Creating a SQL Throttling Rule
Scenarios
SQL throttling allows you to create rules to control concurrent execution of SQL statements by specifying SQL type, keywords, and maximum concurrency. To maintain better performance at high concurrency, SQL statements that meet the specified SQL type and keyword and exceed the maximum concurrency will not be executed.
High SQL concurrency can be caused by the following factors:
- A sharp increase in requests: Concurrent SQL statements of a certain type surge due to cache penetration and abnormal calls.
- Stacked slow queries: If a large number of SQL statements without indexes are called, many slow SQL statements will be generated, affecting services.
Version Constraints
SQL throttling is available to only the versions listed in Table 1. For details about how to query the instance version, see Query the RDS Instance Version.
|
Major Version |
Minor Version (Primary Instance) |
Minor Version (Read Replica) |
Setting Rules for Read Replicas Separately |
|---|---|---|---|
|
8.0 |
≥ 8.0.25.1 |
≥ 8.0.25.1 |
Not supported |
|
5.7 |
≥ 5.7.31.4 |
≥ 5.7.37.1 |
≥ 5.7.38.221000 |
|
5.6 |
≥ 5.6.50.3 |
≥ 5.6.51.6 |
Not supported |
Table 2 lists the version constraints on built-in users and user root.
|
Major Version |
Minor Version |
Built-in User |
Root User |
|---|---|---|---|
|
8.0 |
≥ 8.0.28.231000 |
Not affected by throttling rules |
Subject to throttling rules |
|
8.0.25.1 ≤ Version < 8.0.28.231000 |
Not affected by throttling rules |
Not affected by throttling rules |
|
|
< 8.0.25.1 |
Subject to throttling rules |
Subject to throttling rules |
|
|
5.7 |
≥ 5.7.43.231000 |
Not affected by throttling rules |
Subject to throttling rules |
|
5.7.33.1 ≤ Version < 5.7.43.231000 |
Not affected by throttling rules |
Not affected by throttling rules |
|
|
< 5.7.33.1 |
Subject to throttling rules |
Subject to throttling rules |
|
|
5.6 |
≥ 5.6.51.4 |
Not affected by throttling rules |
Not affected by throttling rules |
|
< 5.6.51.4 |
Subject to throttling rules |
Subject to throttling rules |
If your instance runs version 5.7.43.231000 or later or it runs version 8.0.28.231000 or later, SQL throttling rules will be applied to user root. To disable this function for user root, submit a service ticket.
To achieve better performance at high concurrency, you are advised to upgrade your DB instance to the latest minor version. For details about how to upgrade a minor version, see Upgrading a Minor Version.
Constraints
- A maximum of 100 SQL throttling rules can be configured.
- Only SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT statements are supported for SQL throttling.
- INSERT statements are only supported for RDS for MySQL 5.7 (5.7.44.240100 or later) and 8.0 (8.0.32.240100 or later) for SQL throttling. To use this function, submit a service ticket to apply for required permissions.
- If a SQL statement matches multiple SQL throttling rules, only the most recently added rule is applied.
- SQL statements that have been executed before a SQL throttling rule is added are not counted.
- If the replication delay is too long, adding or deleting a SQL throttling rule for a read replica does not take effect immediately.
- SQL throttling rules are not applied to system tables.
- SQL throttling rules are not applied to SQL statements not used for data query, such as select sleep(***);.
- SQL throttling rules are not applied to stored procedures, triggers, or functions.
- You can run the following SQL statement through DAS to view the execution of SQL throttling rules: select * from information_schema.rds_sql_filter_info;
- Too many SQL throttling rules affect the database performance. Delete unnecessary rules after using them.
- SQL throttling rules are not applied to system databases.
- For instances whose kernel version is earlier than 5.6.51.4, 5.7.33.5, or 8.0.25.220700, SQL throttling rules are applied to all users. You are advised to include table names in keywords when configuring SQL throttling rules. Configuring only the SELECT keyword may impact the functionality.
