Enabling and Querying RocketMQ Message Tracing
Message traces contain complete time and location information during production and consumption of a message. Message tracing enables diagnosis of real messaging status when exceptions (e.g., production and consumption failures) occur. Message traces can be queried by message ID, message key, or topic time range.
Message Tracing Data
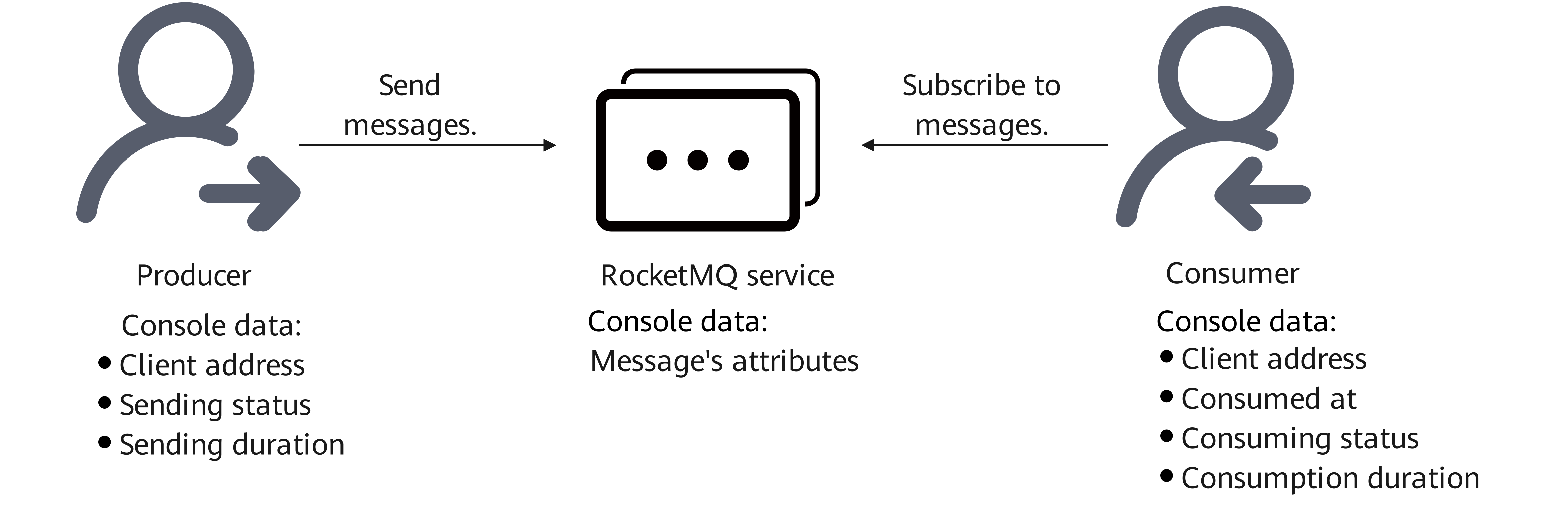
The trace of a RocketMQ message involves the producer, server, and consumer. Each role adds information to the trace when processing a message. These information shows the status of any message.
Prerequisites
Transactional message tracing is available only for Java 4.9.0 and later producers. For RocketMQ instances with SSL enabled, message tracing is available only for Java 4.9.2 and later producers and consumers. To check the client version, see Viewing RocketMQ Consumer Group Details.
Enabling RocketMQ Message Tracing
This function can be enabled using Java or Go, or Spring (Java) as required.
Do as follows to enable message tracing on clients:
- Enabling message tracing on a producer client (tracing messages other than transactional messages)
Set enableMsgTrace of the constructor to true. For example:
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("ProducerGroupName", true); - Enabling message tracing on a producer client (tracing transactional messages)
Set enableMsgTrace of the constructor to true. For example:
TransactionMQProducer producer = new TransactionMQProducer(null, "ProducerGroupName", null, true, null);
- Enabling message tracing on a consumer
Set enableMsgTrace of the constructor to true. For example:
DefaultMQPushConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPushConsumer("ConsumerGroupName", true);
Do as follows to enable message tracing on clients:
- Run the following command to check whether Go has been installed:
go version
If the following information is displayed, Go has been installed. If Go is not installed, download and install it.
[root@ecs-test sarama]# go version go version go1.16.5 linux/amd64
- Go to the bin directory where the Go script is in.
