Application Process Control Overview
What Is Application Process Control?
Application process control helps to enhance the security of applications and processes running on servers. It can automatically identify and analyze application processes, and classify them into trusted, suspicious, and malicious processes. It allows trusted processes to run, and generates alarms for suspicious and malicious processes. This helps to build a secure environment for application processes, and protects servers from untrusted or malicious application processes.
Application Process Control Principles
Application process control analyzes information in multiple dimensions, including process names, behaviors, paths, and reputation databases, to comprehensively identify processes and discover the processes disguised through renaming or obfuscation. After the processes are identified, application process control allows trusted processes (whitelisted processes) to run and generates alarms for untrusted processes. It also provides the names, hashes, file paths, occurrence time (startup time), and other important information about untrusted processes to help you perform source tracing analysis.
Untrusted processes are probably new normal processes or infected malicious processes. If an alarm was generated for a normal process, you can add the process to the whitelist. If an alarm was generated for a malicious process, manually handle it in a timely manner.
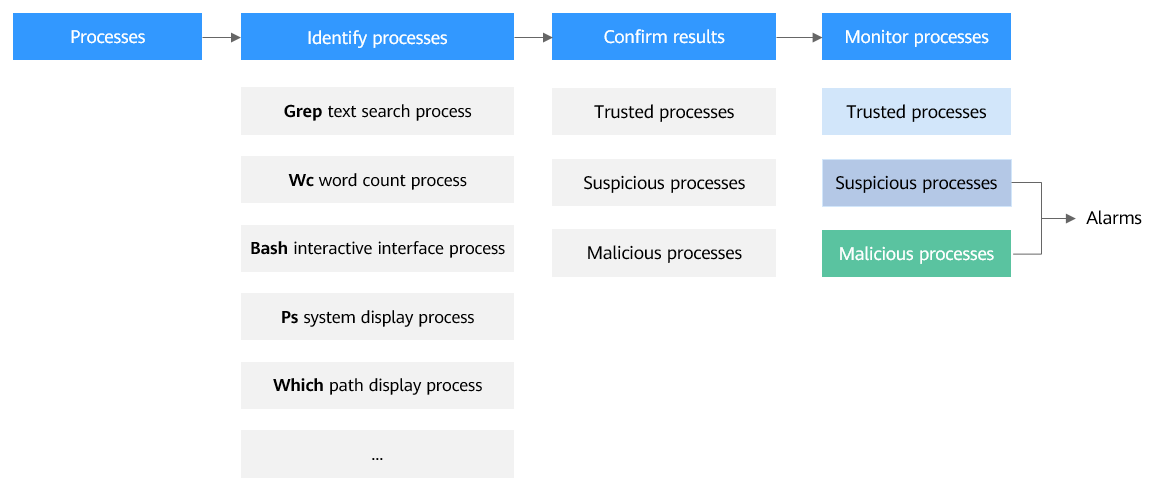
Application Process Control Scenarios
In a cloud server environment, the number and types of processes are usually stable. You can use the application process control function to monitor and manage process statuses and effectively identify suspicious or malicious processes, thereby building a more secure service operation environment.
Constraints
- Application process control is available only in HSS premium, WTP, and container editions. For details about how to purchase and upgrade HSS, see Purchasing an HSS Quota and Upgrading a Protection Quota.
- To use application process control, ensure the agent installed on the server falls within the following range. For details about how to upgrade the agent, see Upgrading the Agent.
- Linux: 3.2.7 or later
- Windows: 4.0.19 or later
Process of Using Application Process Control
|
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
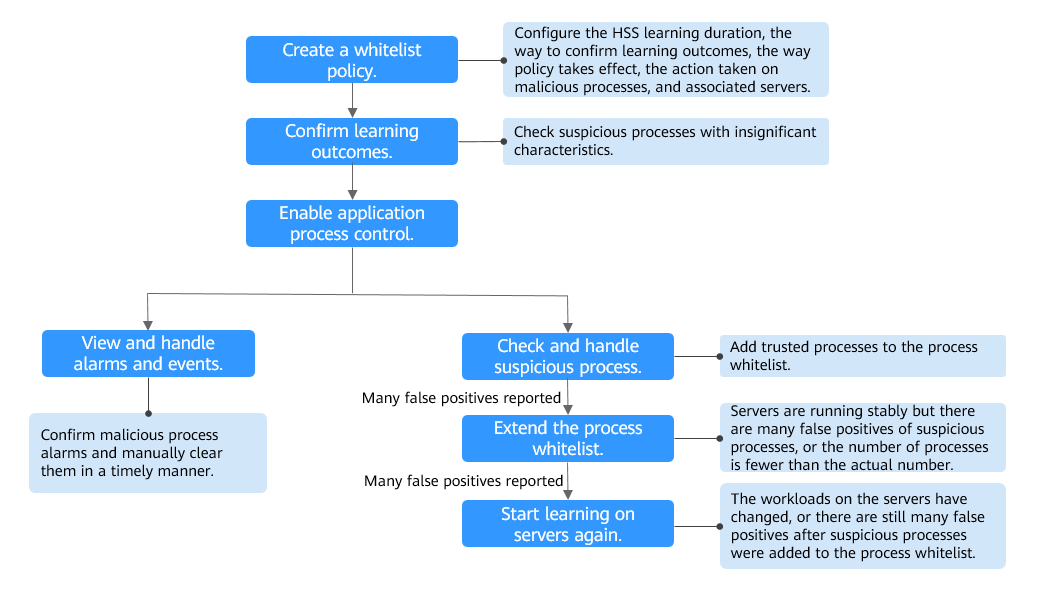
A whitelist policy specifies how HSS learns server behaviors and protect application processes. Application process protection can be enabled only for servers associated with a whitelist policy. |
|
|
After the HSS learns the application processes on servers, there may be some suspicious application processes with insignificant characteristics, and HSS cannot determine whether they are malicious or trustworthy. In this case, you need to confirm the learning outcomes. |
|
|
Enable application process control on the servers associated with a policy. |
|
|
HSS cannot determine whether some suspicious application processes with insignificant characteristics are trustworthy. You need to check their process details, determine whether they are trustworthy, and add them to the process whitelist. |
|
|
HSS reports an alarm once it detects a malicious process. Choose , check and handle the alarms on the Server Alarms tab page, and clear malicious processes in a timely manner. |
|
|
(Optional) Add items to the process whitelist. |
After HSS completes learning, if you think the number of application processes it learned is fewer than the number of process fingerprints collected by the asset fingerprint function, or if it regarded many trustworthy application processes as suspicious, you can extend the HSS process whitelist. HSS will compare the application processes it already learned with the collected process fingerprints to enrich the HSS application process intelligence library and extend the trusted process whitelist. |
|
(Optional) Start learning on the servers again. |
If you have added trustworthy processes to the whitelist but there are still many false positives reported, you can let HSS start learning again on the servers. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






