Dumping DWS Database Audit Logs
DWS records information (audit logs) about connections and user activities in your database. The audit logs help you monitor the database to ensure security, rectify faults, and locate historical operation records. DWS saves audit logs in the database, but they can be viewed outside of it by dumping them to OBS. It is worth mentioning that the audit log dump and kernel audit log dump functions can be enabled or disabled independently. With the kernel audit log dump feature, audit logs stored in the database can be dumped directly to OBS.

- This function cannot be used if OBS is not available.
- Only 9.1.0.100 and later versions support kernel log dump.
- Data may during cluster specifications change, CN addition, or CN deletion. You are advised to disable audit log dump during these operations.
- If a CN node is faulty, data on the CN node may be lost.
- After audit log dumping is enabled, audit logs will be dumped if the size of saved audit logs exceeds 1 GB. This may cause abnormal query results. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
- Version support for the audit log dump directory partition is as follows:
- For version 8.1.3.x clusters, it is only supported by version 8.1.3.322 or later clusters.
- For version 8.2.0.x clusters, it is only supported by version 8.2.0.106 or later clusters.
- It is supported by version 8.2.1 or later clusters.
- To use this feature in earlier versions, contact technical support to upgrade your cluster first. Manually enable this feature after the upgrade.
Prerequisites
After a DWS cluster is created, you can enable log dump for it to dump audit logs to OBS. Before enabling audit log dump, ensure the following conditions are met:
You have created an OBS bucket for storing the audit logs. For details, see "Managing Buckets > Creating a Bucket" in the Object Storage Service Console Operation Guide.
Enabling Audit Log Dumps
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters in the navigation pane.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the cluster for which you want to enable audit log dump. In the navigation pane, choose Security Settings.
- In the Audit Settings area, enable Audit Log Dump.
When you enable audit log dump for a project in a region for the first time, the system prompts you to create an agency named DWSAccessOBS. After the agency is created, DWS can dump audit logs to OBS.
By default, only Huawei Cloud accounts or users with Security Administrator permissions can query and create agencies. IAM users under an account do not have the permission to query or create agencies by default. Contact a user with that permission and complete the authorization on the current page. For details, see Allowing DWS to Manage Resources.
Figure 1 Enabling audit log dumps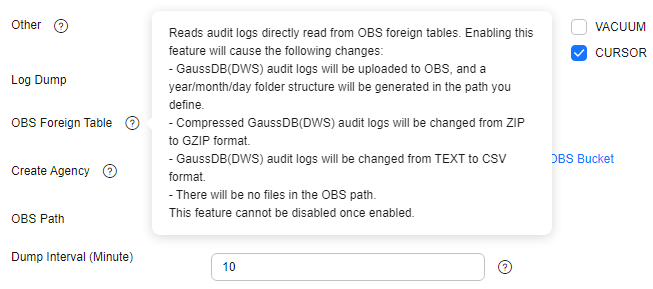
- OBS Foreign Table: Audit logs can be read using OBS foreign tables during dumping. Audit logs are stored in CSV format and compressed in GZ format.
- Create Agency: Select an OBS bucket to store audit data. If no OBS bucket is available, click View OBS Bucket to access the OBS console and create one. For details, see "Managing Buckets" > "Creating a Bucket" in the Object Storage Service Console Operation Guide.
Additionally, you can specify a bucket authorized by another user. However, to dump audit logs to that bucket, you must manually enter its name. Enter at least three characters. For details, see Dumping Audit Logs/Kernel Audit Logs to Another User-Authorized OBS Bucket.
- OBS Path: User-defined directory on OBS for storing audit files. Different directory levels are separated by forward slashes (/). Enter 1 to 50 characters, which cannot start with /. If the specified OBS path is not found, the system will create it and transfer the data to that location.
- Dump Interval (Minute): Interval based on which DWS periodically dumps data to OBS. The value range is 5 to 43200. The unit is minute.
- Click Apply.
If Configuration Status is Applying, the system is saving the settings.
