Buying an RDS for PostgreSQL Instance and Connecting to It Using a PostgreSQL Client
You can connect to your DB instance using a Linux ECS with a PostgreSQL client installed over a private network.
You can use the PostgreSQL client to connect to your DB instance over a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connection. SSL encrypts connections to your DB instance, making in-transit data more secure.
SSL is enabled by default when you create an RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance and cannot be disabled after the instance is created.
Enabling SSL reduces the read-only and read/write performance of your instance by about 20%.
Operation Process
|
Process |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Sign up for a HUAWEI ID, enable Huawei Cloud services, make sure you have a valid payment method configured, create IAM users, and grant them specific RDS permissions. |
|
|
Select required basic settings and additional options and buy an RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance. |
|
|
If you want to use a PostgreSQL client to connect to a DB instance, you need to prepare a server, install the PostgreSQL client on the server, and run the connection command. Purchase a Linux ECS that is in the same region and VPC as your DB instance. |
|
|
Test the network connectivity between the ECS and the floating IP address and port of the DB instance, and install a PostgreSQL client on the ECS. |
|
|
Step 4: Connect to the DB Instance Using a CLI (SSL Connection) |
Use a command-line interface (CLI) to connect to the DB instance using the floating IP address and port. |
Preparations
- Sign up for a HUAWEI ID and enable Huawei Cloud services.
- For fine-grained permissions management on Huawei Cloud resources, use Identity and Access Management (IAM) to create a user and user group and grant the user specific operation permissions. For details, see Creating a User and Granting Permissions.
Step 1: Buy an RDS for PostgreSQL DB Instance
- Go to the Buy DB Instance page.
- On the Quick Config page, set basic parameters.
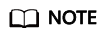
Only mandatory parameters are provided on the Quick Config page. If the available parameters do not match your workloads, try Custom Config.
The following parameter settings are only for reference.
Figure 1 Basic Settings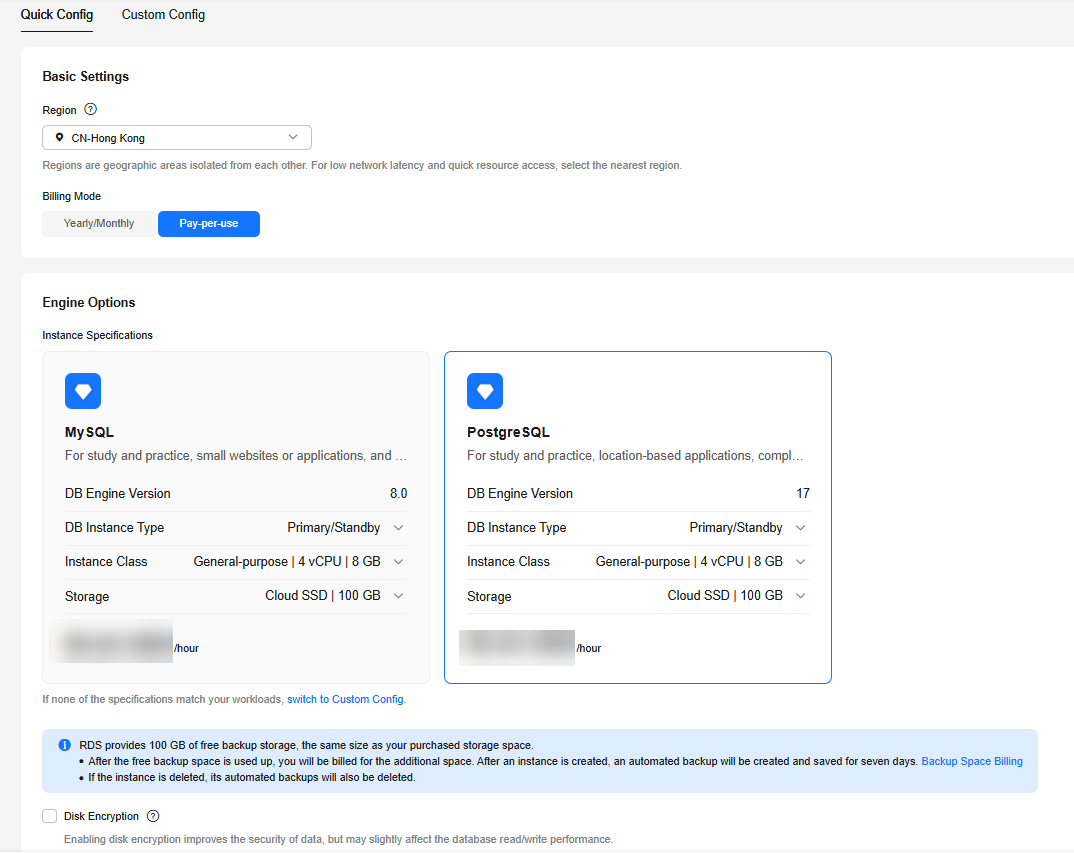
Parameter
Example Value
Description
Billing Mode
Pay-per-use
The billing mode of an instance.
