2, 8) + byteArray[4]; // Obtain the return value of the command execution result from the binary code stream. // Convert data into the JSON format used by the command response. jsonObj = { 'msg_type': MSG_TYPE_COMMAND_RSP, 'request_id': requestId, 'result_code': result_code, 'paras': { 'value': value } }; return outputData(200, jsonObj); } function outputData(status, body) { const output = { 'status': status, 'message': JSON.stringify(body), } console.log("output Data:", output); return output; }Figure 5 FunctionGraph - Copying code to a project (CoAP)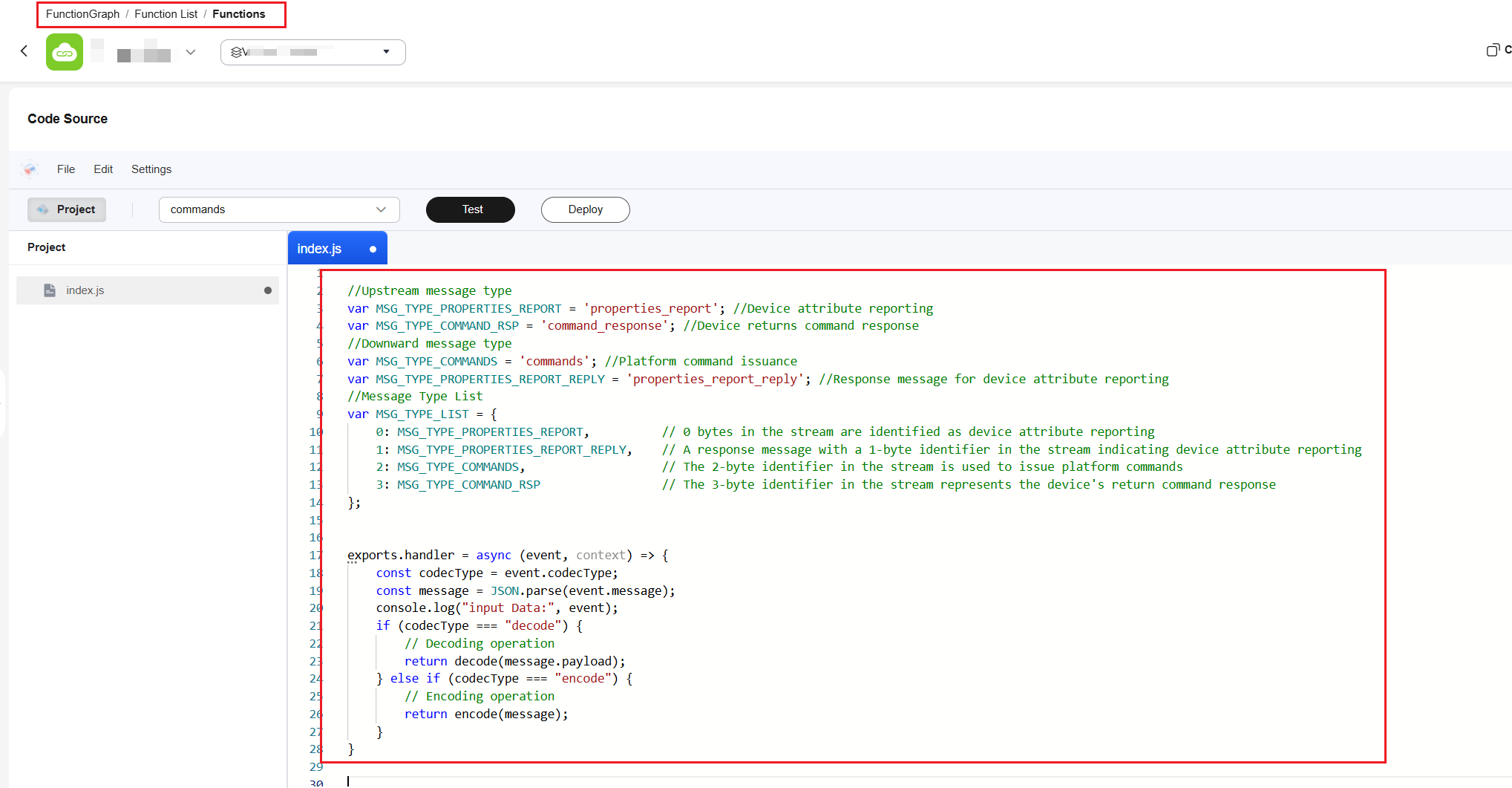
- Debug the script online. After the script is edited, click Configure Test Event on the FunctionGraph console, select a blank template, enter simulated data, and click Create. After configuring the test event, click Test to obtain the function result and logs.