When the status changes to Synchronized, the configurations are saved and take effect.
Enabling Kernel Audit Log Dump
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters in the navigation pane.
- Click the name of the cluster for which you want to enable kernel log dump. In the navigation pane, choose Security Settings.
- In the Audit Settings area, enable Kernel Audit Log Dump.
When you enable the kernel audit log dump feature for a project in a region for the first time, the system prompts you to create an agency named DWSAccessOBS. After the agency is created, DWS can dump audit logs to OBS.
By default, only Huawei Cloud accounts or users with Security Administrator permissions can query and create agencies. IAM users under an account do not have the permission to query or create agencies by default. Contact a user with that permission and complete the authorization on the current page. For details, see Allowing DWS to Manage Resources.
Figure 2 Enabling Kernel Audit Log Dump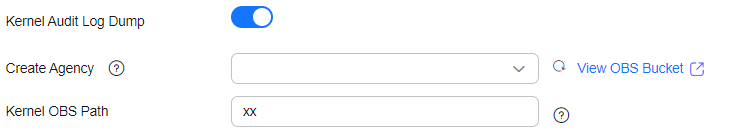
- Create Agency: Select an OBS bucket to store kernel audit data. If no OBS bucket is available, click View OBS Bucket to access the OBS console and create one. For details, see "Managing Buckets" > "Creating a Bucket" in the Object Storage Service Console Operation Guide.
Additionally, you can specify a bucket authorized by another user. However, to dump kernel audit logs to that bucket, you must manually enter its name. Enter at least three characters. For details, see Dumping Audit Logs/Kernel Audit Logs to Another User-Authorized OBS Bucket.
- Kernel OBS Path: user-defined directory for storing kernel logs on OBS. Different directory levels are separated by forward slashes (/). The value is a string containing 1 to 50 characters, which cannot start with a forward slash (/). If the entered OBS path does not exist, the system creates one and dumps data to it.
- Create Agency: Select an OBS bucket to store kernel audit data. If no OBS bucket is available, click View OBS Bucket to access the OBS console and create one. For details, see "Managing Buckets" > "Creating a Bucket" in the Object Storage Service Console Operation Guide.
- Click Apply.
If Configuration Status is Applying, the system is saving the settings.
When the status changes to Synchronized, the configurations are saved and take effect.
- After the kernel audit log dump function is enabled, you can use the pg_query_audit function to view the dumped logs. For details, see Using Functions to View Database Audit Logs.
Alternatively, select the OBS bucket and folder where logs are stored to view the log files. For details, see 6.
Dumping Audit Logs/Kernel Audit Logs to Another User-Authorized OBS Bucket
When you (dumping user) dump audit logs or kernel audit logs, you can specify an OBS bucket authorized by another user (authorizing user).
- Obtain the account ID from the console and provide it to the authorizing user. For details, see Obtaining an Account ID.
- Log in to OBS management console as the authorizing user and create a bucket policy.
For details, see Granting Other Accounts the Read/Write Permission for a Bucket.
- In the bucket list, click the name of your desired bucket to go to the Objects page.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Permissions > Bucket Policies.
- On the Bucket Policies page, click Create.
- In the Visual Editor tab of the displayed Create Bucket Policy slide-out panel, set the parameters based on the table below to create a bucket policy for cross-user authorization. Confirm the settings and click Create in the lower right corner.
Table 1 Parameters for creating a bucket policy Parameter
Example Value
Policy Name
Enter a policy name.
Effect
Select Allow.
Principal
Select Other accounts, click Add Delegated Accounts, and enter the account ID and agency name. The format is domainId/agencyname, where domainId is the account ID obtained in Step 1 and agencyname is DWSAccessOBS.
Resources
Select Entire bucket (including the objects in it).
Actions
Select Customize and configure at least the following four actions for Select Action: ListBucket, HeadBucket, GetObject, and PutObject.
- Return to the Security Settings page as the dumping user and manually enter the OBS bucket name in Create Agency.