- Yearly/Monthly: A prepaid billing mode in which you pay for resources before using it. Bills are settled based on the subscription period. The longer the subscription, the bigger the discount. This mode is a good option for long-term, stable services.
- Pay-per-use: A postpaid billing mode. You pay as you go and just pay for what you use. The DB instance usage is calculated by the second but billed every hour. This mode allows you to adjust resource usage easily. You neither need to prepare for resources in advance, nor end up with excessive or insufficient preset resources.
Region
CN-Hong Kong
The region where your resources are located.
NOTE:Products in different regions cannot communicate with each other through a private network. After a DB instance is created, the region cannot be changed. Therefore, exercise caution when selecting a region.
DB Engine Version
16
The database version.
DB Instance Type
Primary/Standby
The architecture type of an instance.
Primary/Standby: An HA architecture. In a primary/standby pair, each instance has the same instance class. When a primary instance is being created, a standby instance is provisioned along with it to provide data redundancy. The standby instance is invisible to you after being created.
Instance Class
General-purpose | 4 vCPU | 8 GB
The vCPUs and memory of an instance.
Storage
Cloud SSD | 100 GB
The storage space of an instance.
It contains the system overhead required for inodes, reserved blocks, and database operation.
Disk Encryption
Disable
Enabling disk encryption improves data security, but slightly affects the read and write performance of the database.
If a shared KMS key is used, the corresponding CTS events are createdatakey and decrydatakey. Only the key owner can receive the events.
- Complete advanced configurations.
Figure 2 Additional Options
Parameter
Example Value
Description
VPC
default_vpc
The virtual network in which your instance is located. A VPC can isolate networks for different workloads.
If no VPC is available, click Create VPC. After a VPC is created, click
 . For details, see Creating a VPC and Subnet.
. For details, see Creating a VPC and Subnet.Subnet
default_subnet
A subnet provides dedicated network resources that are logically isolated from other networks for network security.
Security Group
default
It can enhance security by controlling access to RDS for PostgreSQL from other services.
Enterprise Project
default
If your account has been associated with an enterprise project, select the target project from the Enterprise Project drop-down list.
For more information about enterprise projects, see Enterprise Management User Guide.
Quantity
1
The number of instances to be created in a batch.
- Click Buy.
- Check the purchased DB instance.
Figure 3 Instance successfully purchased

Step 2: Buy an ECS
- Go to the Elastic Cloud Server console.
- Check whether there is a Linux ECS that meets the requirements.

RDS for PostgreSQL supports the following client installation methods:
- Download the PostgreSQL client installation package. This method is recommended for PostgreSQL 15 and earlier versions. It has requirements on ECS images. For details, see the official PostgreSQL documentation.
- Download the source code. This method has no requirements on PostgreSQL versions or ECS images.
- If yes, go to 3.
- If no, purchase an ECS and select Linux (for example, CentOS 7) as its OS.
To download the PostgreSQL client to the ECS, bind an EIP to the ECS. The ECS must be in the same region, VPC, and security group as the RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance for mutual communications.
