Node.js Demo
This section uses Node.js as an example to describe how to connect an MQTTS client to the platform and receive subscribed messages from the platform
Prerequisites
Knowledge of basic Node.js syntax and how to configure development environments.
Development Environment
In this example, Node.js 13.14.0 is used. Download it from the Node.js official website. After installation, run the following command to check the version:
node --version
Dependency
In this example, mqtt (version 4.0.0) is used. You can run the following command to download the dependency:
npm install mqtt@4.0.0
Sample Code
const mqtt = require('mqtt');
// Name of the subscribed topic
var topic = "your mqtt topic";
// Key value of the access credential, which can be preset using environment variables.
var accessKey = process.env.MQTT_ACCESS_KEY;
// Access credential secret, which can be preset using environment variables.
var accessCode = process.env.MQTT_ACCESS_CODE;
// MQTT access address
var mqttHost = "your mqtt host";
// MQTT access port
var mqttPort = 8883;
// Instance ID
var instanceId = "your instanceId";
// mqtt client id
var clientId = "your clientId";
// MQTT client
var client = null;
connectWithRetry();
async function connectWithRetry() {
// Retries with exponential backoff, from 1s to 20s.
var duration = 1000;
var maxDuration = 20000;
var success = connect(topic);
var times = 0;
while (!success) {
await sleep(duration)
if (duration < maxDuration) {
duration *= 2
}
times++
console.log('connect mqtt broker retry. times: ' + times)
if (client == null) {
connect(topic)
continue
}
client.end(true, function() {
connect(topic)
});
}
}
function sleep(ms) {
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(), ms))
}
function connect(topic) {
try {
client = mqtt.connect(getClientOptions())
if (client == null) {
return false
}
client.on('connect', connectCallBack)
client.subscribe(topic, subscribeCallBack)
client.on('message', messageCallBack)
client.on('error', clientErrorCallBack)
client.on('close', closeCallBack)
return true
} catch (error) {
console.log('connect to mqtt broker failed. err ' + error)
}
return false
}
function getClientOptions() {
var timestamp = Math.round(new Date);
const username = 'accessKey=' + accessKey + '|timestamp=' + timestamp + '|instanceId=' + instanceId;
var options = {
host: mqttHost,
port: mqttPort,
connectTimeout: 4000,
clientId: clientId,
protocol: 'mqtts',
keepalive: 120,
username: username,
password: accessCode,
rejectUnauthorized: false,
secureProtocol: 'TLSv1_2_method'
};
return options;
};
function connectCallBack() {
console.log('connect mqtt server success');
};
function subscribeCallBack(err, granted) {
if (err != null || granted[0].qos === 128) {
console.log('subscribe topic failed. granted: ' + granted[0].qos)
return
}
console.log('subscribe topic success. granted: ' + granted[0].qos);
};
function clientErrorCallBack(err) {
console.log('mqtt client error ' + err);
};
function messageCallBack(topic, message) {
console.log('receive message ' + message);
};
function closeCallBack() {
console.log('Disconnected from mqtt broker')
client.end(true, function() {
console.log('close connection');
connectWithRetry();
});
}
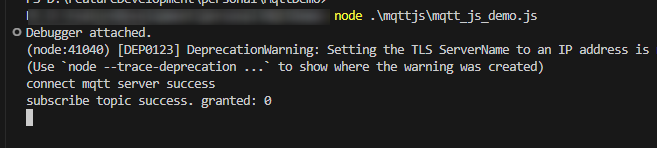
Success Example
After the access is successful, the following information is displayed on the client.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





