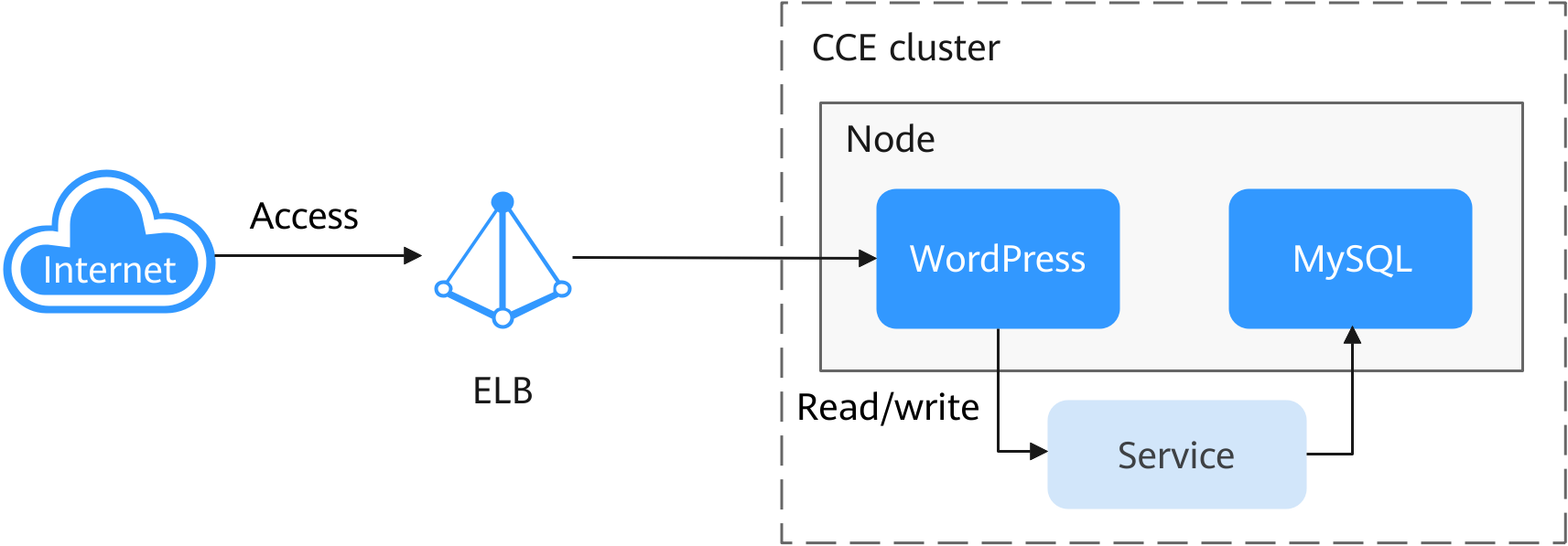
Deploying a WordPress StatefulSet in a CCE Cluster
StatefulSets are a type of workload in Kubernetes. They are designed to manage stateful applications. Unlike Deployments, StatefulSets are ideal for applications that require data consistency and durability. Each StatefulSet pod has its own unique identifier and must be deployed and scaled in a specific sequence. Examples of stateful applications include databases (like MySQL) and message queues (such as Kafka). This section uses WordPress, a popular content management system, and a MySQL database, as an example to describe how to deploy a StatefulSet in a CCE cluster.
WordPress started as a blogging platform using PHP and MySQL, but it has evolved into a complete content management system. You can use a CCE cluster to quickly set up your own blog. For more information about WordPress, see the WordPress official website.
WordPress and a database (a MySQL database in this example) are often used together, with WordPress managing content and the database storing website data. In a containerized deployment, WordPress and MySQL typically run in separate containers. WordPress accesses MySQL through a Service.
Video Tutorial
Procedure
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Sign up for a HUAWEI ID. |
|
|
Obtain the required permissions for your account when you use CCE in the deployment region for the first time. |
|
|
Create a CCE cluster to provide Kubernetes services. |
|
|
Create nodes in the cluster to run containerized applications. |
|
|
Create a MySQL workload in the cluster and create a ClusterIP Service for WordPress access. |
|
|
Create a WordPress workload in the cluster and create a LoadBalancer Service for the workload for Internet access. |
|
|
Access the WordPress website from the Internet to start your blog. |
|
|
Release resources promptly if the cluster is no longer needed to avoid extra charges. |
Preparations
- Before you start, sign up for a HUAWEI ID. For details, see Signing up for a HUAWEI ID and Enabling Huawei Cloud Services.
Step 1: Enable CCE and Perform Authorization
When you first log in to the CCE console, CCE automatically requests permissions to access related cloud services (compute, storage, networking, and monitoring) in the region where the cluster is deployed. If you have authorized CCE in the deployment region, skip this step.
- Log in to the CCE console using your HUAWEI ID.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region.
in the upper left corner and select a region. - If this is your first login to the CCE console in the selected region, the Authorization Statement dialog box will appear. Read it carefully and click OK.
After you agree to delegate permissions, CCE uses IAM to create an agency named cce_admin_trust. This agency is granted Tenant Administrator permissions for the resources of other cloud services (excluding IAM). These permissions are required for CCE to access dependent cloud services and are only valid for the current region. You can view the authorization records in each region by navigating to the IAM console, choosing Agencies in the navigation pane, and clicking cce_admin_trust. For more details, see Cloud Service Agency.
To ensure CCE can run normally, do not delete or modify the cce_admin_trust agency, as CCE requires Tenant Administrator permissions.
CCE has updated the cce_admin_trust agency permissions to enhance security while accommodating dependencies on other cloud services. The new permissions no longer include Tenant Administrator permissions. This update is only available in certain regions. If your clusters are of v1.21 or later, a message will appear on the console asking you to re-grant permissions. After re-granting, the cce_admin_trust agency will be updated to include only the necessary cloud service permissions, with the Tenant Administrator permissions removed.
When creating the cce_admin_trust agency, CCE creates a custom policy named CCE admin policies. Do not delete this policy.
Step 2: Create a Cluster
- Log in to the CCE console and click Buy Cluster.
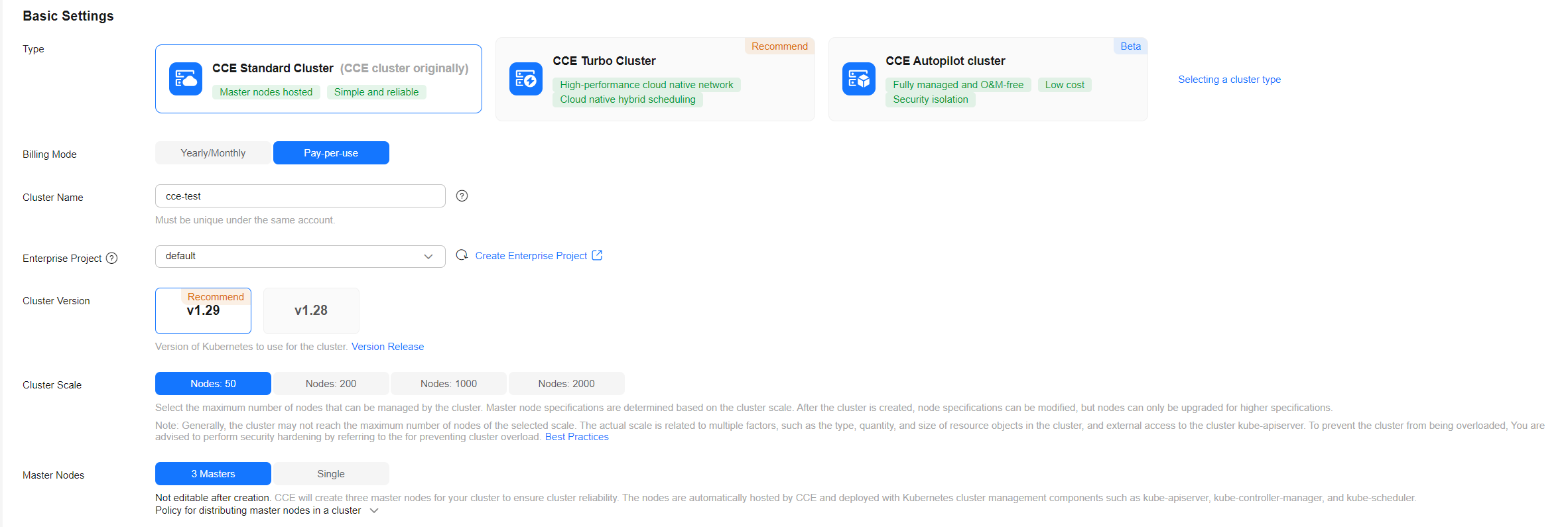
- Configure basic cluster parameters.
This example describes only mandatory parameters. You can keep default settings for most other parameters. For details, see Buying a CCE Standard/Turbo Cluster.
Parameter
Example
Description
Type
CCE Standard Cluster
CCE supports multiple cluster types to meet diverse needs, including highly reliable, highly secure, commercial containers.
You can select CCE Standard Cluster or CCE Turbo Cluster as required.
- CCE standard clusters provide highly reliable, highly secure, commercial containers.
- CCE Turbo clusters use high-performance cloud native networks and support cloud native hybrid scheduling. These clusters offer improved resource utilization and are suitable for a wider range of scenarios.
For more details, see Comparison Between Cluster Types.
Billing Mode
Pay-per-use
Select a billing mode for the cluster.
- Yearly/Monthly: a prepaid billing mode. Resources are billed based on how long you will need the resources for. This mode is more cost-effective when resource usage periods are predictable.
If you choose this option, select the desired duration and decide whether to enable automatic renewal (monthly or yearly). Monthly subscriptions renew automatically every month, and yearly subscriptions renew automatically every year.
- Pay-per-use: a postpaid billing mode. Resources are billed based on actual usage duration. This mode is suitable for flexible scenarios where you may need to provision or delete resources at any time.
For more details, see Billing Modes.
Cluster Name
cce-test
Enter a name for the cluster.
Enterprise Project
default
Enterprise projects facilitate project-level management and grouping of cloud resources and users.
This parameter is only displayed for enterprise users who have enabled enterprise projects.
Cluster Version
v1.29 (recommended)
Select the latest Kubernetes commercial release to benefit from new, reliable, and production-ready features. CCE offers multiple Kubernetes versions.