For details about how to purchase a Linux ECS, see Purchasing a Custom ECS in Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
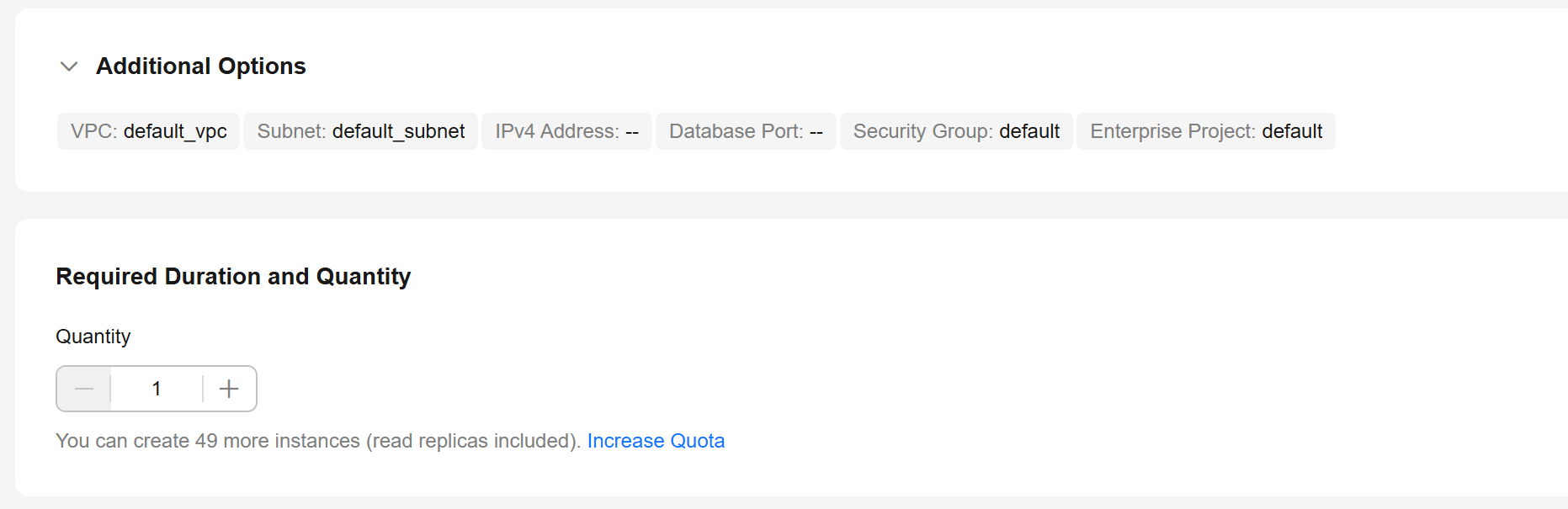
- Check whether the ECS and RDS for PostgreSQL instance are in the same region and VPC.
Figure 4 ECS information
 Figure 5 Overview
Figure 5 Overview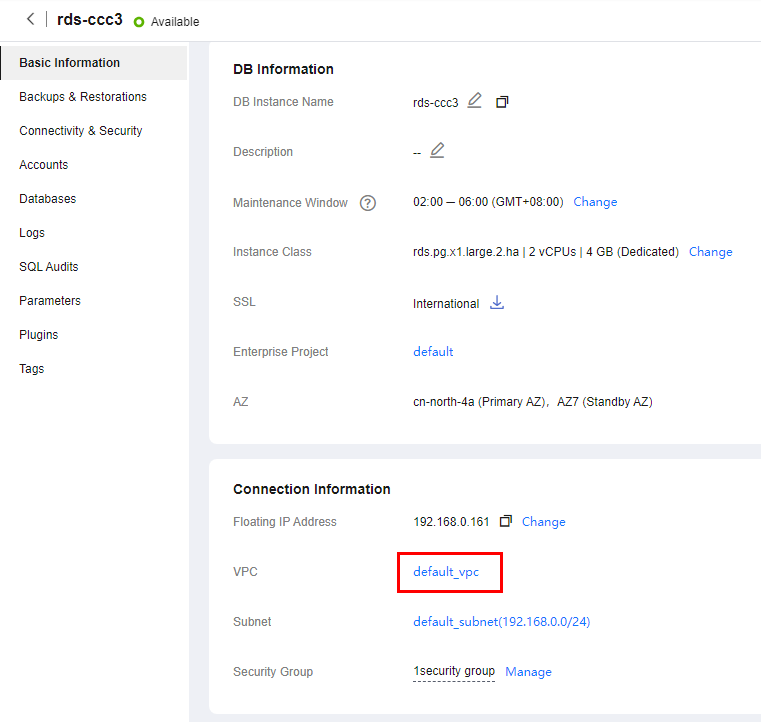
- If they are not in the same region, purchase another ECS. The ECS and DB instance in different regions cannot communicate with each other. To reduce network latency, deploy your DB instance in the region nearest to your workloads.
- If the ECS and DB instance are in different VPCs, change the VPC of the ECS to that of the DB instance. For details, see Changing a VPC.
- Log in to the ECS. For details, see Login Using VNC in the Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
- On the Instances page of the RDS console, click the DB instance name to go to the Overview page.
