Configuring a Job for Synchronizing Data from MySQL to Kafka
Supported Source and Destination Database Versions
|
Source Database |
Destination Database |
|---|---|
|
MySQL database (5.6, 5.7, and 8.x) |
Kafka cluster (2.7 and 3.x) |
Database Account Permissions
Before you use DataArts Migration for data synchronization, ensure that the source and destination database accounts meet the requirements in the following table. The required account permissions vary depending on the synchronization task type.
|
Type |
Required Permissions |
|---|---|
|
Source database account |
The source database account must have the following minimal permissions required for running SQL statements: SELECT, SHOW DATABASES, REPLICATION SLAVE and REPLICATION CLIENT. GRANT SELECT, SHOW DATABASES, REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'Username'@'%'; |
|
Destination database account |
The MRS user must have the read and write permissions on corresponding Kafka topics, that is, the user must belong to the kafka/kafkaadmin/kafkasuperuser user group.
NOTE:
A common Kafka user can access a topic only after being granted the read and write permissions on the topic by the Kafka administrator. |
- You are advised to create independent database accounts for DataArts Migration task connections to prevent task failures caused by password modification.
- After changing the account passwords for the source or destination databases, modify the connection information in Management Center as soon as possible to prevent automatic retries after a task failure. Automatic retries will lock the database accounts.
Supported Synchronization Objects
The following table lists the objects that can be synchronized using different links in DataArts Migration.
|
Type |
Note |
|---|---|
|
Synchronization objects |
|
Important Notes
In addition to the constraints on supported data sources and versions, connection account permissions, and synchronization objects, you also need to pay attention to the notes in the following table.
Procedure
This section uses real-time synchronization from RDS for MySQL to as an example to describe how to configure a real-time data migration job. Before that, ensure that you have read the instructions described in Check Before Use and completed all the preparations.
- Create a real-time migration job by following the instructions in Creating a Real-Time Migration Job and go to the job configuration page.
- Select the data connection type. Select MySQL for Source and for Destination.
Figure 1 Selecting the data connection type

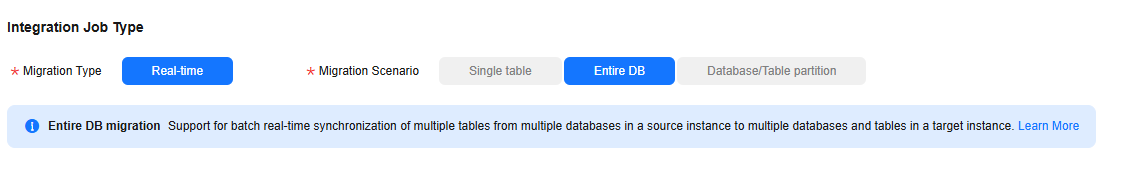
- Select a job type. The default migration type is Real-time. The migration scenarios include Entire DB.
Figure 2 Setting the migration job type
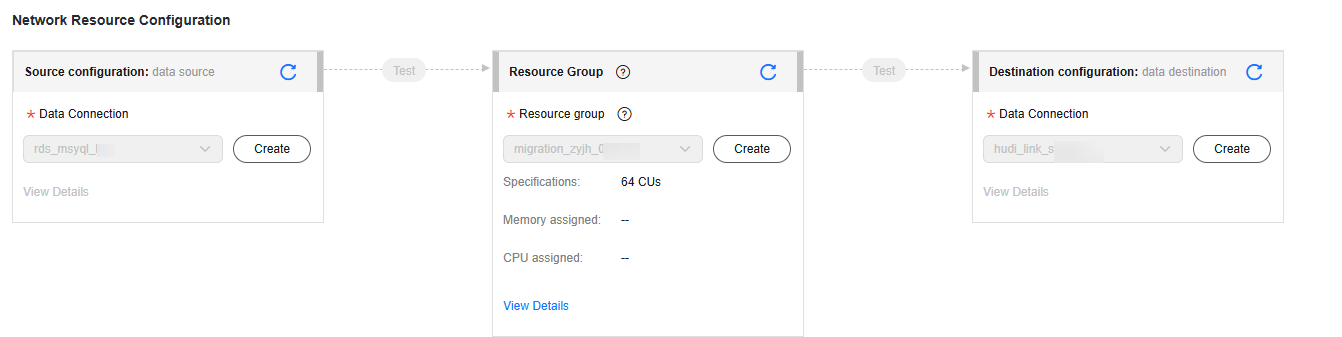
- Configure network resources. Select the created MySQL and data connections and the migration resource group for which the network connection has been configured.
Figure 3 Selecting data connections and a migration resource group
If no data connection is available, click Create to go to the Manage Data Connections page of the Management Center console and click Create Data Connection to create a connection. For details, see Configuring DataArts Studio Data Connection Parameters.
- Configure source parameters.
Select the databases and tables to be synchronized based on the following table.