Cluster Scale
Nodes: 50
This parameter controls the maximum number of worker nodes the cluster can manage. Configure it as needed. After the cluster is created, it can be scaled out, but it cannot be scaled in.
Master Nodes
3 Masters
Select the number of master nodes, also known as control plane nodes. These nodes are hosted on CCE and run Kubernetes components like kube-apiserver, kube-controller-manager, and kube-scheduler.
- Multiple: Three master nodes will be created to ensure high availability.
- Single: Only one master node will be created in your cluster.
This setting cannot be changed after the cluster is created.
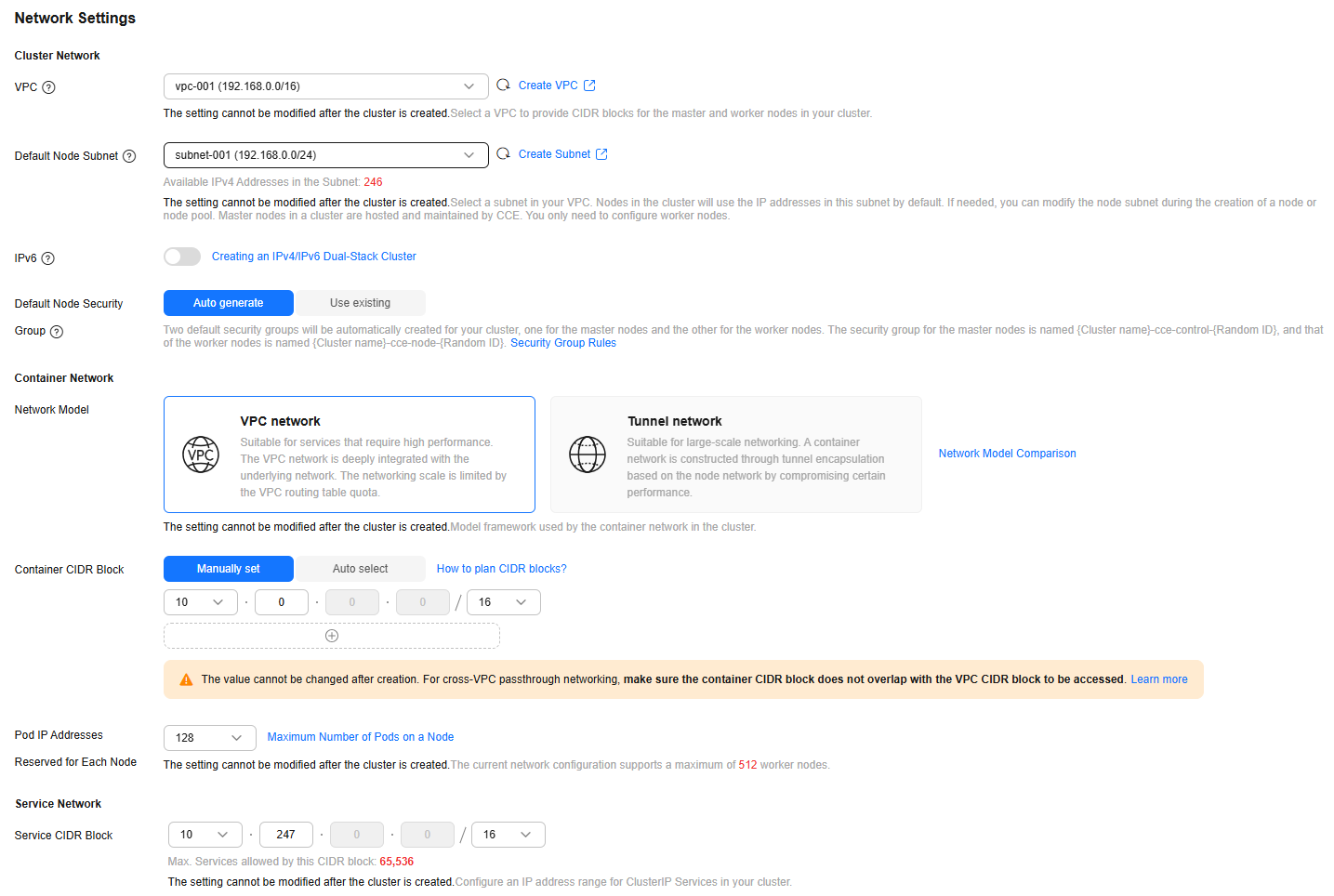
- Configure network parameters.
Parameter
Example
Description
VPC
vpc-001
Select a VPC for the cluster.
If no VPC is available, click Create VPC to create one. After creating the VPC, click the refresh icon. For details, see Creating a VPC and Subnet.
Default Node Subnet
subnet-001
Select a subnet. Nodes in the cluster will be assigned IP addresses from this subnet.
Network Model
VPC network
Select VPC network or Tunnel network. The default value is VPC network.
For details about the differences between container network models, see Container Networks.
Container CIDR Block
Manually set (10.0.0.0/16)
Specify the container CIDR block. The CIDR block determines how many containers you can deploy in the cluster. You can select Manually set or Auto select.
Pod IP Addresses Reserved for Each Node
128
Specify the number of allocatable container IP addresses (the alpha.cce/fixPoolMask parameter) on each node. This determines the maximum number of pods that can be created on each node.
Service CIDR Block
10.247.0.0/16
Configure the cluster-wide IP address range. This controls how many Services can be created. This setting cannot be changed later.
- Click Next: Select Add-on. On the page displayed, select the add-ons to be installed during cluster creation.
This example only includes mandatory add-ons, which are installed automatically.
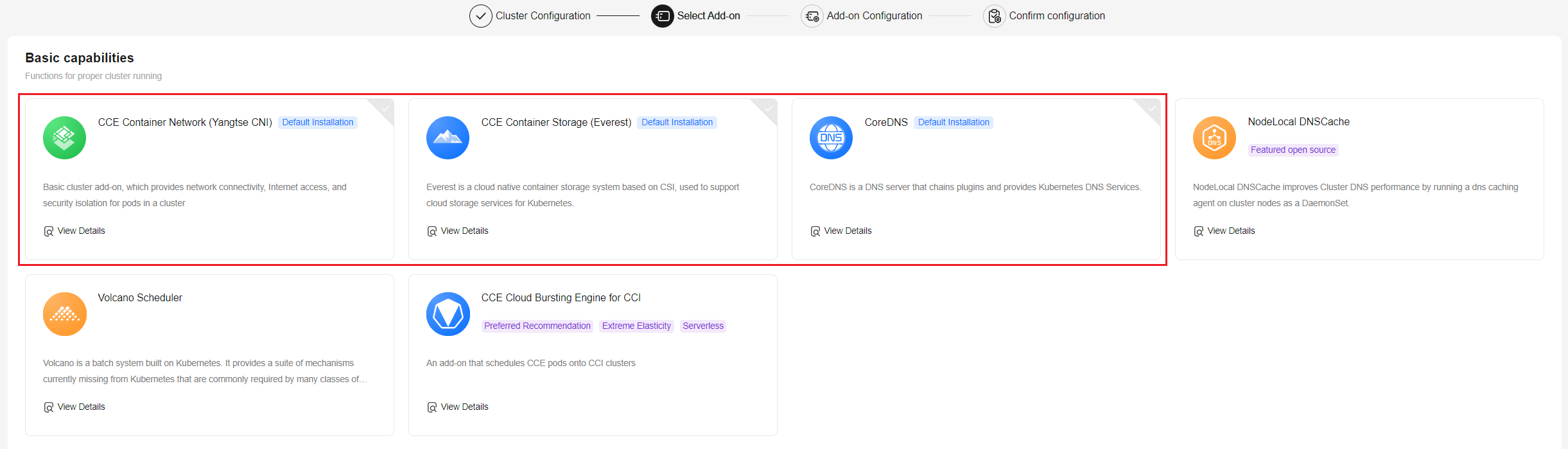
- Click Next: Configure Add-on. No setup is needed for the default add-ons.
- Click Next: Confirm Settings, check the displayed cluster resource list, and click Submit.
Wait for the cluster to be created. It takes approximately 5 to 10 minutes.
The newly created cluster in the Running state with zero nodes will be displayed on the Clusters page.
Figure 1 Cluster created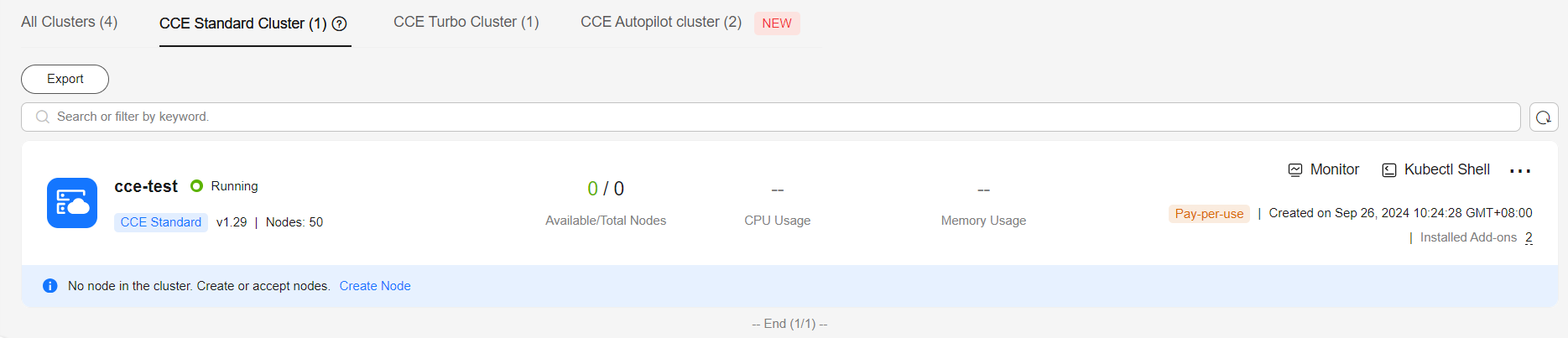
Step 3: Create a Node Pool and Nodes
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Nodes. On the Node Pools tab, click Create Node Pool in the upper right corner.
- Configure the node pool parameters.
This example describes only mandatory parameters. You can keep default settings for most other parameters. For details, see Creating a Node Pool.