Simulated data: payload is the binary data reported by the device, that is, 0x00, 0x00, 0x50, 0x00,0x5a. AABQAFo= is the result value encoded by the platform using Base64.
{ "codecType": "decode", "message": "{\"topic\": null,\"payload\": \"AABQAFo=\"}" }Figure 6 FunctionGraph - Adding a test event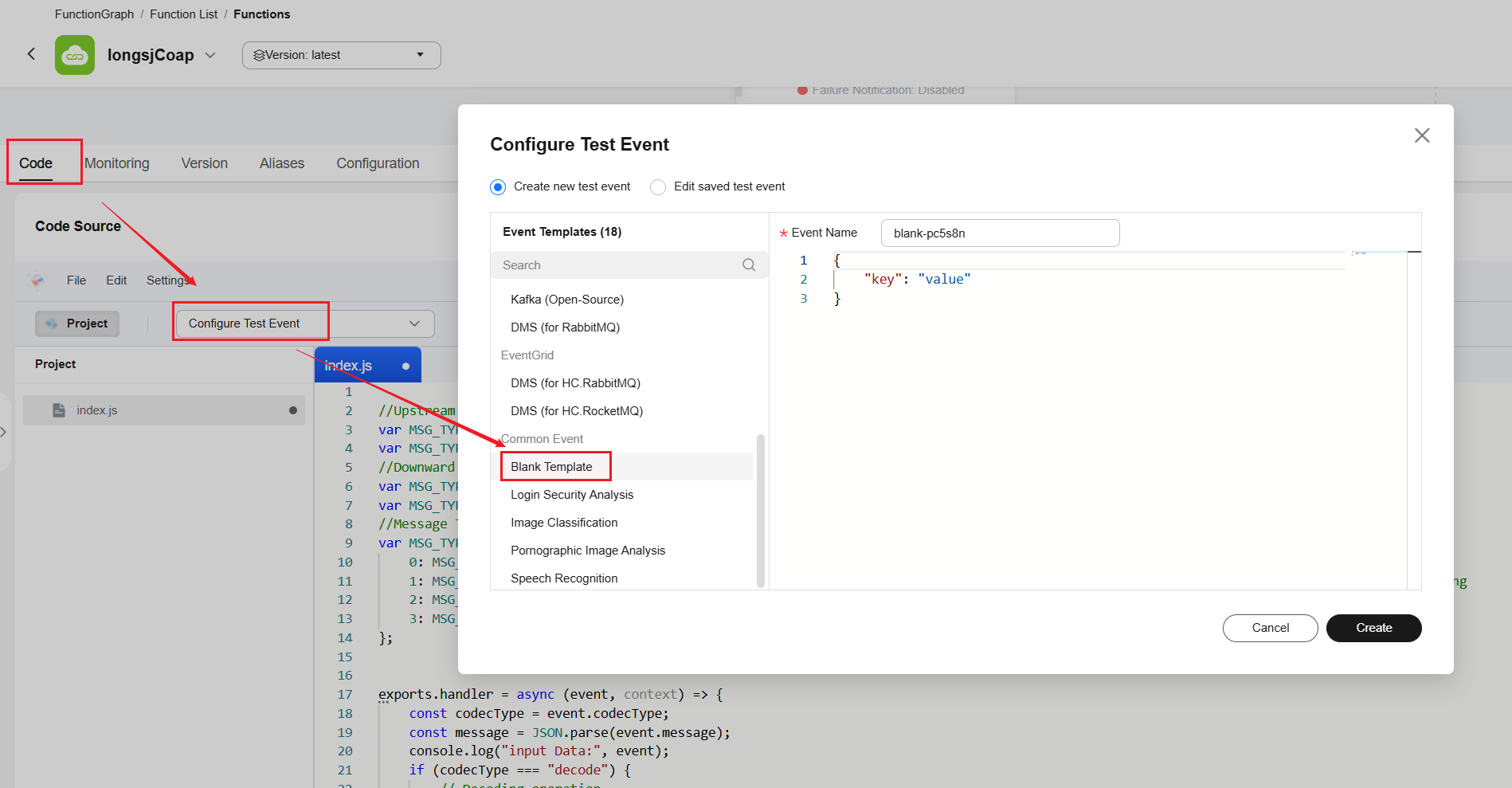 Figure 7 FunctionGraph - Test result (CoAP)