After the dumping user uses the cluster to dump audit logs/kernel audit logs to the OBS bucket, the authorizing user can view the audit log files in the corresponding path within the OBS bucket.
Modifying Audit Log Dump Configurations
After audit log dump is enabled, you can modify the dump configuration. For example, you can modify the OBS bucket and path for storing logs and the dump period.
The procedure is as follows:
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters in the navigation pane.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the cluster for which you want to modify the audit log dump configurations. In the navigation pane, choose Security Settings.
- In the Audit Settings area, modify the Audit Log Dump configurations.
- Click Apply.
If Configuration Status is Applying, the system is saving the settings.
When the status changes to Synchronized, the configurations are saved and take effect.
Viewing Dumped Audit Logs
After audit log dump is enabled, you can view the dumped audit logs on OBS.
To view dumped audit logs, perform the following steps:
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters in the navigation pane.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster for which you want to view the log dump history. In the navigation pane, choose Security Settings.
- In the Audit Settings area, click View Dump Record.
- In the Audit Log Dump Records dialog box, click View OBS Bucket. The OBS console page is displayed.
- Select the OBS bucket and folder where the logs are stored to view the log files.
You can download and decompress the files to view. The fields of audit log files are described as follows:
Table 2 Log file fields Field
Type
Description
begintime
timestamp with time zone
Operation start time.
endtime
timestamp with time zone
Operation end time.
operation_type
text
Operation type. For details, see Table 3.
audit_type
text
Audit type. For details, see Table 4.
result
text
Operation result.
username
text
Name of the user who performs the operation.
database
text
Database name.
client_conninfo
text
Client connection information, that is, gsql, JDBC, or ODBC.
object_name
text
Object name.
object_details
text
Operation object details.
command_text
text
Command used to perform the operation.
detail_info
text
Operation details.
transaction_xid
text
Transaction ID.
query_id
text
Query ID.
node_name
text
Node name.
thread_id
text
Thread ID.
local_port
text
Local port.
remote_port
text
Remote port.
result_rows
text
Number of rows in the operation result.
error_code
text
Error code.
Table 3 operation_type: operation types Operation Type
Description
audit_switch
Indicates that the operations of enabling and disabling the audit log function are audited.
login_logout
Indicates that user login and log-out operations are audited.
system
Indicates that the system startup, shutdown, and instance switchover operations are audited.
sql_parse
Indicates that SQL statement parsing operations are audited.
user_lock
Indicates that user locking and unlocking operations are audited.
grant_revoke
Indicates that user permission granting and revoking operations are audited.
violation
Indicates that user's access violation operations are audited.
ddl
Indicates that DDL operations are audited. DDL operations are controlled at a fine granularity based on operation objects. Therefore, audit_system_object is used to control the objects whose DDL operations are to be audited. (The audit function takes effect as long as audit_system_object is configured, no matter whether ddl is set.)
dml
Indicates that the DML operations are audited.
select
Indicates that the SELECT operations are audited.
internal_event
Indicates that internal incident operations are audited.
user_func
Indicates that operations related to user-defined functions, stored procedures, and anonymous blocks are audited.
special_func
Indicates that special function invoking operations are audited. Special functions include pg_terminate_backend and pg_cancel_backend.
copy
Indicates that the COPY operations are audited.
set
Indicates that the SET operations are audited.
transaction
Indicates that transaction operations are audited.
vacuum
Indicates that the VACUUM operations are audited.
analyze
Indicates that the ANALYZE operations are audited.
cursor
Indicates that cursor operations are audited.
anonymous_block
Indicates that the anonymous block operations are audited.
explain
Indicates that the EXPLAIN operations are audited.
show
Indicates that the SHOW operations are audited.
lock_table
Indicates that table lock operations are audited.
comment
Indicates that the COMMENT operations are audited.
preparestmt
Indicates that the PREPARE, EXECUTE, and DEALLOCATE operations are audited.
cluster
Indicates that the CLUSTER operations are audited.
constraints
Indicates that the CONSTRAINTS operations are audited.
checkpoint
Indicates that the CHECKPOINT operations are audited.
barrier
Indicates that the BARRIER operations are audited.
cleanconn
Indicates that the CLEAN CONNECTION operations are audited.
seclabel
Indicates that security label operations are audited.
notify
Indicates that the notification operations are audited.
load
Indicates that the loading operations are audited.