- Run the touch go.mod command to create a go.mod file and add the following code to it to add the dependency:
module rocketmq-example-go go 1.13 require ( github.com/apache/rocketmq-client-go/v2 v2.1.0 )
- Enable message tracing on the producer. Replace the information in bold with the actual values.
package main import ( "context" "fmt" "os" "time" "github.com/apache/rocketmq-client-go/v2" "github.com/apache/rocketmq-client-go/v2/primitive" "github.com/apache/rocketmq-client-go/v2/producer" ) func main() { namesrvs := []string{"192.168.0.1:8100"} traceCfg := &primitive.TraceConfig{ Access: primitive.Local, Resolver: primitive.NewPassthroughResolver(namesrvs), } p, _ := rocketmq.NewProducer( producer.WithNsResolver(primitive.NewPassthroughResolver([]string{"192.168.0.1:8100"})), producer.WithRetry(2), producer.WithTrace(traceCfg)) // To enable message tracing, add this line. err := p.Start() if err != nil { fmt.Printf("start producer error: %s", err.Error()) os.Exit(1) } res, err := p.SendSync(context.Background(), primitive.NewMessage("topic1", []byte("Hello RocketMQ Go Client!"))) if err != nil { fmt.Printf("send message error: %s\n", err) } else { fmt.Printf("send message success: result=%s\n", res.String()) } time.Sleep(10 * time.Second) err = p.Shutdown() if err != nil { fmt.Printf("shutdown producer error: %s", err.Error()) } }192.168.0.1:8100 is the connection address and port of the RocketMQ instance. Obtain yours from Overview > Connection on the RocketMQ console.
- Enable message tracing on the consumer. Replace the information in bold with the actual values.
package main import ( "context" "fmt" "os" "time" "github.com/apache/rocketmq-client-go/v2" "github.com/apache/rocketmq-client-go/v2/consumer" "github.com/apache/rocketmq-client-go/v2/primitive" ) func main() { namesrvs := []string{"192.168.0.1:8100"} traceCfg := &primitive.TraceConfig{ Access: primitive.Local, Resolver: primitive.NewPassthroughResolver(namesrvs), } c, _ := rocketmq.NewPushConsumer( consumer.WithGroupName("testGroup"), consumer.WithNsResolver(primitive.NewPassthroughResolver([]string{"192.168.0.1:8100"})), consumer.WithTrace(traceCfg), // To enable message tracing, add this line. ) err := c.Subscribe("TopicTest", consumer.MessageSelector{}, func(ctx context.Context, msgs ...*primitive.MessageExt) (consumer.ConsumeResult, error) { fmt.Printf("subscribe callback: %v \n", msgs) return consumer.ConsumeSuccess, nil }) if err != nil { fmt.Println(err.Error()) } // Note: start after subscribe err = c.Start() if err != nil { fmt.Println(err.Error()) os.Exit(-1) } time.Sleep(time.Hour) err = c.Shutdown() if err != nil { fmt.Printf("shutdown Consumer error: %s", err.Error()) } }To obtain the values in bold in the preceding code, see Table 1.
Table 1 Obtaining the values in bold Value
Description
How to Obtain
192.168.0.1:8100
Connection address and port of the RocketMQ instance
Overview > Connection page on the RocketMQ console.
testGroup
Name of the consumer group created in the RocketMQ instance
Instance > Consumer Groups page on the RocketMQ console.
TopicTest
Name of the topic created in the RocketMQ instance
Instance > Topics page on the RocketMQ console.
Do as follows to enable message tracing on clients:
- For producers
Add the following line in the application.properties configuration file:
rocketmq.producer.enable-msg-trace=true
- For consumers
Set parameter enableMsgTrace to true. For example:
@Service @RocketMQMessageListener( topic = "test-topic-1", consumerGroup = "my-consumer_test-topic-1", enableMsgTrace = true ) public class MyConsumer implements RocketMQListener<String> { ... }To obtain the values in bold in the preceding code, see Table 1.
For more information, see Message Tracing. To configure parameter accessChannel, use the default value LOCAL.
Viewing the Message Trace
- Log in to the console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner to select a region.
in the upper left corner to select a region.
DMS for RocketMQ instances in different regions cannot communicate with each other over an intranet. Select a nearest location for low latency and fast access.
