Configuring the TDE Function
Scenarios
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) performs real-time I/O encryption and decryption on data files. Data is encrypted before being written to disks and is decrypted when being read from disks to memory. This effectively protects the security of databases and data files.
TDE ensures data security in the following scenarios:
- Hard disks are stolen, causing data leakage.
- Hackers intrude the system and copy the files, causing data leakage. If TDE is not enabled for a database, hackers can browse all data in it as long as they obtain the database file. If TDE is enabled, all data in the database is encrypted. No one can access the data without a key.
Supported Versions
- 8.0: 8.0.32.250300 and later
- 5.7: 5.7.38.221000 and later
For details about how to query the instance version, see Query the RDS Instance Version.
Impacts on Performance
When there are data reads and writes in an encrypted table, the encryption and decryption algorithms introduce additional computational overhead. This causes the CPU load to increase.
In most cases, if the CPU usage of an instance does not reach the bottleneck, the read and write performance of encrypted tables will decrease by no more than 5%.
In high concurrency and high CPU load scenarios, I/O-intensive workloads involving encrypted tables will cause instances with fewer than 8 vCPUs to struggle more with performance degradation. The extent of deterioration depends on the business model and encryption algorithm used.
Constraints
|
Stage |
Constraints |
|---|---|
|
Before TDE is enabled |
|
|
When TDE is being enabled |
|
|
After TDE is enabled |
|
Enabling Instance-Level TDE
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region.
in the upper left corner and select a region. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service. - On the Instances page, click the target instance name to go to the Overview page.
- Under TDE, click Enable.
Figure 1 Enabling instance-level TDE
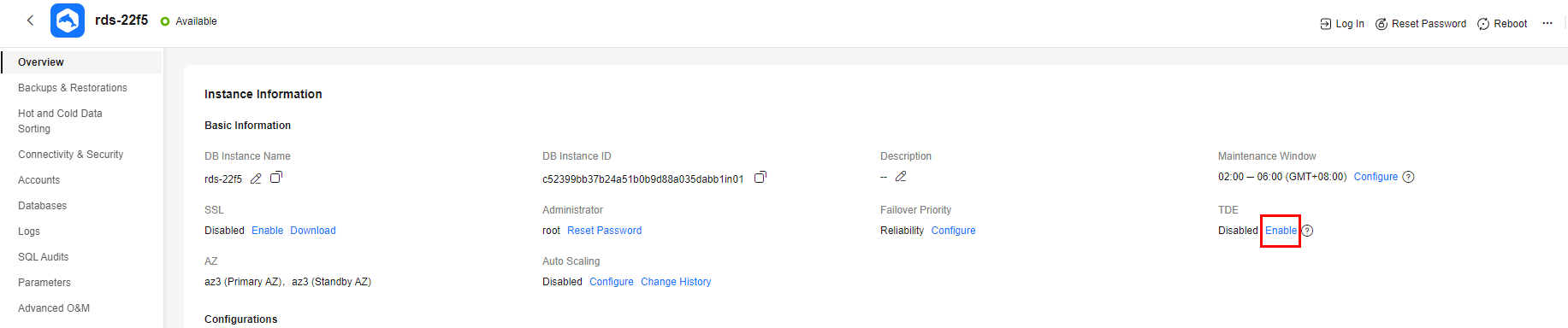
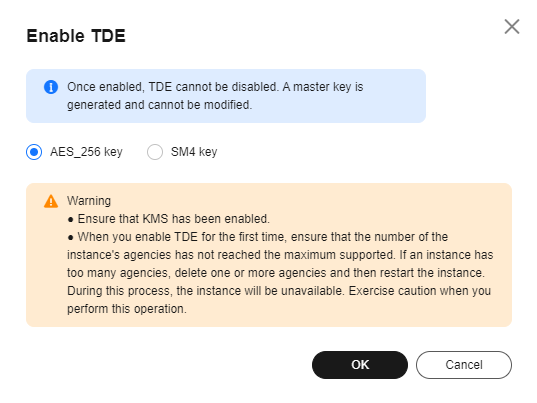
- In the displayed dialog box, click OK.
Figure 2 Enabling TDE
- After TDE is enabled, to restore data to an on-premises database, use either of the following methods.
- Method 1: Decrypt data.
- Decrypt data by referring to Decryption.
- Create a manual backup for the instance to be restored.
- Restore data from the manual backup.
- Method 2: Use the transition key --transition-key.
- When creating a manual backup on the console, enter a custom key string as prompted to re-encrypt the data. For details, see Creating a Manual Backup.
Figure 3 Custom encryption
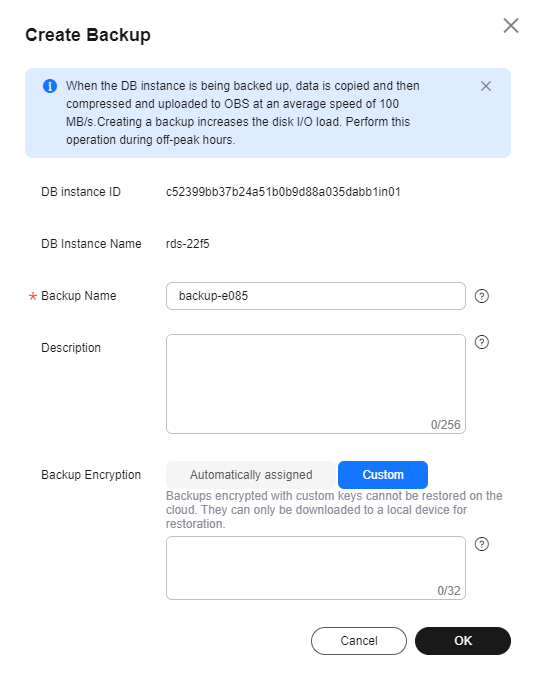
- Download a full backup and use the third-party full backup tool Percona XtraBackup to restore the backup locally.
- prepare phase: --transition-key = {custom_key}
- copy-back phase: --transition-key={custom_key} --generate-new-master-key
- When creating a manual backup on the console, enter a custom key string as prompted to re-encrypt the data. For details, see Creating a Manual Backup.
- Method 1: Decrypt data.
Encrypting or Decrypting a Table
- Connect to the target DB instance.
- Run the following commands to encrypt or decrypt a table. In the commands, tablename indicates the name of the table to be encrypted or decrypted.
Both alter table tablename encryption='Y'; and alter table tablename encryption='N'; are DDL statements that use ALGORITHM=COPY. Such statements are executed by creating a table, copying all data to the table, and then renaming the table. This results in the following symptoms:
- After a DDL statement is executed, there will be brief fluctuations in the performance of queries on that table.
- If the buffer pool is not fully used, the memory load increases.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