Table 4 audit_type parameters Parameter
Description
audit_open/audit_close
Indicates that the audit type is operations enabling or disabling audit logs.
user_login/user_logout
Indicates that the audit type is operations and users with successful login/logout.
system_start/system_stop/system_recover/system_switch
Indicates that the audit type is system startup, shutdown, and instance switchover.
sql_wait/sql_parse
Indicates that the audit type is SQL statement parsing.
lock_user/unlock_user
Indicates that the audit type is successful user locking and unlocking.
grant_role/revoke__role
Indicates that the audit type is user permission granting and revoking.
user_violation
Indicates that the audit type is unauthorized user access operations.
ddl_database_object
Indicates that successful DDL operations are audited. DDL operations are controlled at a fine granularity based on operation objects. So, audit_system_object is used to control the objects whose DDL operations are to be audited. (The audit function takes effect as long as audit_system_object is configured, no matter whether ddl is set.)
For example, ddl_sequence indicates that the audit type is sequence-related operations.
dml_action_insert/dml_action_delete/dml_action_update/dml_action_merge/dml_action_select
Indicates that the audit type is DML operations such as INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE, and MERGE.
internal_event
Indicates that the audit type is internal events.
user_func
Indicates that the audit type is user-defined functions, stored procedures, or anonymous block operations.
special_func
Indicates that the audit type is special function invocation. Special functions include pg_terminate_backend and pg_cancel_backend.
copy_to/copy_from
Indicates that the audit type is COPY operations.
set_parameter
Indicates that the audit type is SET operations.
trans_begin/trans_commit/trans_prepare/trans_rollback_to/trans_release/trans_savepoint/trans_commit_prepare/trans_rollback_prepare/trans_rollback
Indicates that the audit type is transaction-related operations.
vacuum/vacuum_full/vacuum_merge
Indicates that the audit type is VACUUM operations.
analyze/analyze_verify
Indicates that the audit type is ANALYZE operations.
cursor_declare/cursor_move/cursor_fetch/cursor_close
Indicates that the audit type is cursor-related operations.
codeblock_execute
Indicates that the audit type is anonymous blocks.
explain
Indicates that the audit type is EXPLAIN operations.
show
Indicates that the audit type is SHOW operations.
lock_table
Indicates that the audit type is table locking operations.
comment
Indicates that the audit type is COMMENT operations.
prepare/execute/deallocate
Indicates that the audit type is PREPARE, EXECUTE, or DEALLOCATE operations.
cluster
Indicates that the audit type is CLUSTER operations.
constraints
Indicates that the audit type is CONSTRAINTS operations.
checkpoint
Indicates that the audit type is CHECKPOINT operations.
barrier
Indicates that the audit type is BARRIER operations.
cleanconn
Indicates that the audit type is CLEAN CONNECTION operations.
seclabel
Indicates that the audit type is security label operations.
notify
Indicates that the audit type is notification operations.
load
Indicates that the audit type is loading operations.
Disabling Audit Log Dump/Kernel Audit Log Dump
After the audit log dump or kernel audit log dump is enabled, you can disable it if you no longer need to dump audit logs or kernel audit logs to OBS.
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters in the navigation pane.
- Click the name of the cluster for which you want to disable Audit Log Dump or Kernel Audit Log Dump. In the navigation pane, choose Security Settings.
- In the audit configuration area, toggle the audit log dump/kernel audit log dump function off.
- Click Apply.
If Configuration Status is Applying, the system is saving the settings.
When the status changes to Synchronized, the configurations are saved and take effect.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