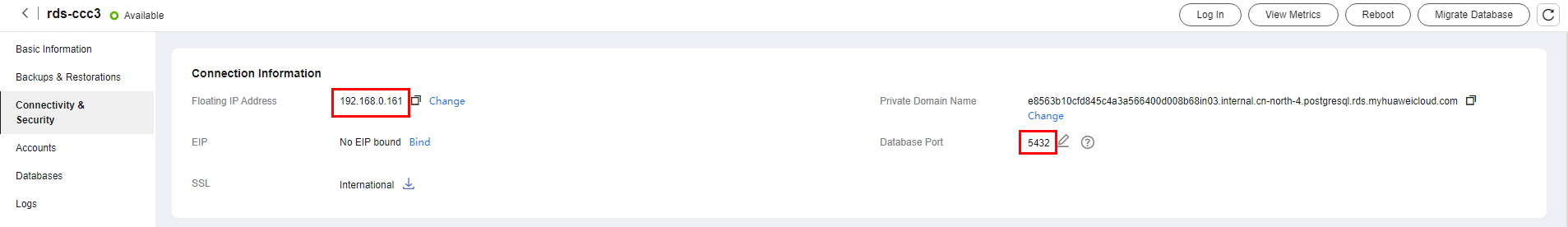
- Choose Connectivity & Security from the navigation pane. In the Connection Information area, obtain the floating IP address and database port of the DB instance.
Figure 6 Connection information
- On the ECS, check whether the floating IP address and database port of the DB instance can be connected.
curl -kv 192.168.0.7:5432
- If yes, network connectivity is normal.
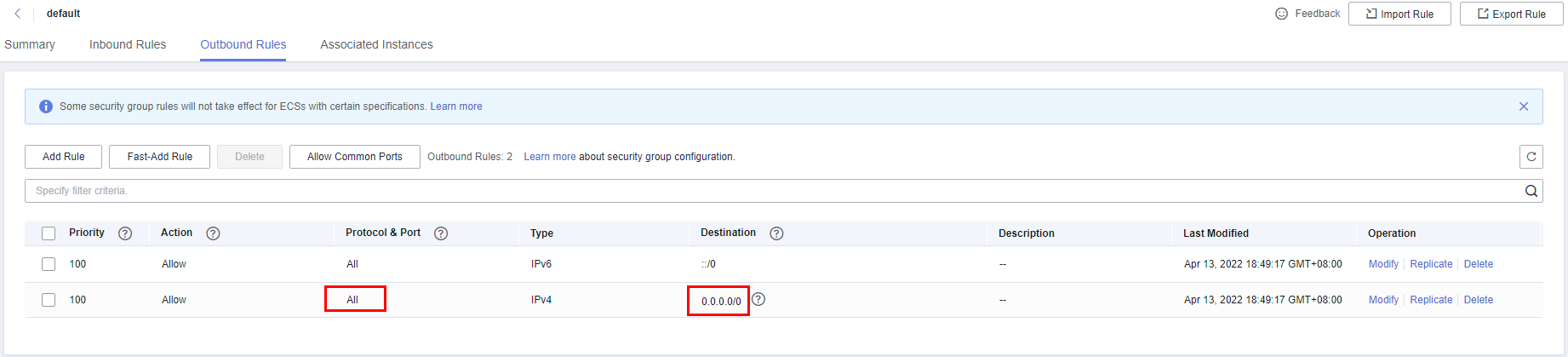
- If no, check the security group rules.
- If in the security group of the ECS, there is no outbound rule with Destination set to 0.0.0.0/0 and Protocol & Port set to All, add an outbound rule for the floating IP address and port of the DB instance.
Figure 7 ECS security group
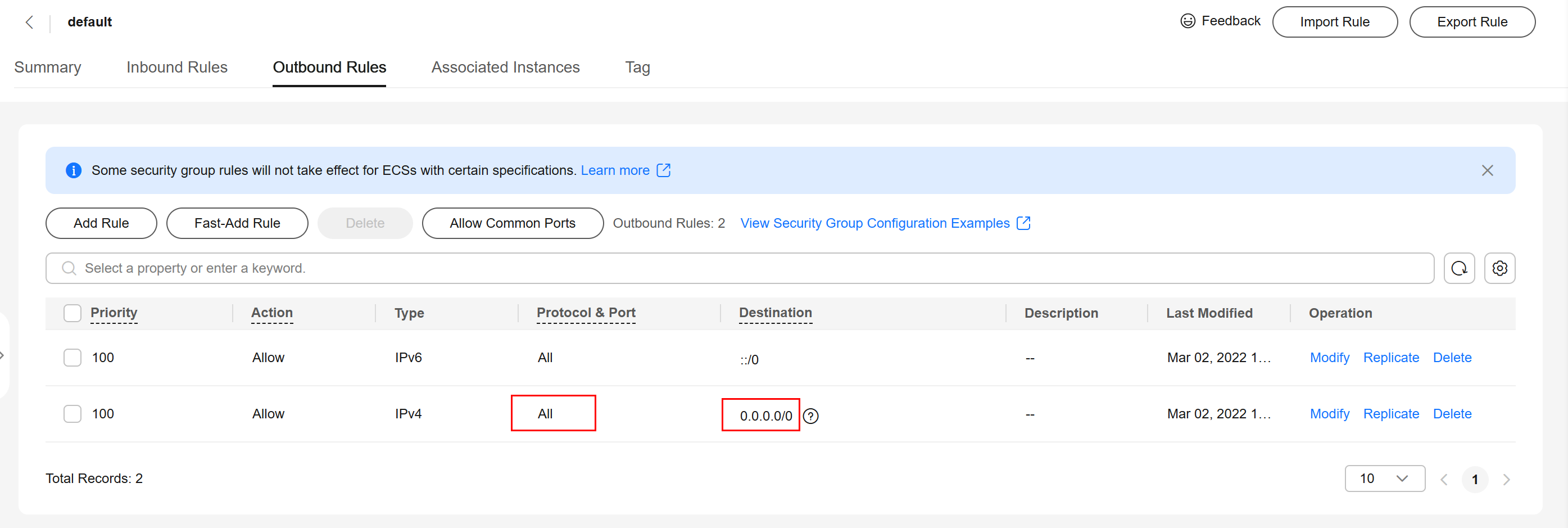
- If in the security group of the DB instance, there is no inbound rule allowing the access from the private IP address and port of the ECS, add an inbound rule for the private IP address and port of the ECS.