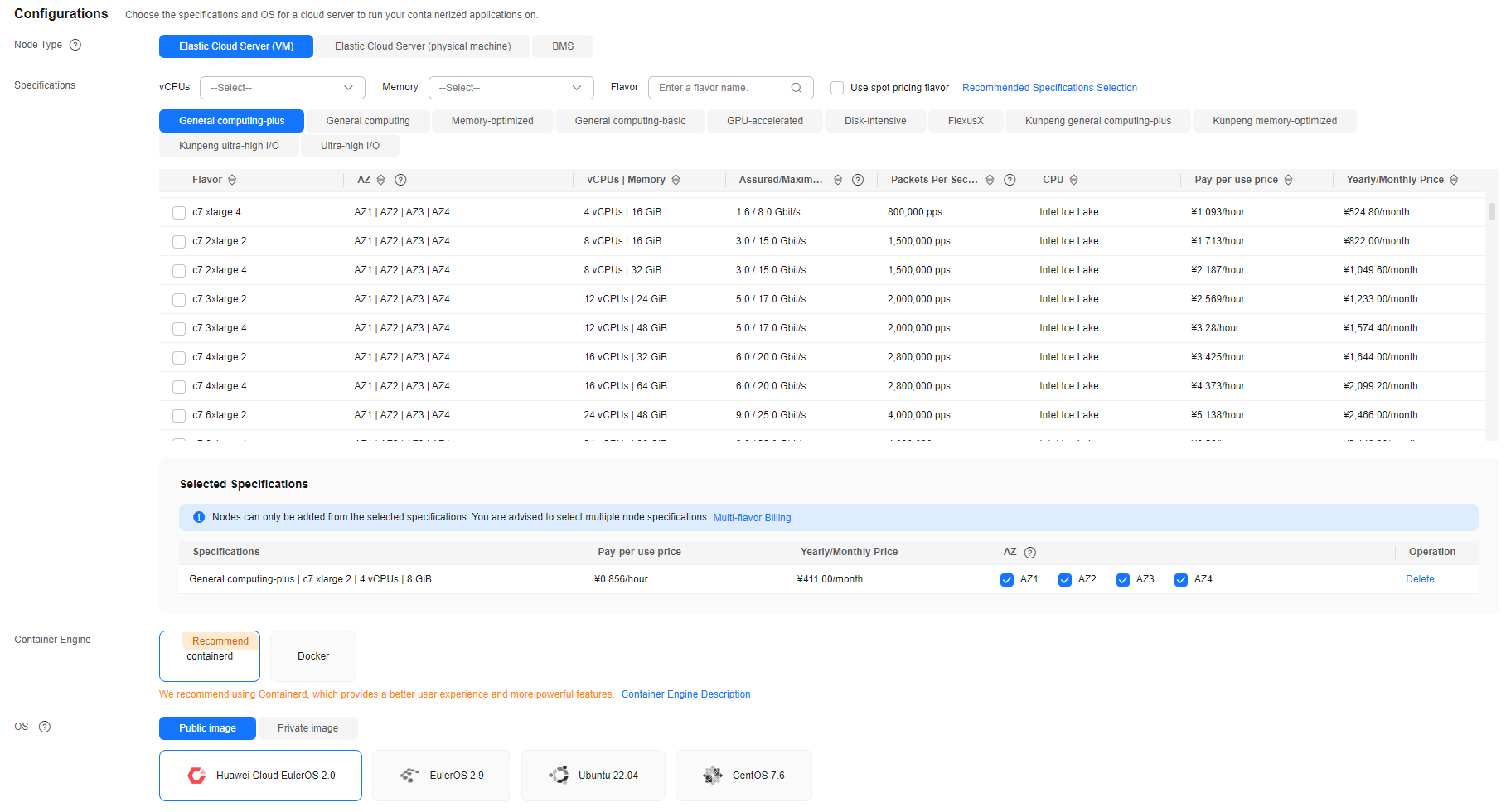
Parameter
Example
Description
Node Type
Elastic Cloud Server (VM)
Select a node type based on service requirements. The available node flavors will then be displayed in the Specifications area for you to choose from.
Specifications
General computing-plus
4 vCPUs | 8 GiB
Select a node flavor that best fits your service needs.
- In this example, there are no specific requirements for memory or GPU resources. General computing-plus or general computing nodes are recommended.
- General computing-plus nodes use dedicated vCPUs and next-generation network acceleration engines to provide strong compute and network performance.
- General computing nodes provide a balance of compute, memory, and network resources and a baseline level of vCPU performance with the ability to burst above the baseline.
- For optimal cluster component performance, choose a node with at least 4 vCPUs and 8 GiB of memory.
Container Engine
containerd
Select a container engine based on service requirements. For details about the differences between container engines, see Container Engines.
OS
Huawei Cloud EulerOS 2.0
Select an OS for the nodes.
Login Mode
A custom password
- Password: Set and confirm a password for node login. The default username is root.
Keep the password secure. It cannot be retrieved if forgotten.
- Key Pair: Select a key pair for node login and confirm that you have the key file. Without this file, you will not be able to log in.
Key pairs are used for identity authentication when you remotely access nodes. If you do not have a key pair, click Create Key Pair. For details, see Creating a Key Pair on the Management Console.
- In this example, there are no specific requirements for memory or GPU resources. General computing-plus or general computing nodes are recommended.
- Configure parameters in Storage Settings and Network Settings. In this example, keep the default settings. Select I have confirmed that the security group rules have been correctly configured for nodes to communicate with each other. and click Next: Confirm.
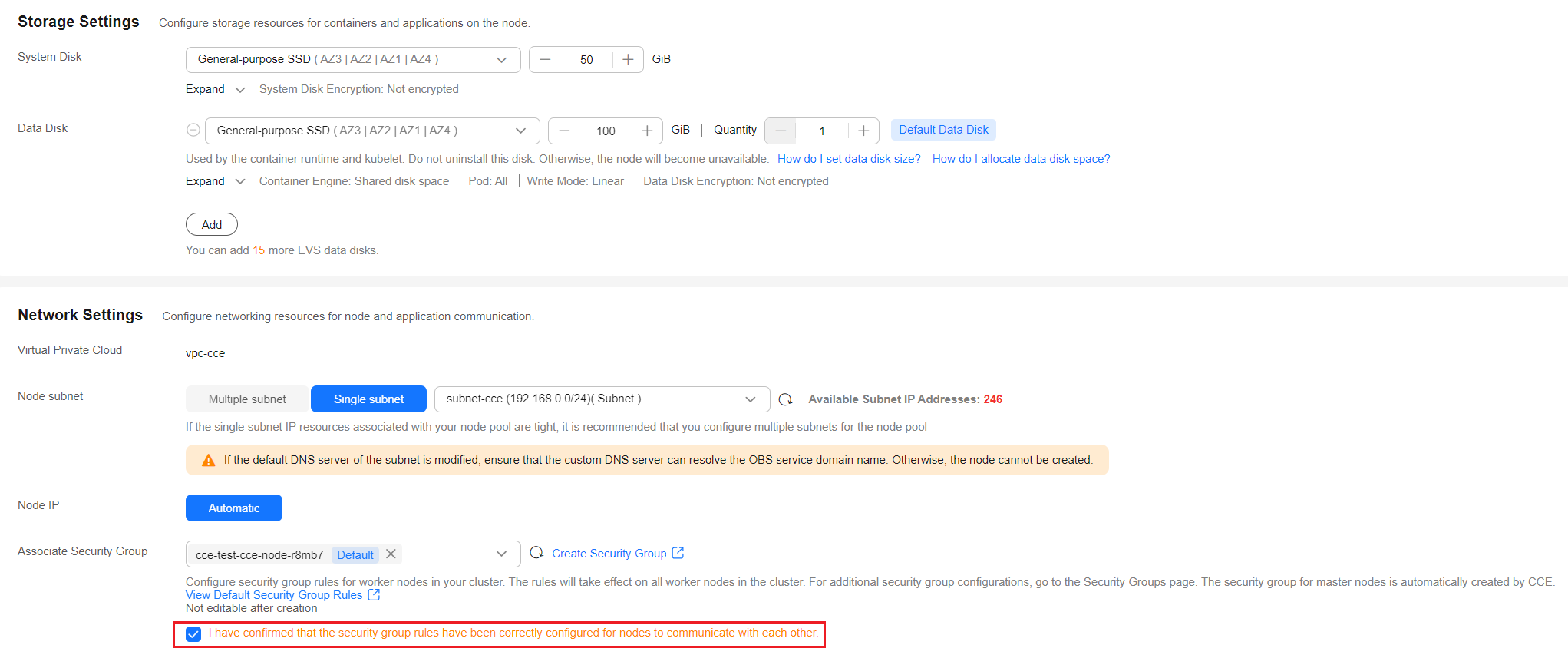
- Review the node specifications, read and confirm the instructions on the page, and click Submit.
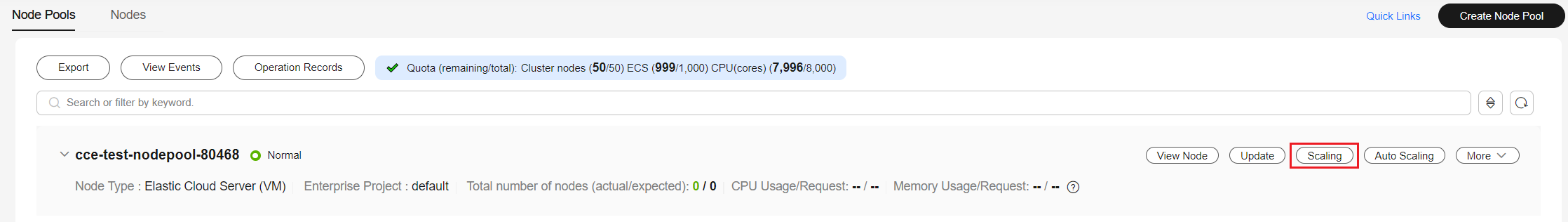
- Locate the newly created node pool and click Scaling. The node pool initially contains zero nodes.
- Set the number of nodes to add to 2. This will create two more nodes in the node pool.