Figure 7 FunctionGraph - Test result (CoAP)
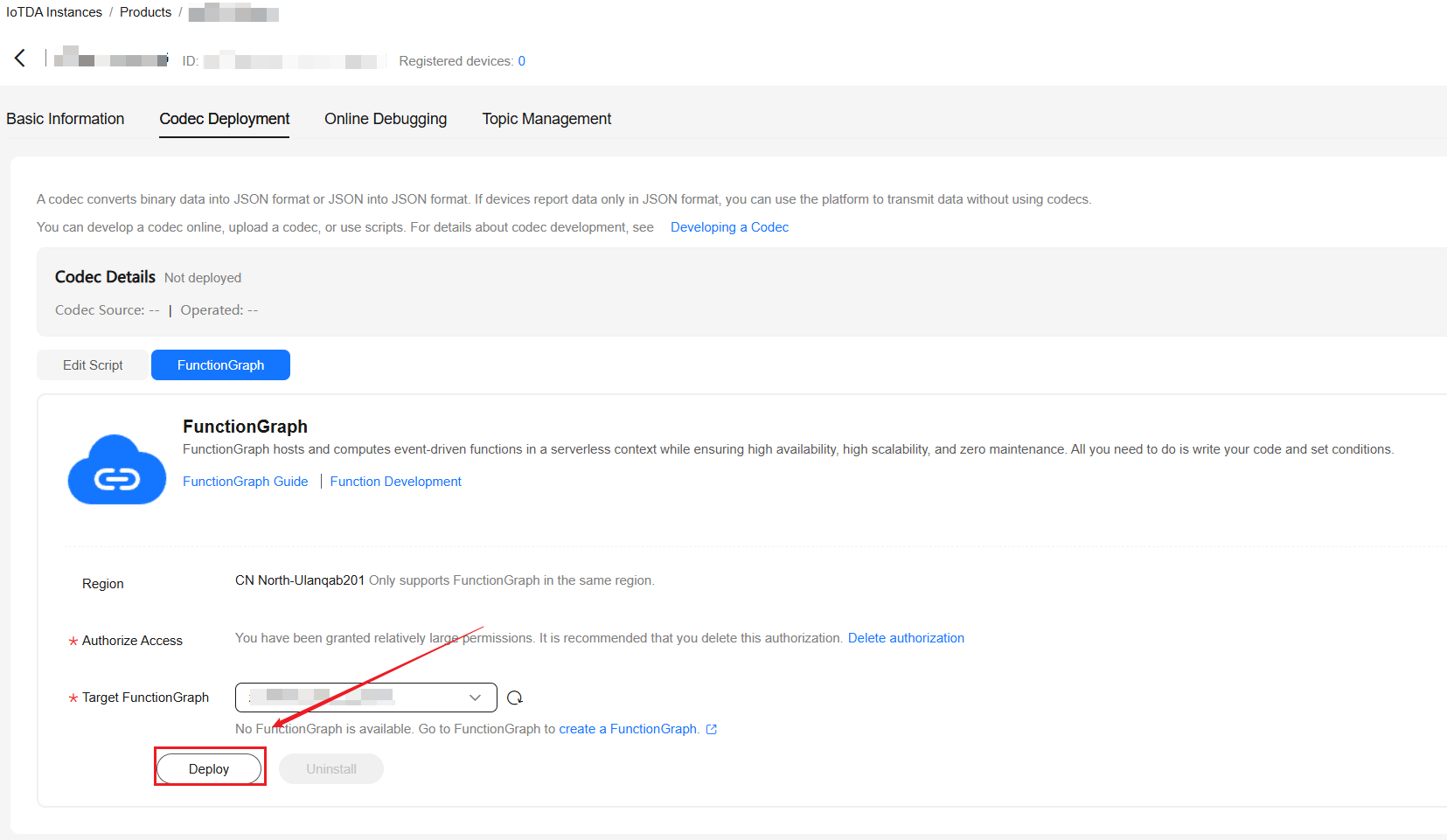
- After the debugging is successful, select the created FunctionGraph function from the drop-down list in 1 and click Deploy.
Figure 8 FunctionGraph-based Development - Codec deployment
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