- If in the security group of the ECS, there is no outbound rule with Destination set to 0.0.0.0/0 and Protocol & Port set to All, add an outbound rule for the floating IP address and port of the DB instance.
- Install a PostgreSQL client.
The PostgreSQL community provides client installation methods for different OSs. You can download and install a client using the installation tool of the OS. This installation method is simple but can be used only for the OSs supported by the PostgreSQL community.
In this example, CentOS 7 is used. Use the default installation tool of the OS to install a client (PostgreSQL 15 or earlier).
Figure 8 Obtaining the installation tool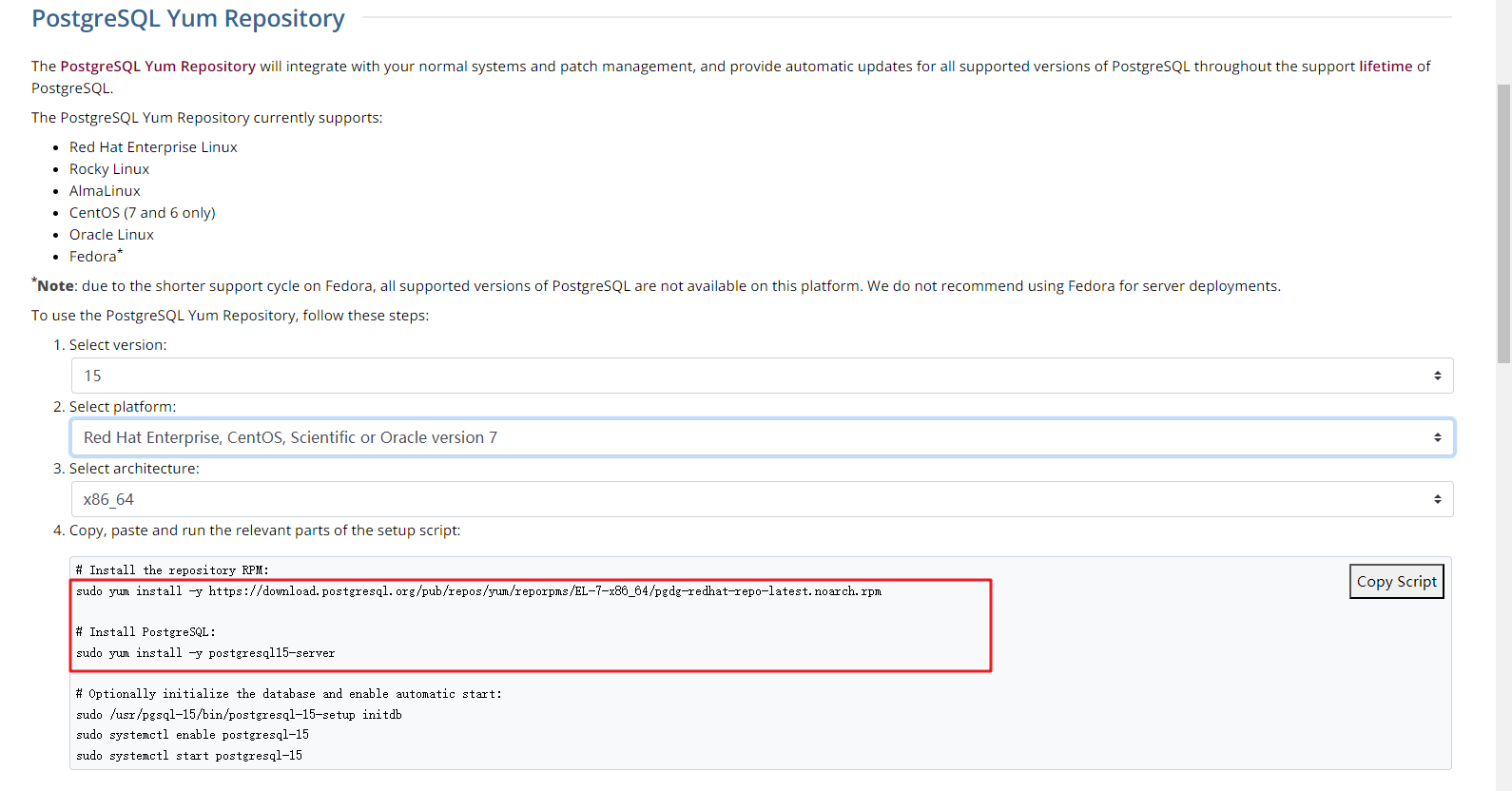
Run the installation commands:
sudo yum install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm sudo yum install -y postgresql15-server
Check whether the installation is successful.