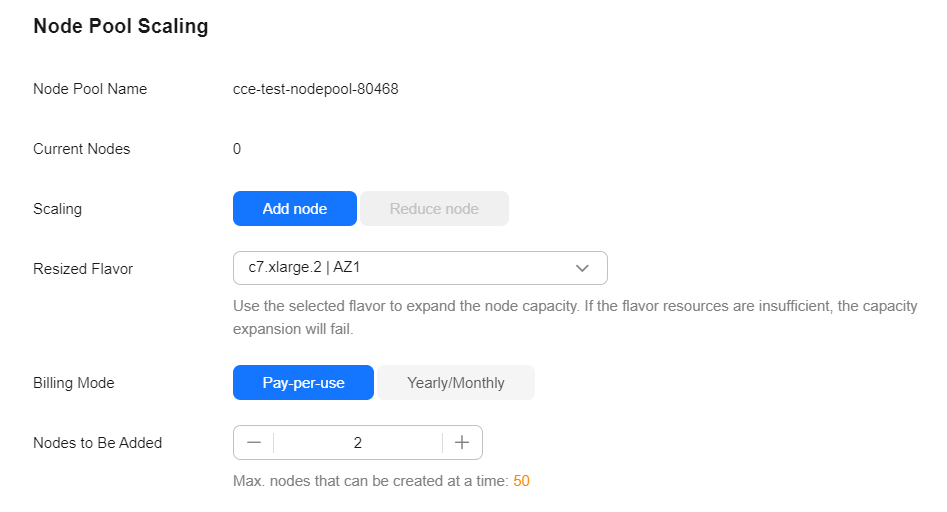
- Wait for the nodes to be created. It takes approximately 5 to 10 minutes.

- Log in to the CCE console.
- Click the name of the cluster to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Workloads. In the right pane, click Create Workload in the upper right corner.
- Configure the basic information for the workload.
In this example, configure the parameters shown in the table and keep the default settings for other parameters. For more details, see Creating a StatefulSet.
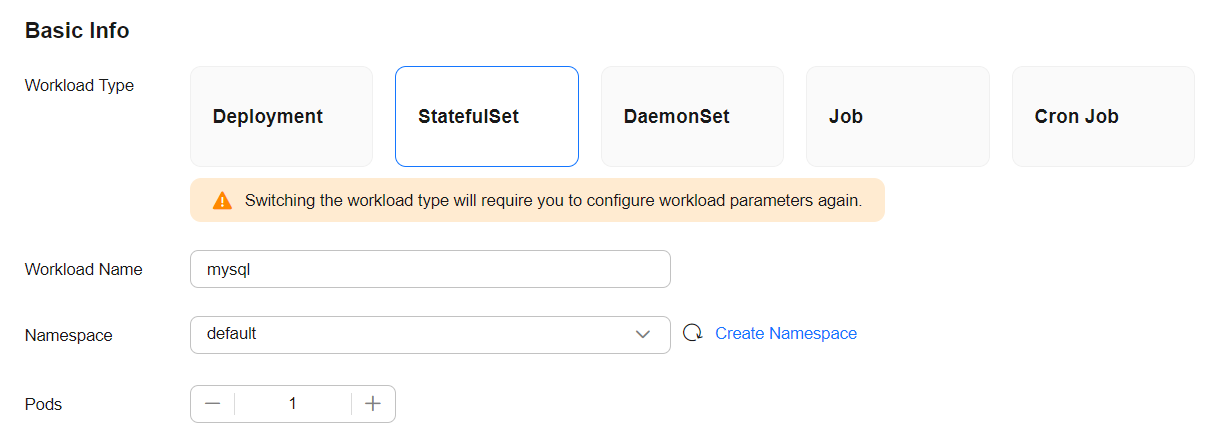
Parameter
Example
Description
Workload Type
StatefulSet
A workload is an application running on Kubernetes. Various built-in workload types are available, each designed for different functions and scenarios. For more details, see Workload Overview.
Workload Name
mysql
Enter a workload name.
Namespace
default
In Kubernetes, a namespace is a conceptual grouping of resources or objects, providing isolation from other namespaces.
After a cluster is created, a namespace named default is generated by default. You can use this namespace directly.
Pods
1
Specify the number of pods for the workload.
- Configure the basic information about the container.
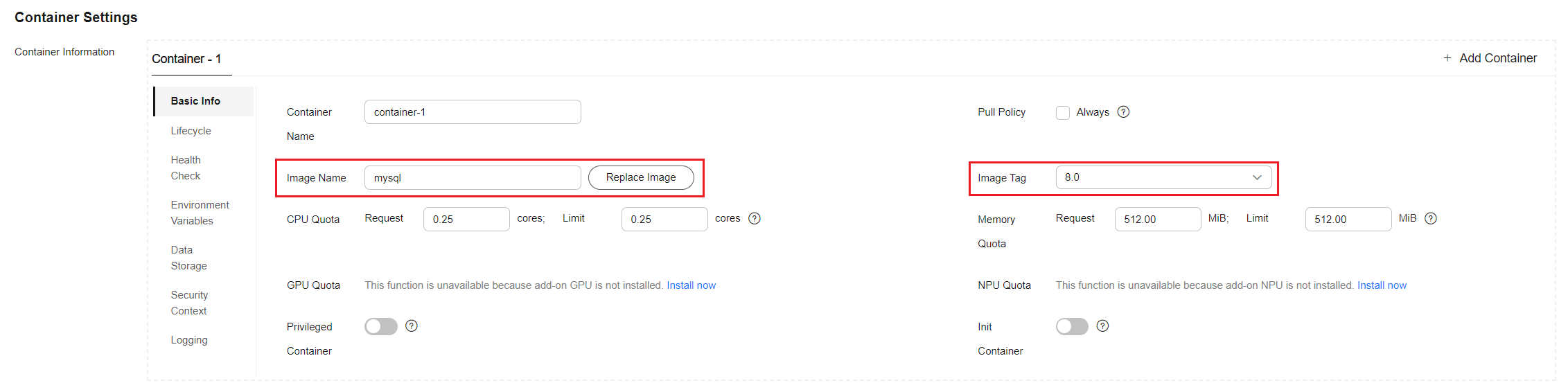
Parameter
Example
Description
Image Name
A MySQL image of tag 8.0
In the Container Settings area, click Basic Info and click Select Image. In the dialog box displayed, select Open Source Images, search for mysql, select the mysql image, and configure the image tag. To ensure compatibility, set the image tag to 8.0. The compatibility between other tags and WordPress has not been verified. Any other tags may create compatibility issues with WordPress. For details, see FAQs.
CPU Quota
Request: 0.25 cores
Limit: 0.25 cores
- Request: the number of CPU cores pre-allocated to containers. The default value is 0.25 cores.
- Limit: the maximum number of CPU cores that containers can use. The default value is the same as the Request. If Limit exceeds Request, containers can temporarily use more resources in burst scenarios.
For details, see Configuring Container Specifications.
Memory Quota
Request: 512 MiB
Limit: 512 MiB
- Request: the memory pre-allocated to containers. The default value is 512 MiB.
- Limit: the maximum amount of memory that containers can use. The default value is the same as the Request. If Limit exceeds Request, containers can temporarily use more resources in burst scenarios.
For details, see Configuring Container Specifications.
- Click Environment Variables and add the four required environment variables. For details about the environment variables supported by MySQL, see MySQL.
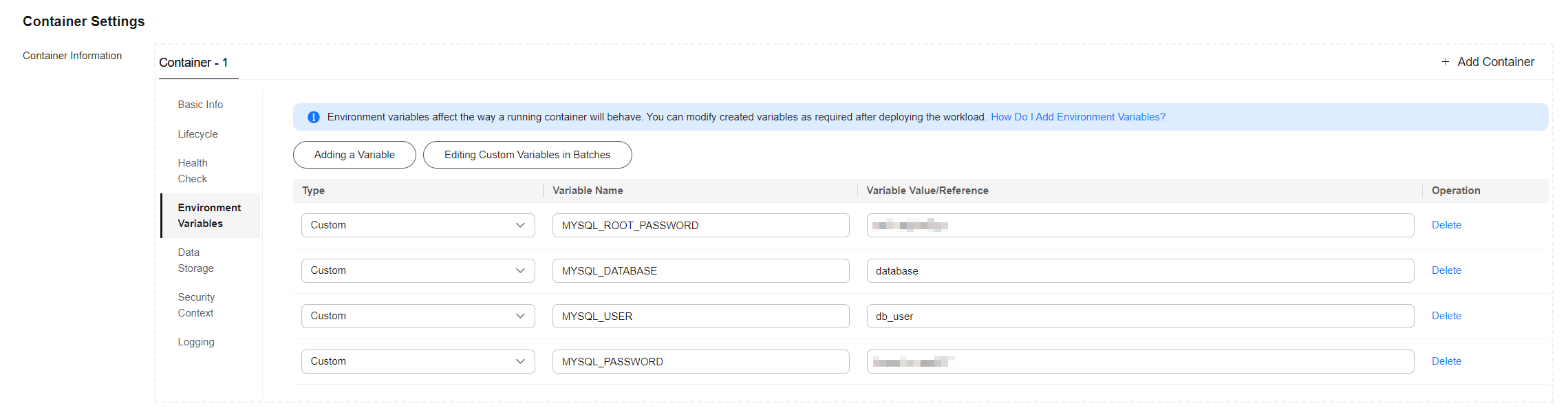
Environment Variable
Example
Description
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
A custom password
The password of the root user of the MySQL database. You configure your own password.
MYSQL_DATABASE
database
The name of the database to be created when the image is started. You configure your own database name.
MYSQL_USER
db_user
The database username. You configure your own username.
MYSQL_PASSWORD
A custom password
The database user password. You configure your own password.
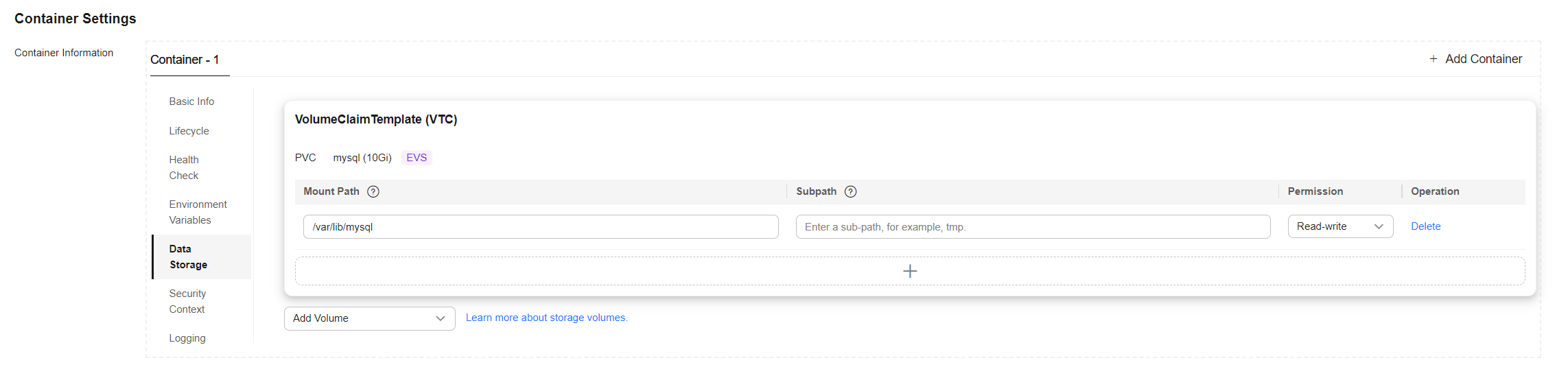
- Click Data Storage, click Add Volume, select VolumeClaimTemplate (VTC) from the drop-down list, and add an EVS disk for MySQL.
Click Create PVC, configure the parameters shown here, and keep the default values for other parameters.
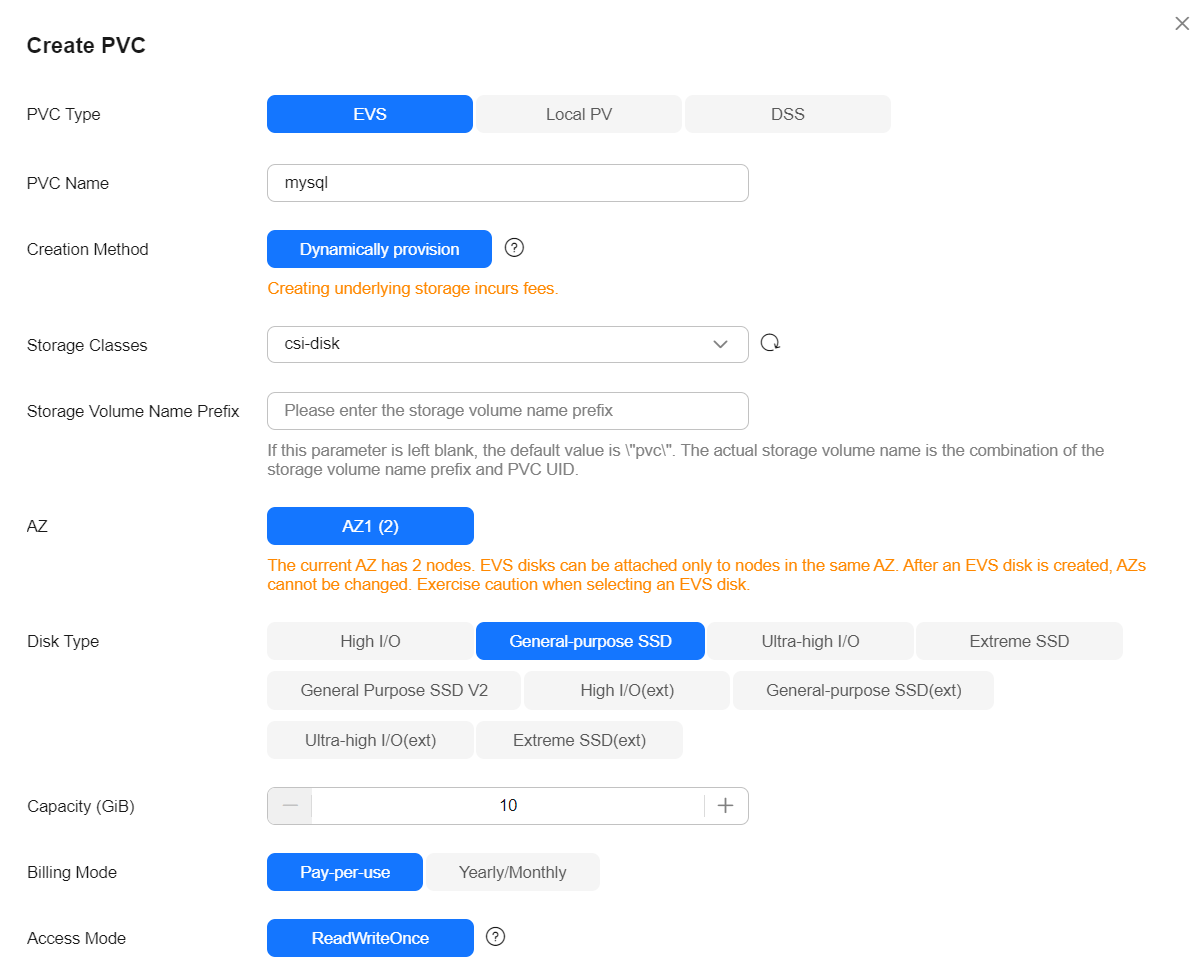
Parameter
Example
Description
PVC Type
EVS
Select a type for the underlying storage volume used by the PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC).
PVC Name
mysql
Enter a custom PVC name, for example, mysql.
Storage Classes
csi-disk
The default value is csi-disk.
AZ
AZ1
Select an AZ. The EVS disk can only be attached to nodes in the same AZ. After an EVS disk is created, the AZ where the disk locates cannot be changed.
Disk Type
General-purpose SSD
Select a proper type as required.
Capacity (GiB)
10
Enter the capacity required. The default capacity is 10 GiB.
Click Create and enter the path for mounting the storage volume to the container. The default path used by MySQL is /var/lib/mysql.
- In the Headless Service Parameters area, configure a headless Service.
The headless Service is used for networking between StatefulSet pods. It generates a domain name for each pod for accessing a specific StatefulSet pod. For a MySQL database that has primary/secondary relationship and multiple replicas, a headless Service is needed to read and write data from and into the MySQL database server (known as a source) and copy the data to other replicas. In this example, MySQL is deployed in a single pod. For details about how to deploy MySQL in multiple pods, see Run a Replicated Stateful Application.
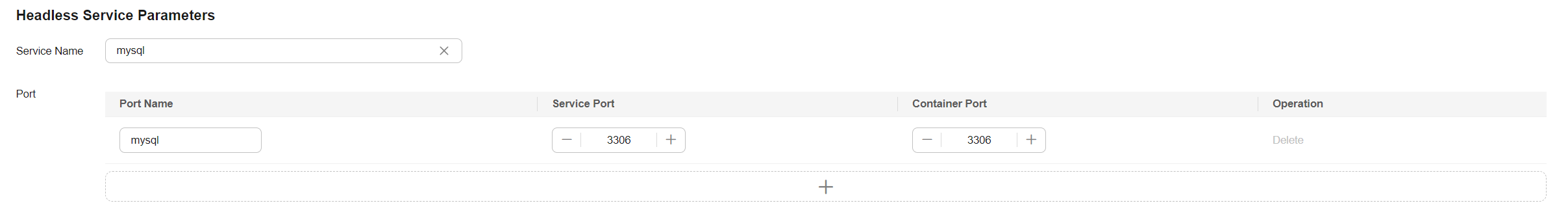
Parameter
Example
Description
Service Name
mysql
Enter a custom headless Service name.
Port Name
mysql
Enter a custom port name. The port name is used to distinguish different ports in a given Service. In this example, only one port is used.
Service Port
3306
Enter a custom port number. This port is used by the Service for external access. In this example, the port is the same as the container port.
Container Port
3306
The actual listening port of the application in the container. It is determined by the port opened by the application image. For example, the MySQL database open port is 3306.
- Click Create Workload.
Wait until the workload is created. After it is created, it will be displayed on the StatefulSets tab.
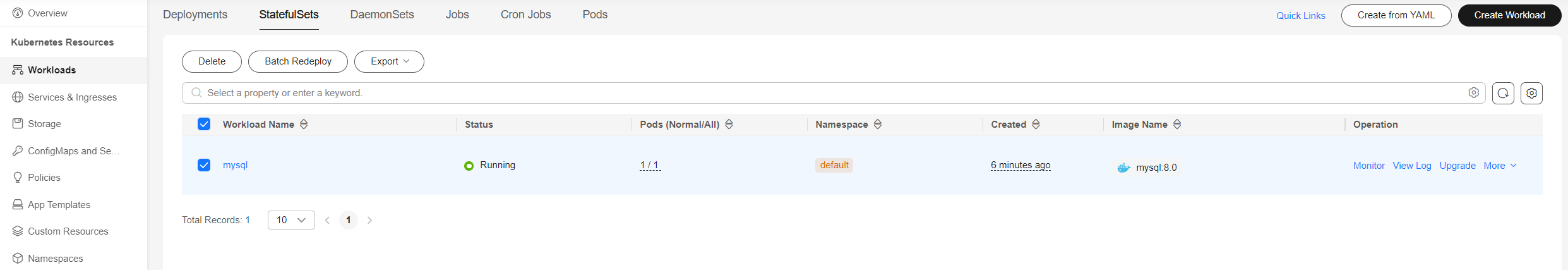

You need to create an ECS bound with an EIP in the same VPC as the cluster first.
- Install kubectl on the ECS.
You can check whether kubectl has been installed by running kubectl version. If kubectl has been installed, you can skip this step.
The Linux environment is used as an example to describe how to install and configure kubectl. For more installation methods, see kubectl.
- Download kubectl.
cd /home curl -LO https://dl.k8s.io/release/{v1.29.0}/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl{v1.29.0} specifies the version. You can replace it as required.
- Install kubectl.
chmod +x kubectl mv -f kubectl /usr/local/bin
- Download kubectl.
- Configure a credential for kubectl to access the Kubernetes cluster.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console. Choose Overview in the navigation pane.
- On the page displayed, locate the Connection Information area, click Configure next to kubectl, and view the kubectl connection information.
- In the window that slides out from the right, locate the Download the kubeconfig file area, select Intranet access for Current data, and download the corresponding configuration file.
- Log in to the VM where the kubectl client has been installed and copy and paste the configuration file (for example, kubeconfig.yaml) downloaded in the previous step to the /home directory.
- Save the kubectl authentication file to the configuration file in the $HOME/.kube directory.
cd /home mkdir -p $HOME/.kube mv -f kubeconfig.yaml $HOME/.kube/config - Run the kubectl command to see whether the cluster can be accessed.