- Click
 and choose Middleware > Distributed Message Service for RocketMQ to open the console of DMS for RocketMQ.
and choose Middleware > Distributed Message Service for RocketMQ to open the console of DMS for RocketMQ. - Click a RocketMQ instance to go to the instance details page.
- In the navigation pane, choose Instance > Message Query.
- Query messages in either of the following ways:
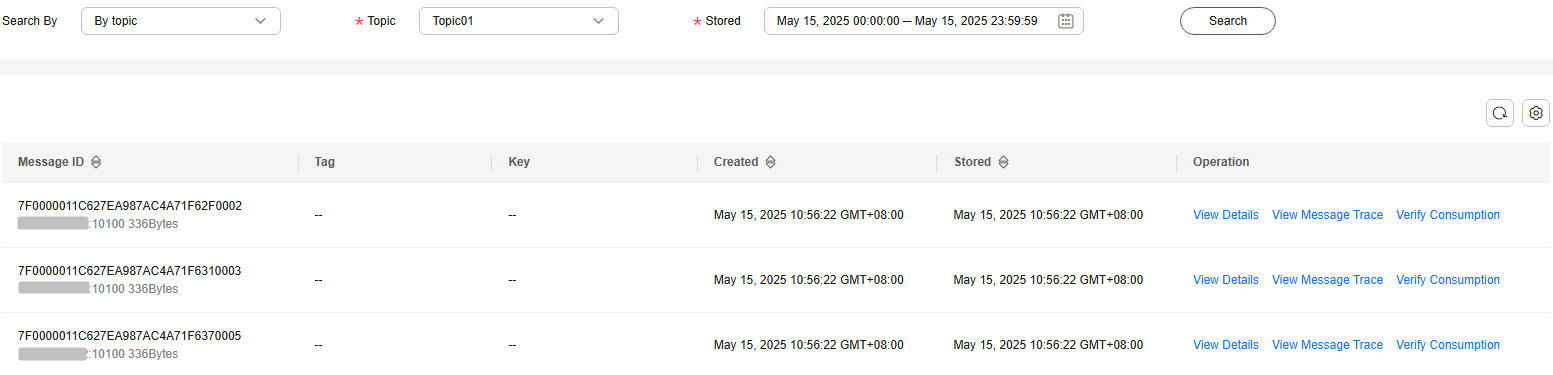
- By topic: Select the topic to be queried from the Topic drop-down list and the queue to the queried from the Queue drop-down list (only for RocketMQ 4.8.0). For Stored, select a time period.
Figure 2 Querying messages by topic
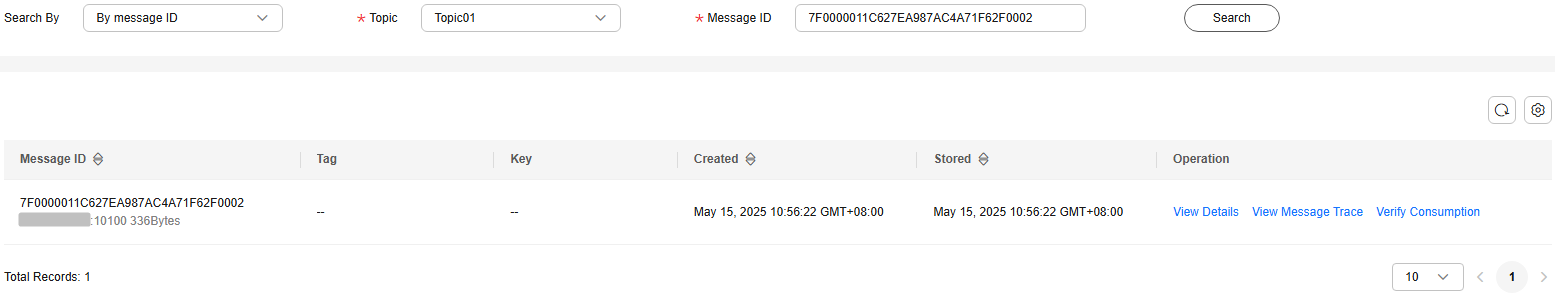
- By message ID: Select the name of the topic to be queried from the Topic drop-down list, enter the ID of the message to be queried, and click Search.
Figure 3 Querying messages by ID
- By message key: Select the name of the topic to be queried from the Topic drop-down list, enter the key of the message to be queried, and click Search.