psql -V
Figure 9 Successful installation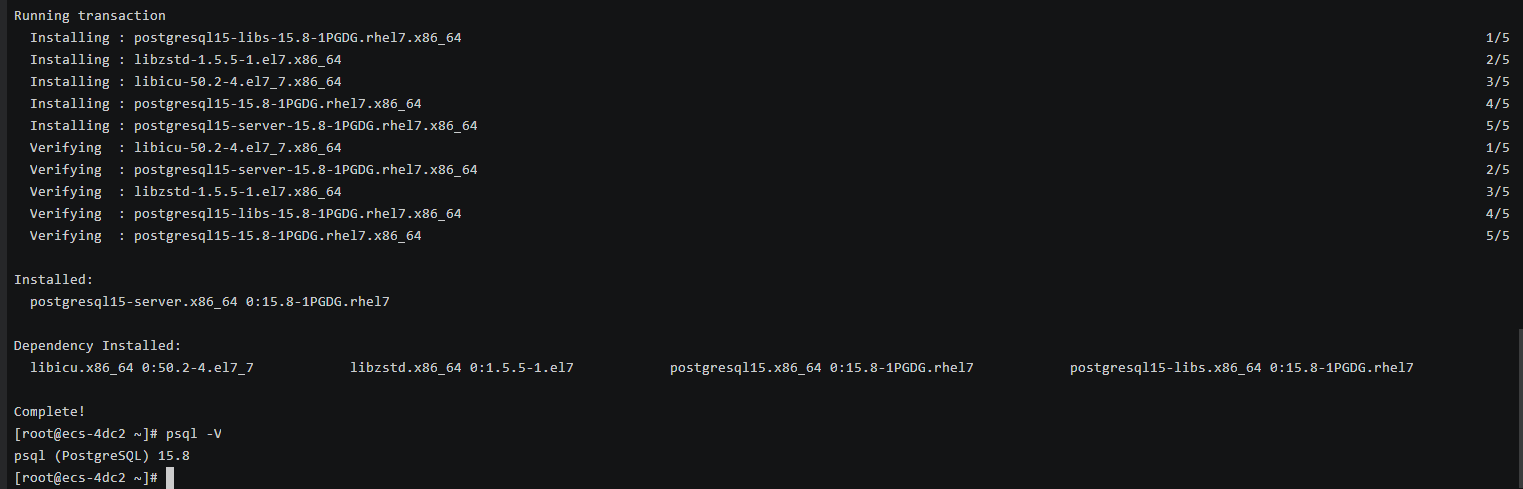
- Log in to the ECS. For details, see Login Using VNC in the Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
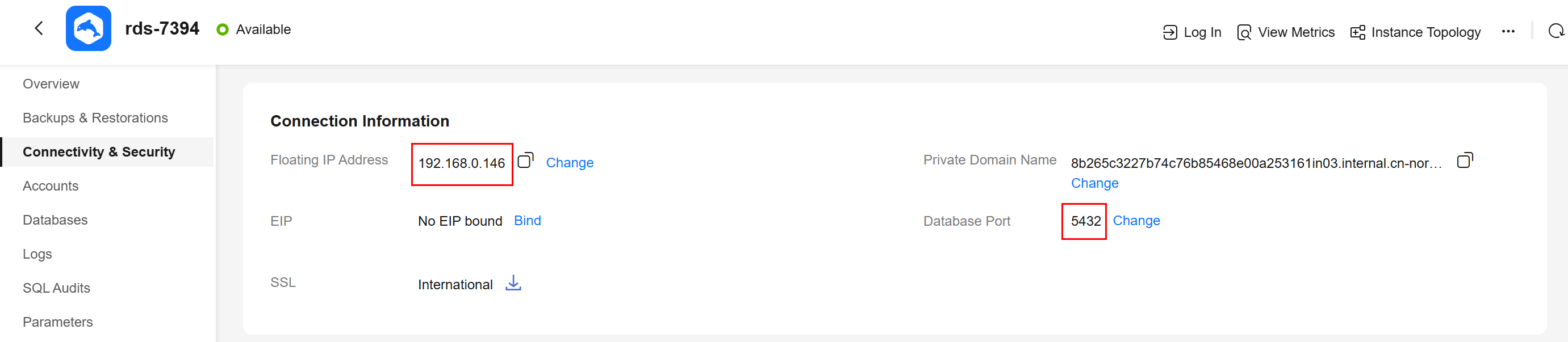
- On the Instances page of the RDS console, click the DB instance name to go to the Overview page.