Table 5 Selecting the databases and tables to be synchronized Synchronization Scenario
Configuration Method
Entire DB
Select the MySQL databases and tables to be migrated.Figure 4 Selecting databases and tables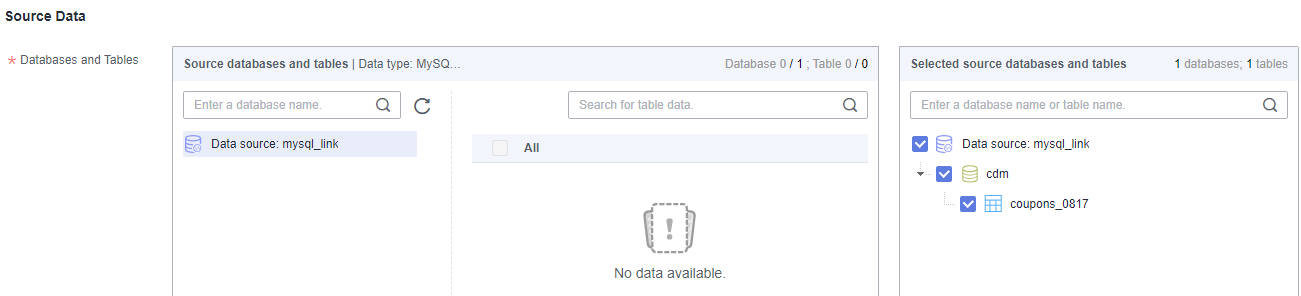
Both databases and tables can be customized. You can select one database and one table, or multiple databases and tables.
- Configure destination parameters.
Figure 5 Kafka destination parameters
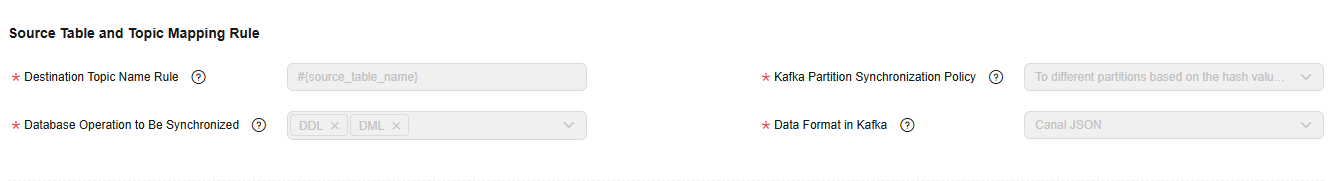
- Destination Topic Name Rule
Configure the rule for mapping source MySQL database tables to destination Kafka topics.
Table 6 Destination topic name rule Synchronization Scenario
Configuration Method
Entire DB
Configure the rule for mapping source MySQL database tables to destination Kafka topics. You can specify a fixed topic or use built-in variables to synchronize data from source tables to destination topics.
The following built-in variables are available:
- Source database name: #{source_db_name}
- Source table name: #{source_table_name}
- Kafka Partition Synchronization Policy
The following three policies are available for synchronizing source data to specified partitions of destination Kafka topics:
- To partition 0
- To different partitions based on the hash values of database names/table names
- To different partitions based on the hash values of table primary keys
If the source has no primary key, data is synchronized to partition 0 at the destination by default.
- Partitions of New Topic
If the destination Kafka does not have the corresponding topic, the topic automatically created by DataArts Migration has three partitions.
- Destination Kafka Attributes
You can add Kafka configuration items with the properties. prefix. The job automatically removes the prefix and transfers configuration items to the underlying Kafka client. For details about the parameters, see the configuration descriptions in Kafka documentation.
- Advanced Settings
You can add custom attributes in the Configure Task area to enable some advanced functions. For details about the parameters, see the following table.
Figure 6 Adding custom attributes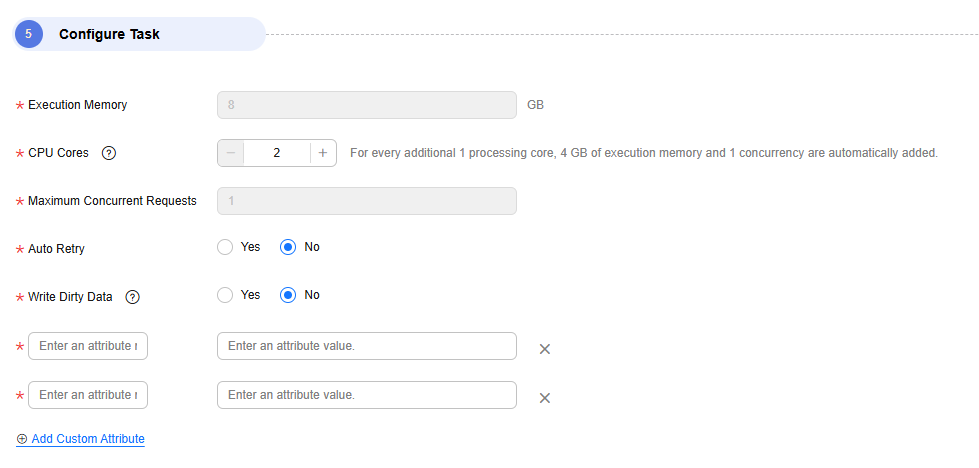
Table 7 Advanced parameters of the job for migrating data from MySQL to Kafka Parameter
Type
Default Value
Unit
Description
source.server.timezone
string
Local time zone
N/A
Session time zone specified for connecting to the source database. The standard time zone format is supported, for example, UTC+08:00.
source.convert.timestampWithServerTimeZone
boolean
true
N/A
Whether to convert the output timestamp data to data with the source time zone.
source.convert.bit1AsInt
boolean
true
N/A
Whether to output bit1 data as int data
sink.delivery-guarantee
string
at-least-once
N/A
Semantic assurance when Flink writes data to Kafka
- at-least-once: At a checkpoint, the system waits for all data in the Kafka buffer to be confirmed by the Kafka producer. No message will be lost due to events that occur on the Kafka broker. However, duplicate messages may be generated when Flink is restarted because Flink processes old data again.
- exactly-once: In this mode, the Kafka sink writes all data through the transactions submitted at a checkpoint. Therefore, if the consumer reads only submitted data, duplicate data will not be generated when Flink is restarted. However, data is visible only when a checkpoint is complete, so you need to adjust the checkpoint interval as needed.
- Destination Topic Name Rule
- Update the mapping between the source table and destination table and check whether the mapping is correct.
Table 8 Mapping between source and destination tables Synchronization Scenario
Configuration Method
Entire DB
You can change the names of mapped destination topics as needed. You can map one source topic to one destination topic or map multiple source topics to one destination topic.
Figure 7 Mapping between the source and destination tables in the entire database migration scenario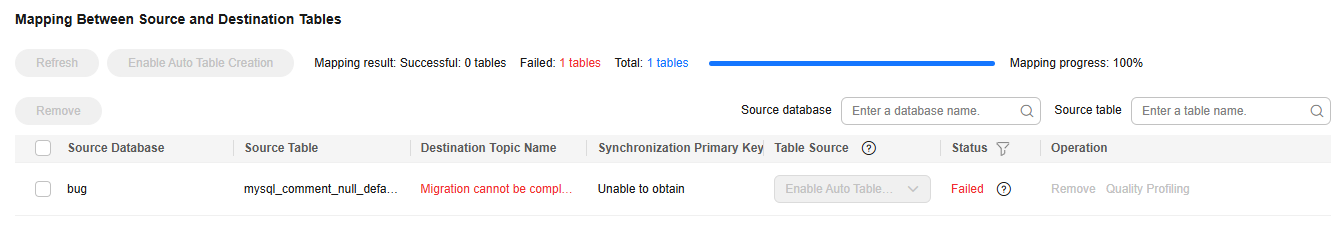
- Configure task parameters.
Table 9 Task parameters Parameter
Description
Default Value
Execution Memory
Memory allocated for job execution, which automatically changes with the number of CPU cores
8GB
CPU Cores
Value range: 2 to 32
For each CPU core added, 4 GB execution memory and one concurrency are automatically added.
2
Maximum Concurrent Requests
Maximum number of jobs that can be concurrently executed. This parameter does not need to be configured and automatically changes with the number of CPU cores.
1
Custom attributes
You can add custom attributes to modify some job parameters and enable some advanced functions. For details, see Job Performance Optimization.
-
- Submit and run the job.
After configuring the job, click Submit in the upper left corner to submit the job.
Figure 8 Submitting the job
After submitting the job, click Start on the job development page. In the displayed dialog box, set required parameters and click OK.
Figure 9 Starting the job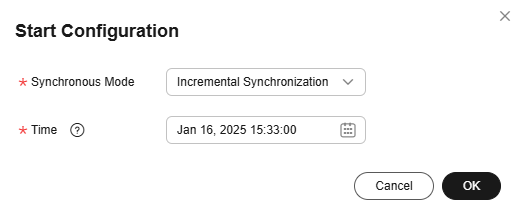
Table 10 Parameters for starting the job Parameter
Description
Offset Parameter
- Incremental synchronization: Incremental data synchronization starts from a specified time point.
- Full and incremental synchronization: All data is synchronized first, and then incremental data is synchronized in real time.
Time
This parameter must be set for incremental synchronization, and it specifies the start time of incremental synchronization.
NOTE:If you set a time that is earlier than the earliest binlog time, the latest log time is used.
- Monitor the job.
On the job development page, click Monitor to go to the Job Monitoring page. You can view the status and log of the job, and configure alarm rules for the job. For details, see Real-Time Migration Job O&M.
Figure 10 Monitoring the job
Performance Optimization
If the synchronization speed is too slow, rectify the fault by referring to Job Performance Optimization.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