Figure 4 Querying messages by key
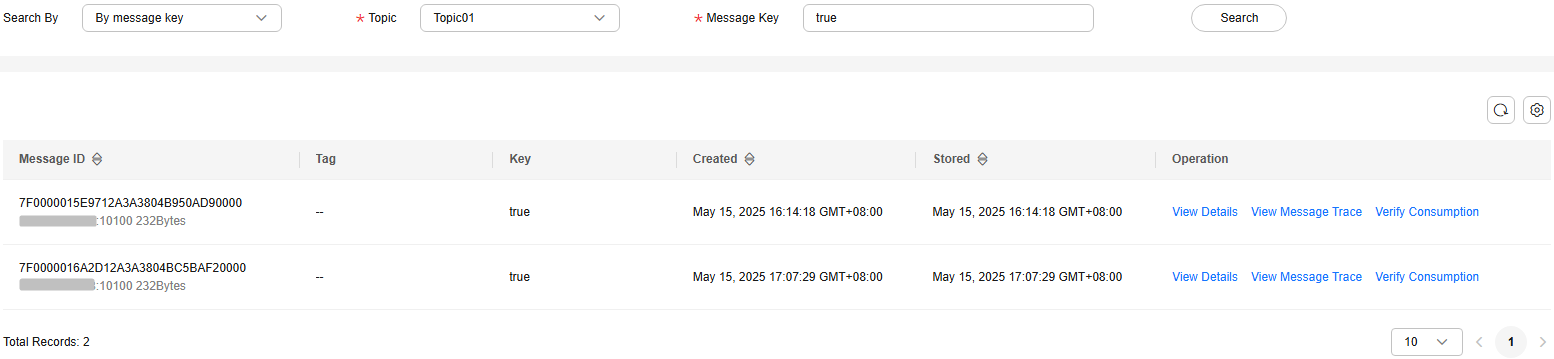
- By topic: Select the topic to be queried from the Topic drop-down list and the queue to the queried from the Queue drop-down list (only for RocketMQ 4.8.0). For Stored, select a time period.
- Locate the row containing the message to be queried. Click View Message Trace.
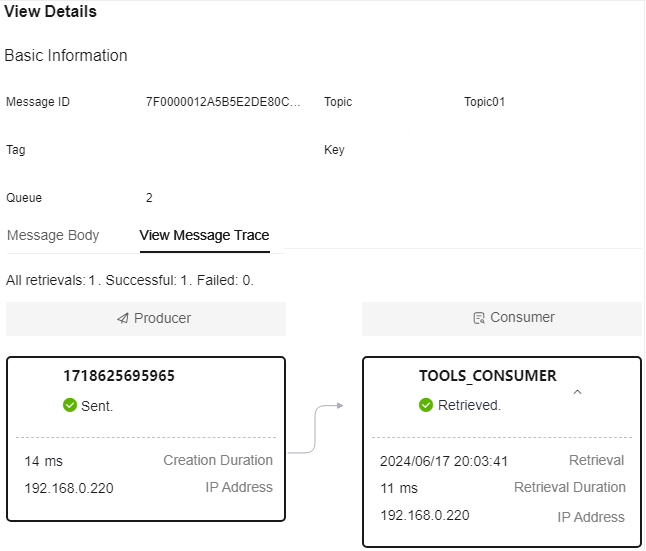
- View the message trace to check whether the message is successfully produced or consumed, as shown in Figure 5.
Table 2 describes message trace parameters.
Table 2 Message trace parameters Parameter
Description
Producer status
A producer can be in one of the following states:
- Sent: The message is sent successfully, and the server has successfully stored the message.
- Committed: The message can be retrieved by consumers.
- Rollback: The message will be discarded and cannot be retrieved by consumers.
- Unknown: The status of the message cannot be determined. After a period of time, the server initiates a check request to the producer.
Creation duration
Time taken to send the message by the producer.
Unit: millisecond
Producer address
IP address of the producer.
Consumer status
A consumer can be in one of the following states:
- Retrieved
- Retrieval timed out
- Abnormal retrieval
- NULL returned
- Retrieval failed
Retrieved
Time when the message is retrieved.
The time format is YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss.
Retrieval duration
Time taken to retrieve the message by the consumer.
Unit: millisecond
Consumer address
IP address of the consumer.
Related Document
To query message traces by calling an API, see Querying the Message Trace.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot