Comprehensive Monitoring of GPU, Virtualization, and Pod Resource Metrics
Monitoring GPU metrics optimizes performance, identifies faults quickly, and allocates resources efficiently. It improves GPU utilization and lowers O&M costs. Using Prometheus and Grafana, you can comprehensively monitor GPU resources and accurately obtain resource usage. This section describes how to configure Prometheus and Grafana.
For more information, see GPU Metrics Provided by CCE.
Prerequisites
- The Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on has been installed in the cluster.
- The CCE AI Suite (NVIDIA GPU) add-on has been installed in the cluster, and the add-on version is 2.0.10 or later.
- At least one NVIDIA GPU node is available in the cluster.
- To monitor GPU virtualization metrics, ensure Volcano Scheduler has been installed in the cluster and the add-on version is 1.10.5 or later.
Process
|
Step |
Description |
Billing |
|---|---|---|
|
GPU metrics are automatically reported when a GPU-backed workload is deployed in a cluster. |
N/A |
|
|
You can access Prometheus to view GPU monitoring metrics. |
|
|
|
You can access Grafana to view GPU monitoring metrics on the built-in dashboard. Additionally, you can customize the dashboard as needed. |
A load balancer must be associated, which will be billed. |
Deploying a GPU Workload
Create a GPU-backed workload. After the workload runs properly, access Prometheus or Grafana to monitor GPU metrics.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console. The Overview page is displayed.
- In the navigation pane, choose Workloads. In the upper right corner of the displayed page, click Create Workload.
- Click Basic Info in the Container Information area under Container Settings. Select GPU card for GPU Quota and set Number of GPUs to 1.
- Configure other workload parameters and click Create Workload. If the workload status is Running, the GPU workload has been created.
Accessing Prometheus
To view GPU metrics in Prometheus, enable Local Data Storage in Data Storage Configuration of Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring. For details, see Installing the Add-on.
After Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring is installed, its associated workloads and Services are automatically deployed in the cluster. The Prometheus server will be deployed as a StatefulSet in the monitoring namespace. You can create a public LoadBalancer Service to enable Prometheus access from the Internet.
- In the navigation pane, choose Services & Ingresses. In the upper right corner, click Create from YAML and create a public LoadBalancer Service.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: prom-lb # Service name, which is customizable. namespace: monitoring labels: app: prometheus component: server annotations: kubernetes.io/elb.id: 038ff*** # Replace it with the ID of the public load balancer in the VPC that the cluster belongs to. spec: ports: - name: cce-service-0 protocol: TCP port: 88 # Service port, which is user-defined. targetPort: 9090 # Default Prometheus port. Retain the default value. selector: # The label selector can be adjusted based on the label of a Prometheus server instance. app.kubernetes.io/name: prometheus prometheus: server type: LoadBalancer - After the Service is created, enter Public IP address of the load balancer:Service port in your browser's address bar to access Prometheus.
Figure 1 Accessing Prometheus

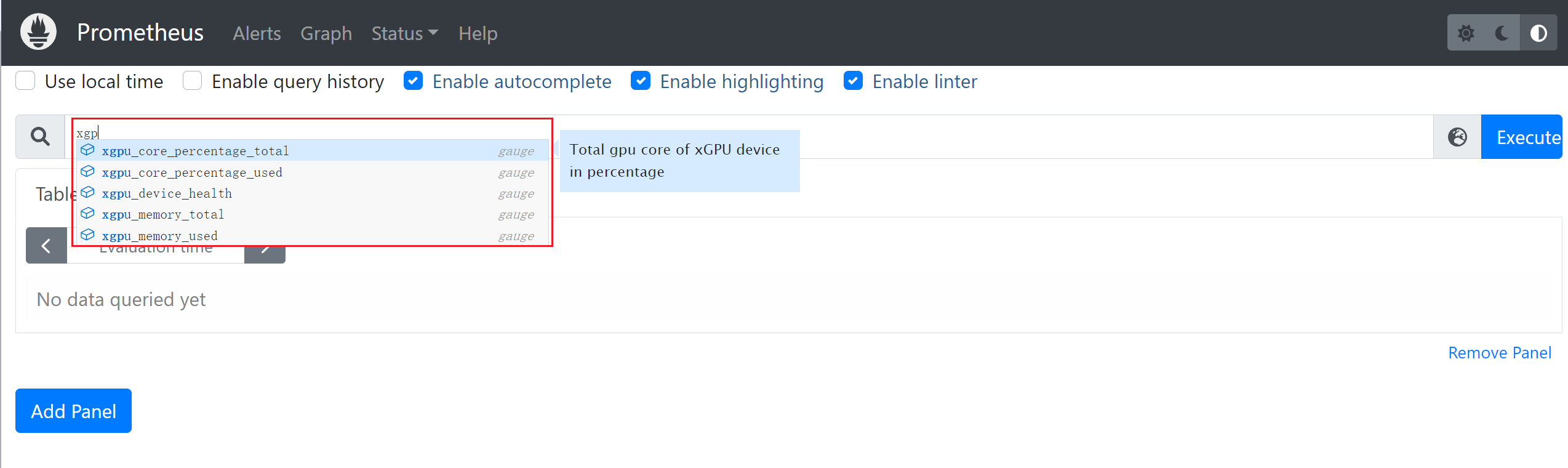
- Click Graph in the upper part of the page, search for the required GPU metric, and view its details.
Figure 2 Viewing GPU metrics
- Choose Status > Targets to view all metrics monitored by Prometheus.
Figure 3 Viewing monitored targets

Accessing Grafana
To view GPU metrics in Grafana, install Grafana and enable Public Access. Grafana supports AOM and Prometheus data sources.
- To use an AOM data source, enable Report Monitoring Data to AOM in Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring and Interconnect with AOM in Grafana. In addition, make sure to use the same AOM instances for both add-ons. Then, Grafana will automatically generate the prometheus-aom data source.
- To use a Prometheus data source, enable Local Data Storage in Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring. Then, you can directly use the prometheus data source provided by Grafana.
- Test connectivity of the data source. Ensure the prometheus-aom or prometheus data source is accessible to Grafana. Otherwise, it will not be available in Grafana.
- In the navigation pane, choose Cluster > Add-ons. In the right pane, find the Grafana add-on and click Access to go to its GUI.
- Enter the username and password when you access the Grafana GUI for the first time. The default username and password are both admin. After logging in, reset the password as prompted.
- In the upper left corner of the page, click
 . Then, click
. Then, click  on the left of Connections. Click Data sources to access the Data sources page.
on the left of Connections. Click Data sources to access the Data sources page. - In the data source list, click prometheus-aom or prometheus. Click Save & test at the bottom of the data source page to verify connectivity. If "Successfully queried the Prometheus API" is displayed, the connectivity test has been passed.
- In the navigation pane, choose Dashboards. Then, choose GPU XGPU View in the right pane to view GPU resource statuses. You can also customize the dashboard as needed.
Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring does not automatically collect GPU pod monitoring metrics. To view data in Grafana, set up a dashboard. For details, see "Monitoring > Collecting GPU Pod Monitoring Metrics and Setting Up a Grafana Dashboard" in Best Practices.
Figure 4 Viewing GPU metrics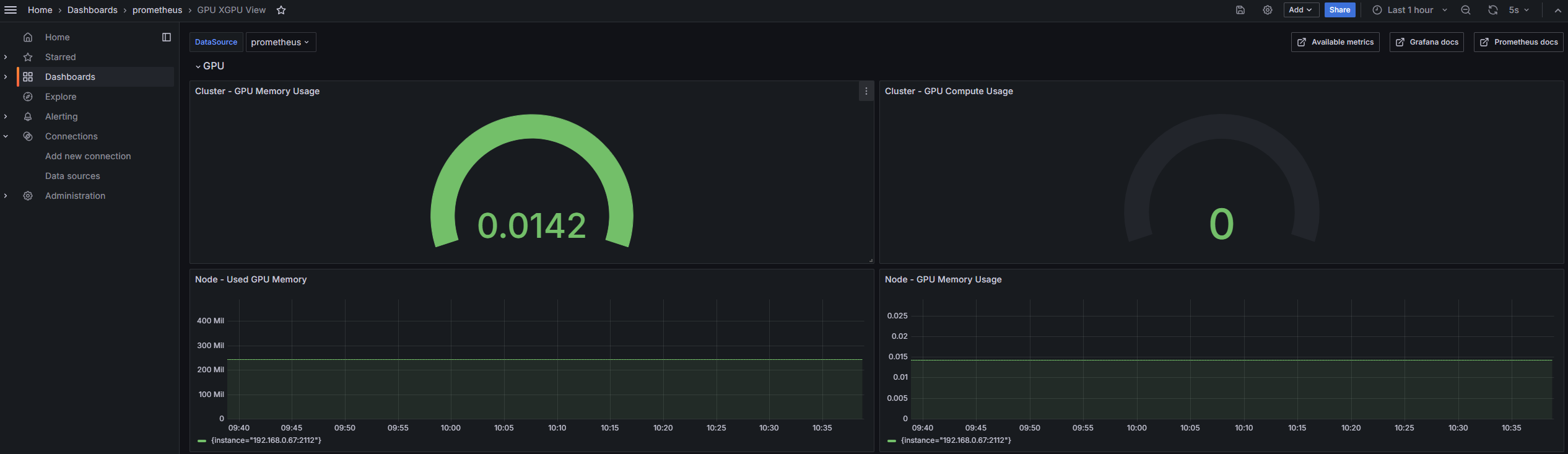
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