For example, to view the cluster information, run the following command:
kubectl cluster-info
Information similar to the following is displayed:
Kubernetes master is running at https://*.*.*.*:5443 CoreDNS is running at https://*.*.*.*:5443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/coredns:dns/proxy To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
- Create a description file named mysql.yaml. mysql.yaml is an example file name. You can rename it as required.
vi mysql.yamlThe file content is as follows:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: mysql namespace: default spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: mysql version: v1 template: metadata: labels: app: mysql version: v1 spec: containers: - name: container-1 image: mysql:8.0 env: - name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD # The password of the root user of the MySQL database. You configure your own password. value: ***** - name: MYSQL_DATABASE # The name of the database to be created when the image is started. You configure your own database name. value: database - name: MYSQL_USER # The database username. You configure your own username. value: db_user - name: MYSQL_PASSWORD # The database user password. You configure your own password. value: ***** resources: requests: cpu: 250m memory: 512Mi limits: cpu: 250m memory: 512Mi volumeMounts: - name: mysql mountPath: /var/lib/mysql imagePullSecrets: - name: default-secret serviceName: mysql # The name of the headless Service, which must be the same as that defined in the headless Service volumeClaimTemplates: # Dynamically attach an EVS disk to the workload. - apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: mysql namespace: default annotations: everest.io/disk-volume-type: SSD # EVS disk type labels: failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/region: eu-west-101 # Region where the EVS disk is in failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/zone: # AZ where the EVS disk is in. It must be the same as the AZ of the node that runs the workload. spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce # ReadWriteOnce for an EVS disk resources: requests: storage: 10Gi storageClassName: csi-disk # Storage class name. The value is csi-disk for an EVS disk. --- # Define the headless Service. apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: mysql # Name of the headless Service, which must be the same as the name of the Service mounted to the workload namespace: default labels: app: mysql version: v1 spec: selector: # Label selector, which must be the same as the labels of the workload. It is used to match the desired workload. app: mysql version: v1 clusterIP: None ports: - name: mysql # The port name. You configure your own port name. protocol: TCP port: 3306 # The Service port. You configure your own Service port. targetPort: 3306 # The container port. The value is fixed to 3306 for MySQL. type: ClusterIP - Create a MySQL workload.
kubectl apply -f mysql.yamlIf information similar to the following is displayed, the workload is being created:
statefulset.apps/mysql created service/mysql created
- Check the workload status.
kubectl get statefulset
If information similar to the following is displayed, the workload has been created:
NAME READY AGE mysql 1/1 4m5s
- Check the Service.
kubectl get svc
If information similar to what is shown here is displayed, the workload's access mode has been configured.
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 10.247.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 3d mysql ClusterIP None <none> 3306/TCP 51s
- Log in to the CCE console.
- Click the name of the cluster to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Workloads. In the right pane, click Create Workload in the upper right corner.
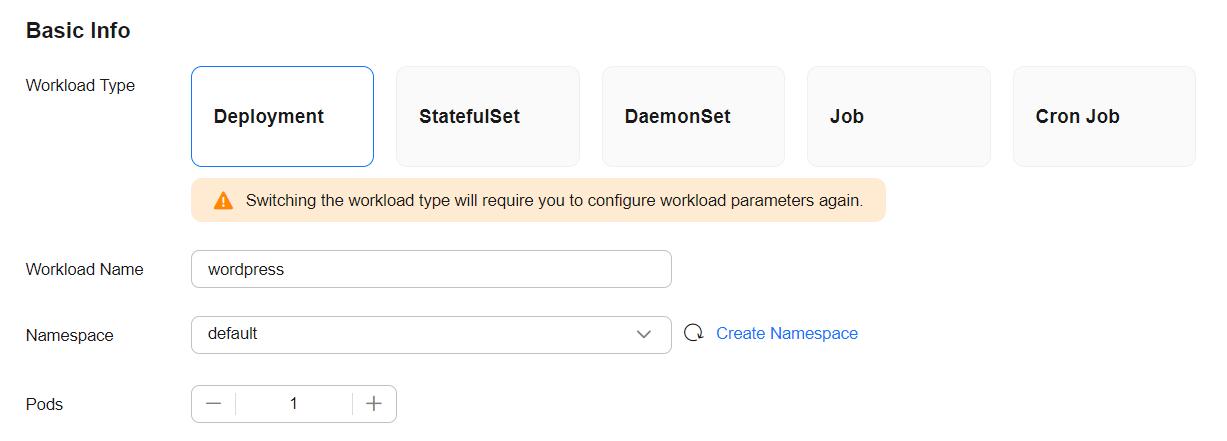
- Configure the basic information for the workload.
In this example, configure the parameters shown in the table and keep the default settings for other parameters. For more details, see Creating a StatefulSet.
Parameter
Example
Description
Workload Type
Deployment
A workload is an application running on Kubernetes. Various built-in workload types are available, each designed for different functions and scenarios. For more details, see Workload Overview.
Workload Name
wordpress
Enter a workload name.
Namespace
default
In Kubernetes, a namespace is a conceptual grouping of resources or objects, providing isolation from other namespaces.
After a cluster is created, a namespace named default is generated by default. You can use this namespace directly.
Pods
1
Specify the number of pods for the workload.
- Configure the basic information about the container.
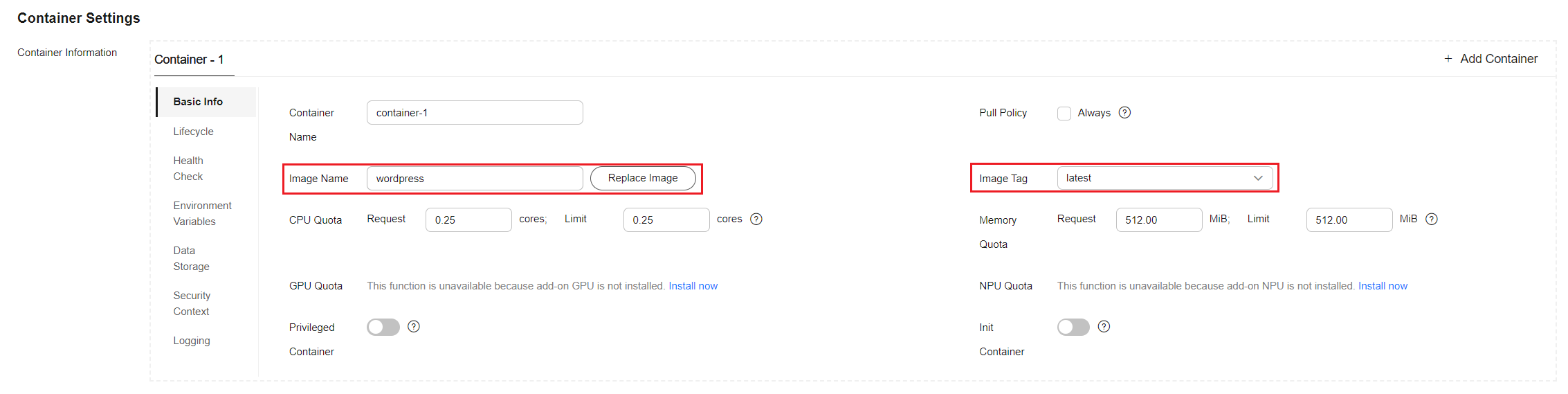
Parameter
Example
Description
Image Name
The wordpress image of the latest version
In the Container Information area, click Basic Info and click Select Image. In the dialog box displayed, select Open Source Images, search for wordpress, select the wordpress image, and select latest from the drop-down list for Image Tag.
CPU Quota
Request: 0.25 cores
Limit: 0.25 cores
- Request: the number of CPU cores pre-allocated to containers. The default value is 0.25 cores.
- Limit: the maximum number of CPU cores that containers can use. The default value is the same as the Request. If Limit exceeds Request, containers can temporarily use more resources in burst scenarios.
For details, see Configuring Container Specifications.
Memory Quota
Request: 512 MiB
Limit: 512 MiB
- Request: the memory pre-allocated to containers. The default value is 512 MiB.
- Limit: the maximum amount of memory that containers can use. The default value is the same as the Request. If Limit exceeds Request, containers can temporarily use more resources in burst scenarios.
For details, see Configuring Container Specifications.
- Click Environment Variables and add environment variables listed in the table to add the MySQL database information to WordPress.
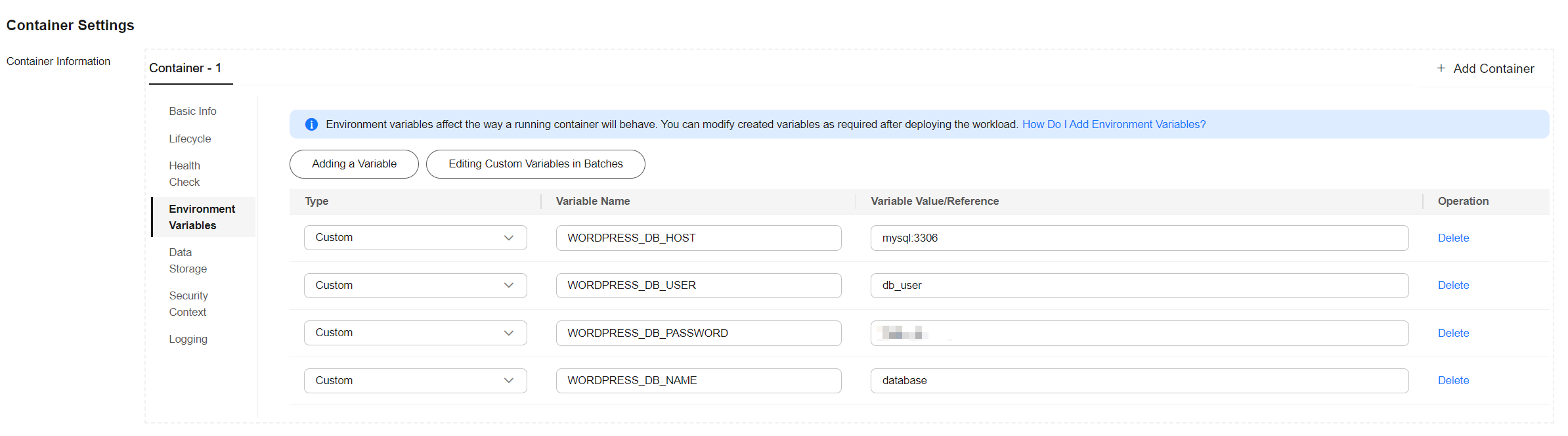
Environment Variable
Example
Description
WORDPRESS_DB_HOST
mysql:3306
The IP address for accessing the database. In this example, you need to enter the access mode of the MySQL workload, that is, the headless Service in Step 4: Deploy MySQL. You can use the internal domain name mysql.default.svc.cluster.local:3306 of the cluster to access the workload. You can omit .default.svc.cluster.local and simply use mysql:3306.
WORDPRESS_DB_USER
db_user
The username for accessing data. The value must be the same as that of MYSQL_USER in Step 4: Deploy MySQL. This username is used to establish a connection with the MySQL database.
WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD
A custom database password
The password for accessing the database. The value must be the same as that of MYSQL_PASSWORD in Step 4: Deploy MySQL.
WORDPRESS_DB_NAME
database
The name of the database to be accessed. The value must be the same as that of MYSQL_DATABASE in Step 4: Deploy MySQL.
- Click Data Storage, click Add Volume, select PVC, and add an EVS disk as the MySQL storage.
Click Create PVC, configure the parameters shown here, and keep the default values for other parameters.
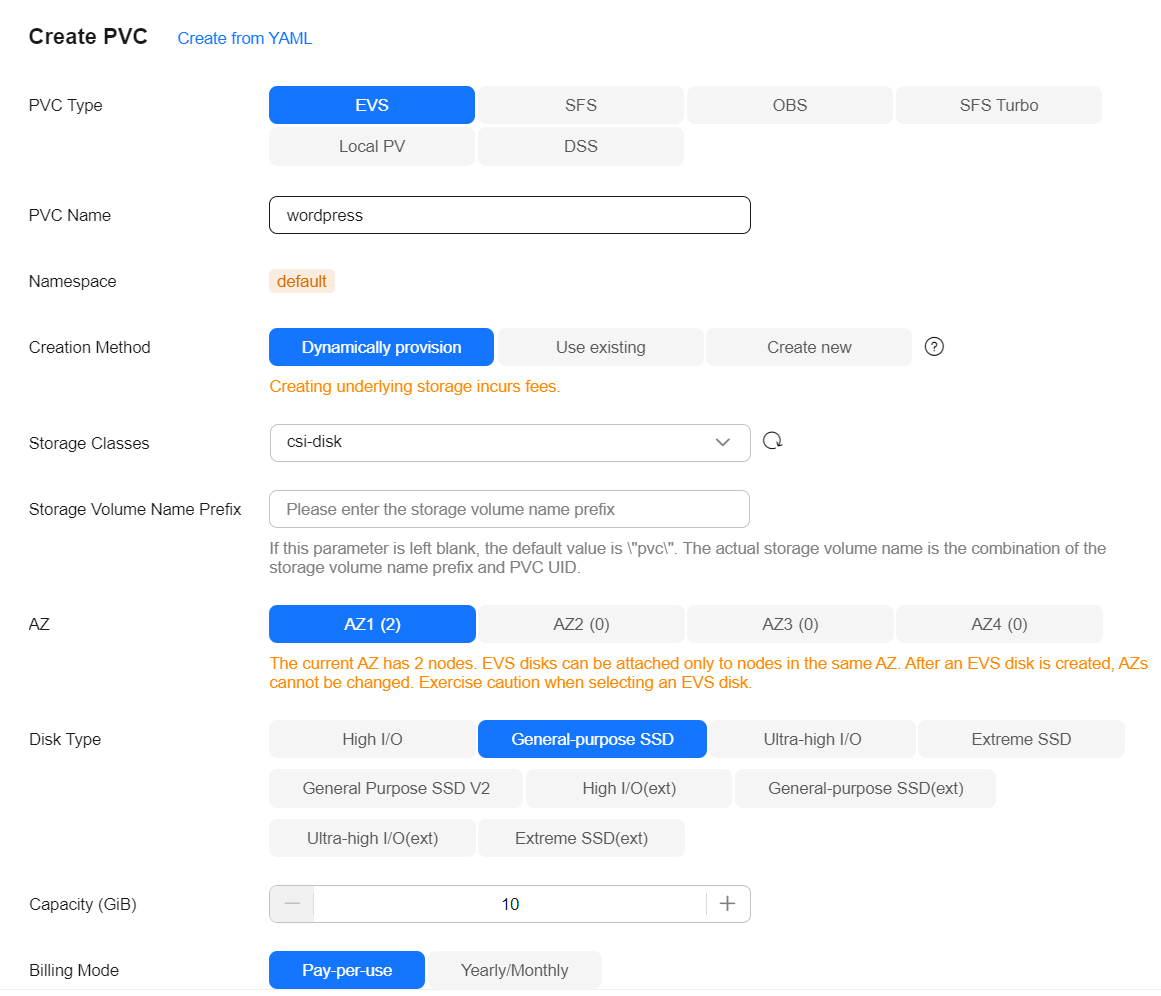
Parameter
Example
Description
PVC Type
EVS
Select a type for the underlying storage volume used by the PVC.
PVC Name
wordpress
Enter a custom PVC name.
Creation Method
Dynamically provision
In this example, select Dynamically provision. The PVC, PV, and underlying storage volume will be automatically created. This method is ideal when no underlying storage volume is available.
Storage Classes
csi-disk
The default value is csi-disk.
AZ
AZ1
Select an AZ. The EVS disk can only be attached to nodes in the same AZ. After an EVS disk is created, the AZ where the disk locates cannot be changed.
Disk Type
General-purpose SSD
Select a proper type as required.
Capacity (GiB)
10
Enter the capacity required. The default capacity is 10 GiB.
Click Create and enter the path for mounting the storage volume to the container. The default path used by WordPress is /var/www/html.
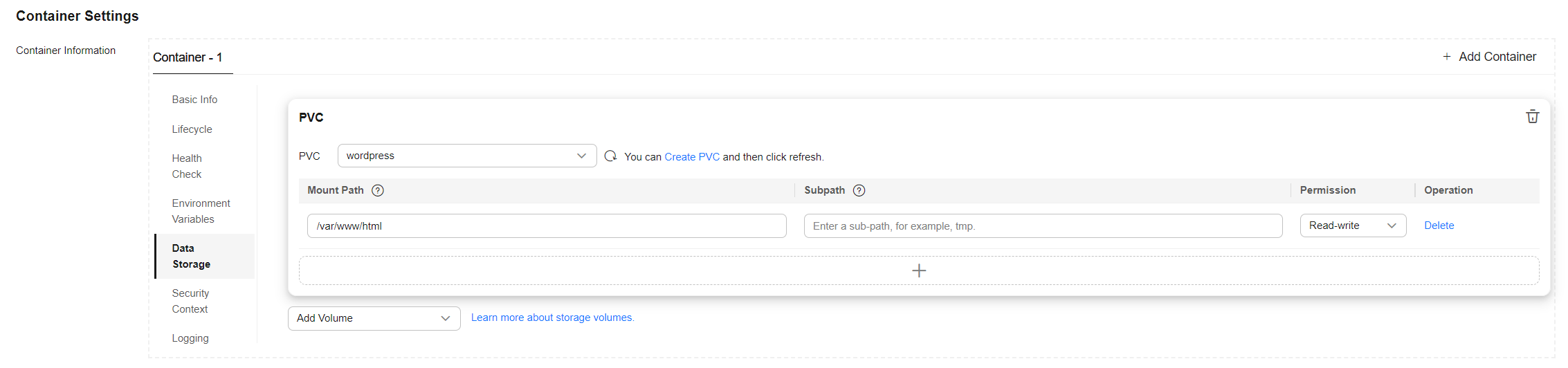
- Configure access settings.
In the Service Settings area, click the plus sign (+) and create a Service for external network access to the workload. This example shows how to create a LoadBalancer Service. Configure the below parameters in the sliding window on the right.
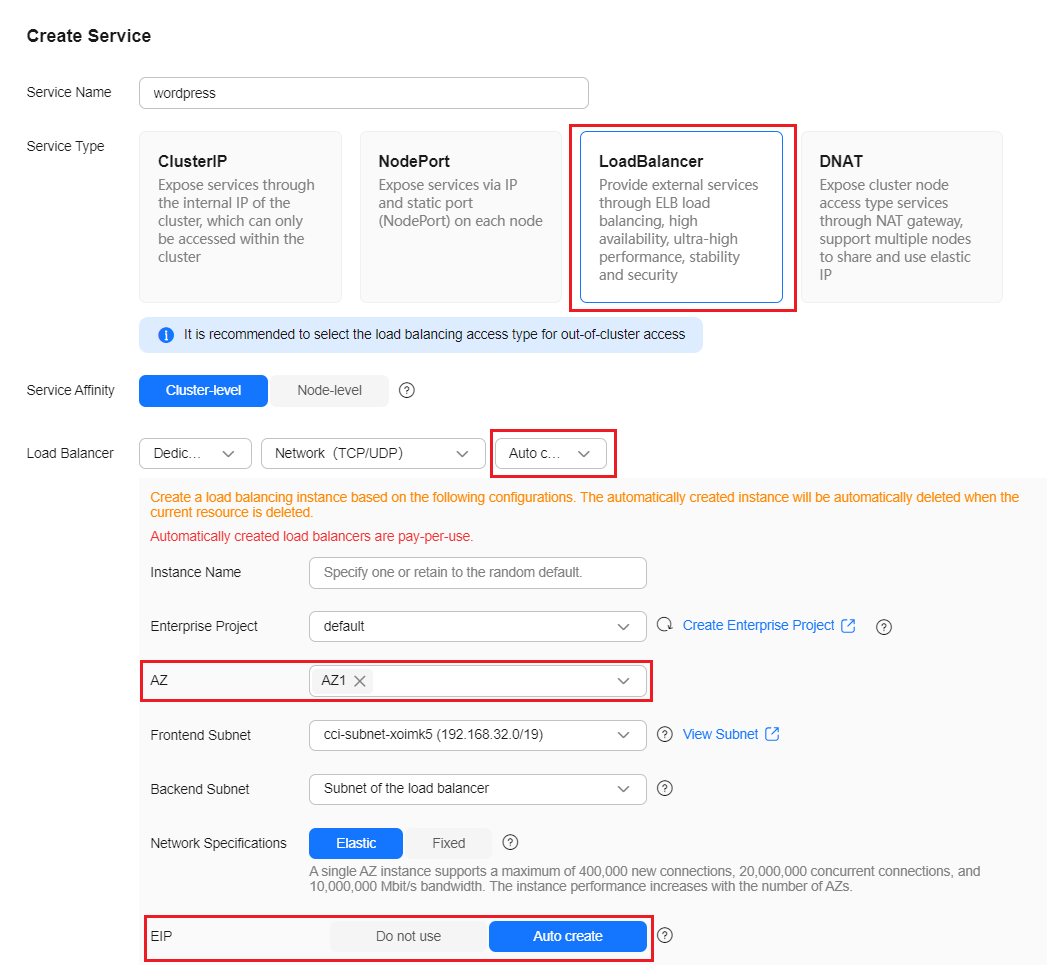
Parameter
Example
Description
Service Name
wordpress
Specify the Service name.
Service Type
LoadBalancer
Select a Service type. The Service type refers to the Service access mode. For details about the differences between Service types, see Service Overview.
Load Balancer
- Type: Dedicated
- AZ: at least one AZ, for example, AZ1
- EIP: Auto create
Keep the default settings for other parameters.
Select Use existing if a load balancer is available.
If there is no load balancer available, select Auto create to create one and bind an EIP to it. For details, see Creating a LoadBalancer Service.
Ports
- Protocol: TCP
- Container Port: 80
- Service Port: 8080
- Protocol: applies to the load balancer listener.
- Container Port: The port that the containerized application listens on. This value must be the same as the listening port provided by the application for external access. If the wordpress image is used, set this parameter to 80.
- Service Port: The port used by the load balancer to create a listener and provide an entry for external access. You can change this port if necessary.
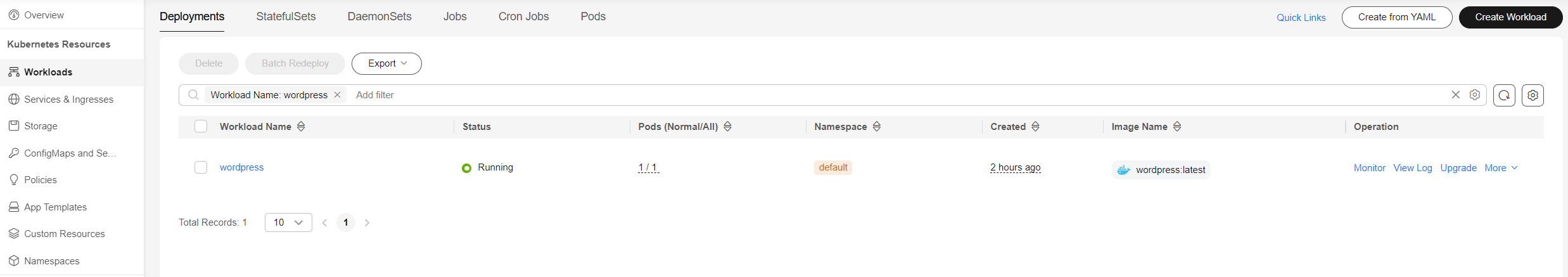
- Click Create Workload.
Wait until the workload is created. After it is created, it will be displayed on the Deployments tab.
- Log in to the ECS where kubectl has been installed.
- Create a description file named wordpress-deployment.yaml. wordpress-deployment.yaml is an example file name. You can rename it as required.
vi wordpress-deployment.yamlThe file content is as follows:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: wordpress namespace: default spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: wordpress version: v1 template: metadata: labels: app: wordpress version: v1 spec: containers: - name: container-1 image: wordpress:latest env: - name: WORDPRESS_DB_HOST # Database access address, that is, <headless-service-name>:service-port in MySQL. In this example, the value is mysql:3306. value: mysql:3306 - name: WORDPRESS_DB_USER # Username for accessing the database, which must be the same as the value of MYSQL_USER in MySQL. This username is used to establish a connection with MySQL. value: db_user - name: WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD # Password for accessing the database, which must be the same as the value of MYSQL_PASSWORD in MySQL value: ***** - name: WORDPRESS_DB_NAME # Name of the database to be accessed, which must be the same as the value of MYSQL_DATABASE in MySQL value: database resources: requests: cpu: 250m memory: 512Mi limits: cpu: 250m memory: 512Mi volumeMounts: # Mount storage. - name: wordpress readOnly: false mountPath: /var/www/html # The default path used by WordPress is /var/www/html. imagePullSecrets: - name: default-secret volumes: - name: wordpress persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: wordpress --- # Dynamically create a storage volume. apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: wordpress namespace: default annotations: everest.io/disk-volume-type: SSD everest.io/enterprise-project-id: '0' labels: failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/region: eu-west-101 # Region where the EVS disk is in failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/zone: # AZ where the EVS disk is in. It must be the same as the AZ of the node that runs the workload. spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 10Gi storageClassName: csi-disk - Create the WordPress workload.
kubectl apply -f wordpress-deployment.yamlCheck the workload status.
kubectl get deployment
If information similar to the following is displayed, the workload has been created:
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE wordpress 1/1 1 1 4m5s
- Create a description file named wordpress-service.yaml. wordpress-service.yaml is an example file name. You can rename it as required.
vi wordpress-service.yamlThe file content is as follows:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: wordpress namespace: default annotations: kubernetes.io/elb.class: union kubernetes.io/elb.autocreate: '{ "type": "public", "bandwidth_name": "cce-wordpress", "bandwidth_chargemode": "bandwidth", "bandwidth_size": 5, "bandwidth_sharetype": "PER", "eip_type": "5_bgp" }' spec: selector: # Label selector, which must be the same as the labels of the WordPress workload. It is used to match the desired workload. app: wordpress externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster ports: - name: cce-service-0 targetPort: 80 # Container port. If the wordpress image is used, set this parameter to 80. nodePort: 0 port: 8080 # Service port. You configure your own Service port. protocol: TCP type: LoadBalancer - Create a Service.
kubectl create -f wordpress-service.yamlIf information similar to the following is displayed, the Service has been created:
service/wordpress created
- Check the Service.
kubectl get svc
If information similar to what is shown here is displayed, the workload's access mode has been configured. You can use the LoadBalancer Service to access the WordPress workload from the Internet. **.**.**.** specifies the EIP of the load balancer, and 8080 indicates the access port.
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 10.247.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 3d mysql ClusterIP 10.247.202.20 <none> 3306/TCP 8m wordpress LoadBalancer 10.247.130.196 **.**.**.** 8080:31540/TCP 51s
Step 6: Access WordPress
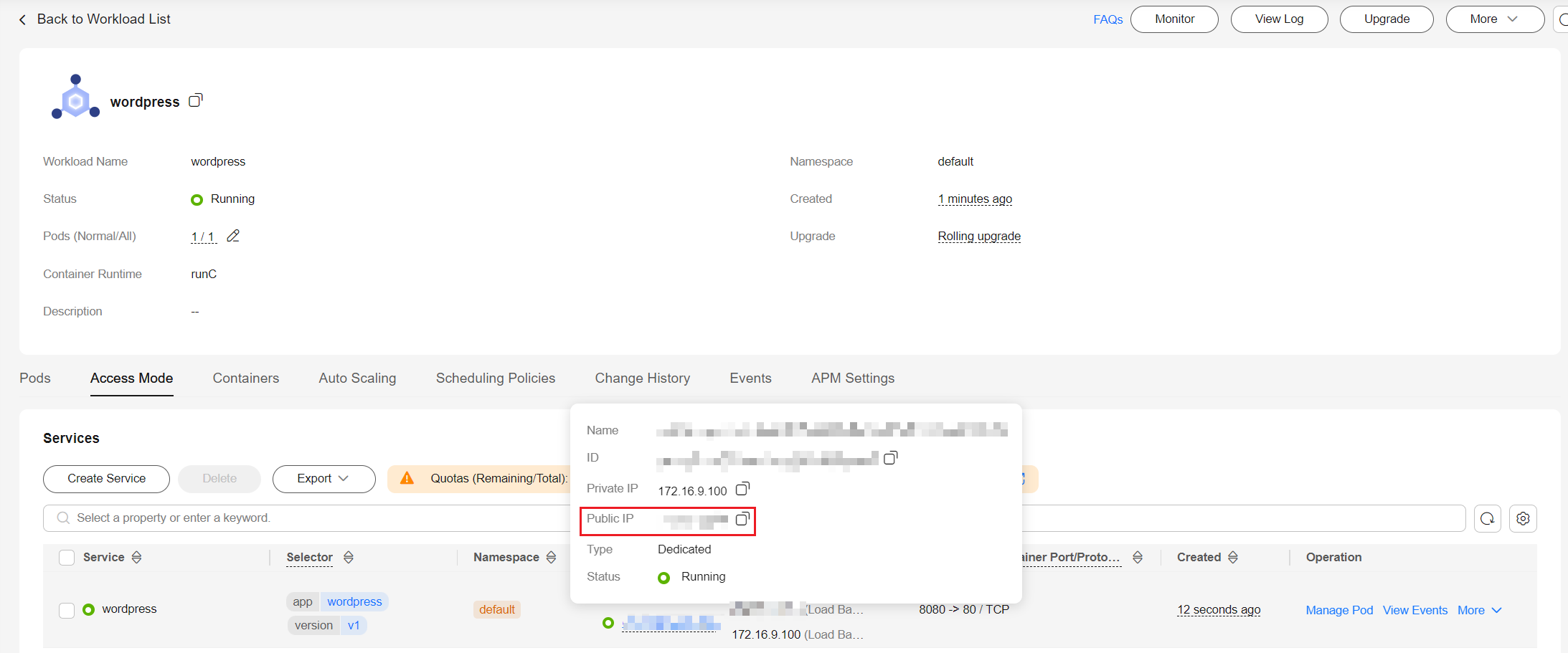
- Obtain the external access address of WordPress.
Click the name of the wordpress workload to enter its details page. On the page displayed, click the Access Mode tab, view the IP address of WordPress. The public IP address is the external access address.
- Enter <external-access-address>:port in the address box of a browser to access the application. The port is the same as the Service port configured in 8. It should be 8080.
Follow-up Operations: Release Resources
Release resources promptly if the cluster is no longer needed to avoid extra charges. For details, see Deleting a Cluster.
FAQs
Problem: WordPress cannot be accessed. The error message Error establishing a database connection is displayed.
Solution
- Version incompatibility: Change the MySQL image tag to the recommended MySQL 8.0 tag.
- Inconsistent access address: Change the value of the WORDPRESS_DB_HOST environment variable in WordPress to the access address of the headless Service in MySQL.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






