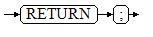RETURN
Syntax
Figure 1 shows the syntax diagram for a return statement.
The syntax details are as follows:
This statement returns control from a stored procedure or function to a caller.
Example
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 |
-- Create the stored procedure proc_staffs: CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_staffs ( section NUMBER(6), salary_sum out NUMBER(8,2), staffs_count out INTEGER ) IS BEGIN SELECT sum(salary), count(*) INTO salary_sum, staffs_count FROM staffs where section_id = section; END; / -- Create the stored procedure proc_return: CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_return AS v_num NUMBER(8,2); v_sum INTEGER; BEGIN proc_staffs(30, v_sum, v_num); --Invoke a statement dbms_output.put_line(v_sum||'#'||v_num); RETURN; --Return a statement END; / -- Invoke a stored procedure proc_return: CALL proc_return(); -- Delete a stored procedure: DROP PROCEDURE proc_staffs; DROP PROCEDURE proc_return; --Create the function func_return. CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION func_return returns void language plpgsql AS $$ DECLARE v_num INTEGER := 1; BEGIN dbms_output.put_line(v_num); RETURN; --Return a statement END $$; -- Invoke the function func_return. CALL func_return(); 1 -- Delete the function: DROP FUNCTION func_return; |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.