- Choose Connectivity & Security from the navigation pane. In the Connection Information area, obtain the floating IP address and database port of the DB instance.
Figure 10 Connection information
- On the ECS, check whether the floating IP address and database port of the DB instance can be connected.
curl -kv 192.168.0.7:5432
- If yes, network connectivity is normal.
- If no, check the security group rules.
- If in the security group of the ECS, there is no outbound rule with Destination set to 0.0.0.0/0 and Protocol & Port set to All, add an outbound rule for the floating IP address and port of the DB instance.
Figure 11 ECS security group
- If in the security group of the DB instance, there is no inbound rule allowing the access from the private IP address and port of the ECS, add an inbound rule for the private IP address and port of the ECS.
- If in the security group of the ECS, there is no outbound rule with Destination set to 0.0.0.0/0 and Protocol & Port set to All, add an outbound rule for the floating IP address and port of the DB instance.
- Install a PostgreSQL client.
Installation from source code: This installation method has no restrictions on RDS PostgreSQL instance versions and ECS OS types.
The following uses an ECS using the Huawei Cloud EulerOS 2.0 image as an example to describe how to install a PostgreSQL 16.4 client.
Figure 12 Checking the ECS image
- To use SSL, download OpenSSL to the ECS in advance.
sudo yum install -y openssl-devel
- Obtain the code download link, run wget to download the installation package to the ECS, or download the installation package to the local PC and then upload it to the ECS.
wget https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/source/v16.4/postgresql-16.4.tar.gz
- Decompress the installation package.
tar xf postgresql-16.4.tar.gz
- Compile the source code and then install the client.
cd postgresql-16.4 ./configure --without-icu --without-readline --without-zlib --with-openssl make -j 8 && make install
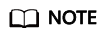
If --prefix is not specified, the default path is /usr/local/pgsql. The client can be installed in the simplest way.
Figure 13 Compilation and installation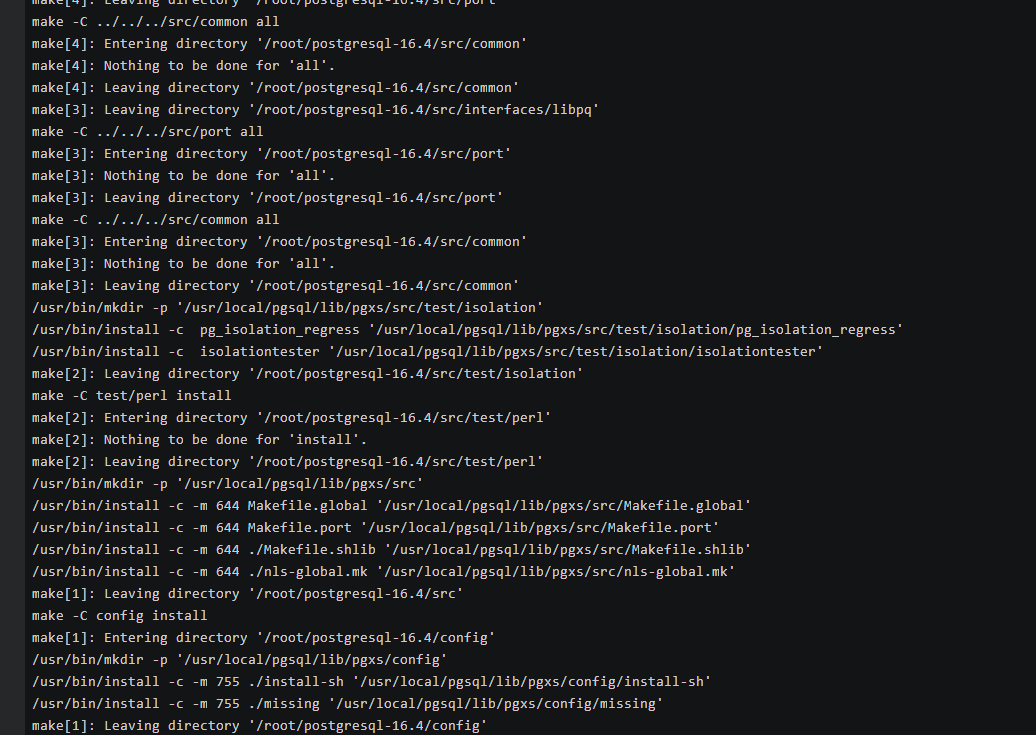
- Add the following code to the /etc/profile file to configure environment variables:
export PATH=/usr/local/pgsql/bin:$PATH export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/pgsql/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH source /etc/profile
- Test whether the psql is available.