Procedure
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region.
in the upper left corner and select a region. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service. - On the Instances page, click the target instance name to go to the Summary page.
- In the navigation pane, choose SQL Analysis and Tunning under DBA Assistant.
- Click the SQL Throttling tab.
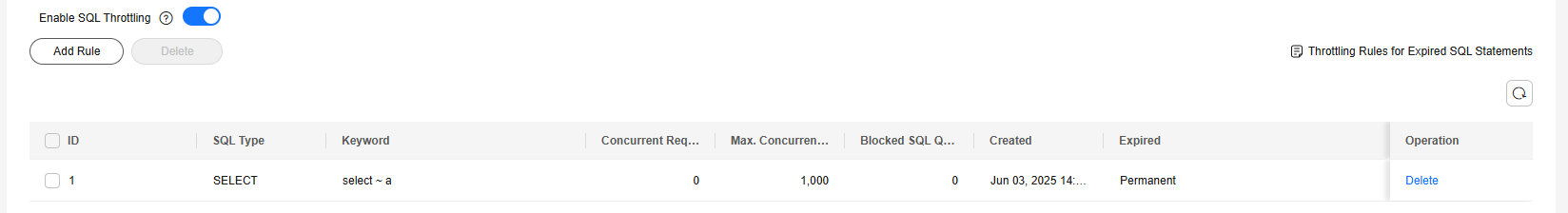
- Toggle on the SQL throttling switch
 . SQL throttling rules take effect only after SQL throttling is enabled.
. SQL throttling rules take effect only after SQL throttling is enabled. - Click Add Rule. Configure the parameters listed in Table 3.
Figure 1 Adding a rule (entering keywords)
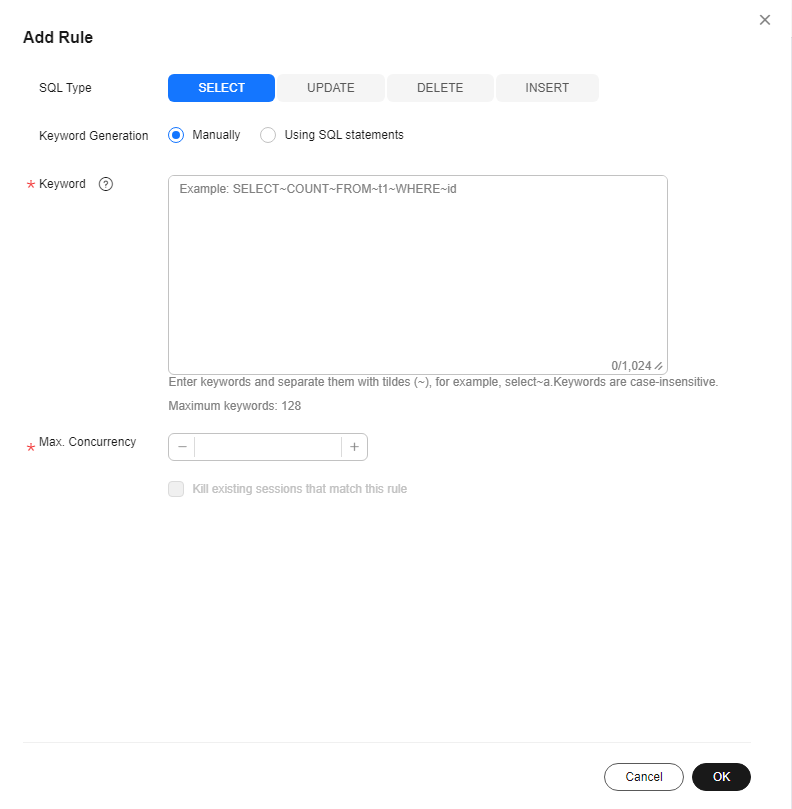 Figure 2 Adding a rule (generating keywords from a SQL statement)
Figure 2 Adding a rule (generating keywords from a SQL statement)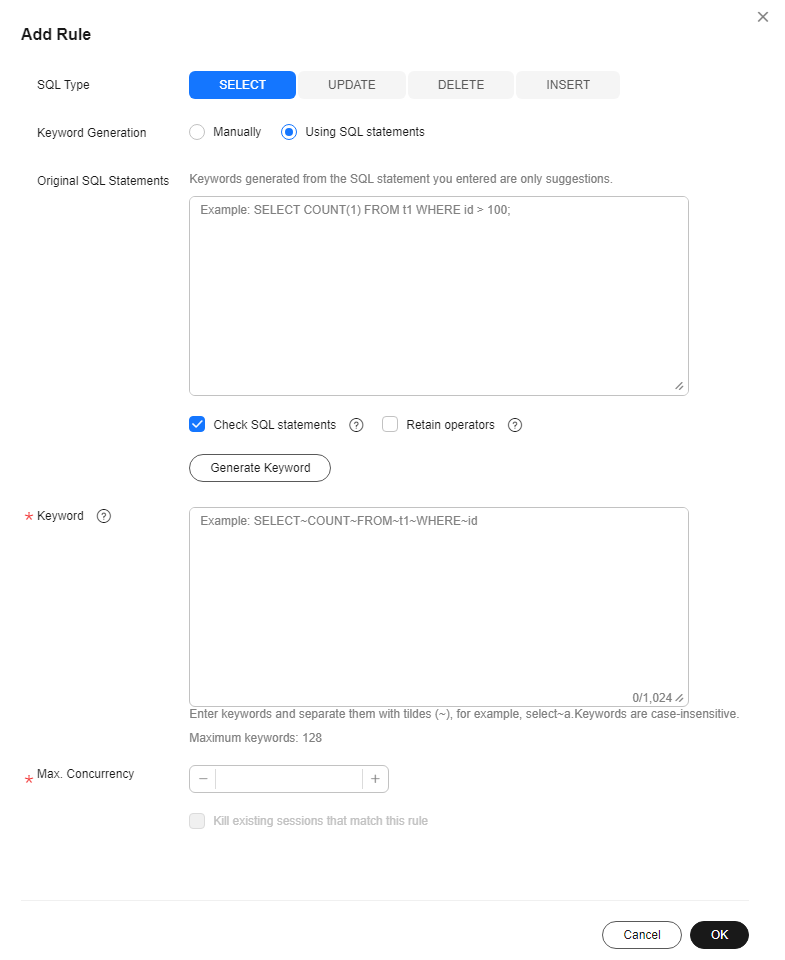
Table 3 Parameter description Parameter
Description
SQL Type
There are four options: SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT.
Keyword
A maximum of 128 keywords (case-insensitive) are supported. You can specify keywords in either of the following ways:
- Manually: Take select~a as an example. select and a are two keywords contained in a SQL throttling rule. The keywords are separated by a tilde (~). In this example, the rule restricts the execution of only the SQL statements containing keywords select and a.
- Using SQL statements: You can enter a SQL statement and then click Generate Keyword. The generated keywords are for reference only. Exercise caution when using them.
SQL statements match the keywords from first to last. For example, if one rule contains the keyword a~and~b, the statement *** a>1 and b>2 can match the keyword, but *** b>2 and a>1 cannot.
Empty characters before and after each keyword will be ignored, for example, spaces, '\n', '\r', and '\t'.
Max. Concurrency
If the number of concurrent SQL statements matching the keyword exceeds this limit, the SQL statements will not be executed. The value ranges from 0 to 1,000,000,000.
Kill existing sessions that match this rule
If this option is selected, all sessions generated by users subject to this SQL throttling rule will be killed.
For details about the versions where user root is not subject to SQL throttling rules, see Version Constraints.
- Confirm the settings and click OK.
Follow-up Operations
To delete a SQL throttling rule, locate it in the rule list and click Delete in the Operation column. In the displayed dialog box, click OK.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