psql -V
Figure 14 Testing psql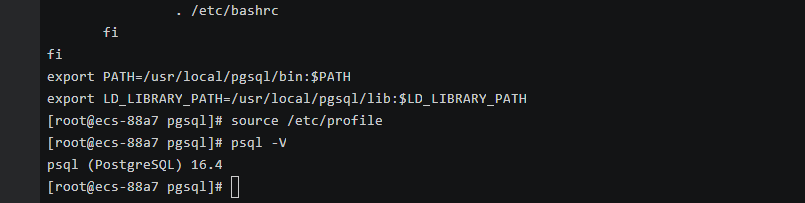
- To use SSL, download OpenSSL to the ECS in advance.
Step 4: Connect to the DB Instance Using a CLI (SSL Connection)
- On the Instances page of the RDS console, click the DB instance name to go to the Overview page.
- In the navigation pane, choose Connectivity & Security.
- In the Connection Information area, click
 next to the SSL field to download Certificate Download.zip, and extract the root certificate ca.pem and bundle ca-bundle.pem from the package.
Figure 15 Downloading a certificate
next to the SSL field to download Certificate Download.zip, and extract the root certificate ca.pem and bundle ca-bundle.pem from the package.
Figure 15 Downloading a certificate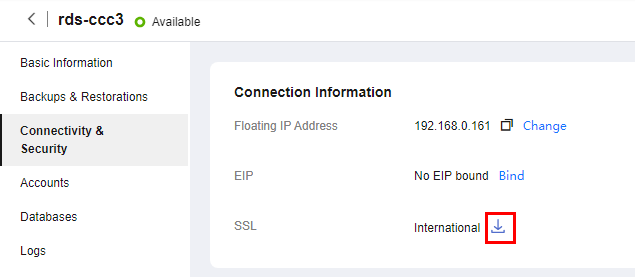
- Upload ca.pem to the ECS.
- TLS v1.2 or later is recommended. Versions earlier than TLS v1.2 have security risks.
- The recommended protocol algorithm is EECDH+ECDSA+AESGCM:EECDH+aRSA+AESGCM:EDH+aRSA+AESGCM:EDH+aDSS+AESGCM:!aNULL:!eNULL:!LOW:!3DES:!MD5:!EXP:!SRP:!RC4. Using other options have security risks.
- ca-bundle.pem contains both the new certificate provided as of April 2017 and the old certificate.
- Both ca.pem and ca-bundle.pem can be used for SSL connections because ca-bundle.pem contains ca.pem.
- Run the following command on the ECS to connect to the DB instance:
psql --no-readline -h <host> -p <port> "dbname=<database> user=<user> sslmode=verify-ca sslrootcert=<ca-file-directory>"
Example:
psql --no-readline -h 192.168.0.7 -p 5432 "dbname=postgres user=root sslmode=verify-ca sslrootcert=/root/ca.pem"
Table 1 Parameter description Parameter
Example Value
Description
<host>
192.168.0.7
Floating IP address obtained in 3.
<port>
5432
Database port obtained in 3. The default value is 5432.
<database>
postgres
Name of the database to be connected. The default database name is postgres.
<user>
root
Administrator account root.
<ca-file-directory>
/root/ca.pem
Directory of the CA certificate used for the SSL connection. This certificate should be stored in the directory where the command is executed.
sslmode
verify-ca
SSL connection mode. Set it to verify-ca to use a CA to check whether the service is trusted.
- Enter the password of the database account as prompted.
Password:
If the following information is displayed, the connection is successful.SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.2, cipher: ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, bits: 256, compression: off)
Follow-up Operations
After logging in to the DB instance, you can create or migrate databases.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





