Overview
What Is Private Domain Resolution?
A private domain name is a domain name that takes effect in a VPC. DNS allows you to map private domain names to private IP addresses and resolves domain names for other cloud services within VPCs.
Private domain names have the following features:
- You can create any private domain names without registering them.
- One private domain name can be associated with multiple VPCs and is valid only in VPCs. There is no limit on the number of associated VPCs.
To resolve private domain names, you need to create a private zone and associate it with VPCs as needed.
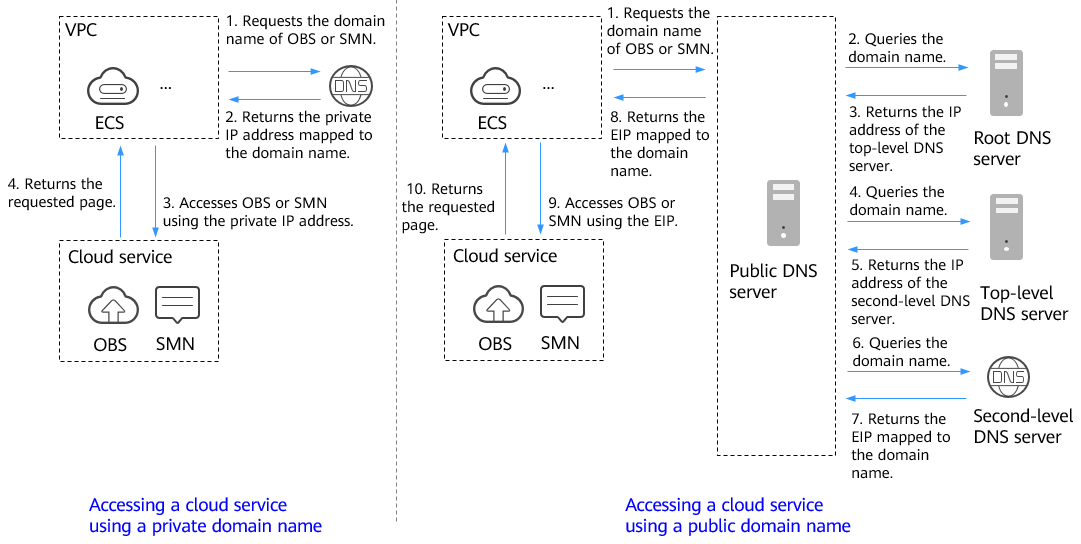
Private DNS resolution translates domain names like ecs.com and their subdomains used within one or more VPCs to private IP addresses (such as 192.168.1.1). With private domain name resolution, ECSs within a VPC can communicate with each other using private zones. These ECSs can also access cloud services, such as Object Storage Service (OBS) and Simple Message Notification (SMN), over a private network.
Resolution Process
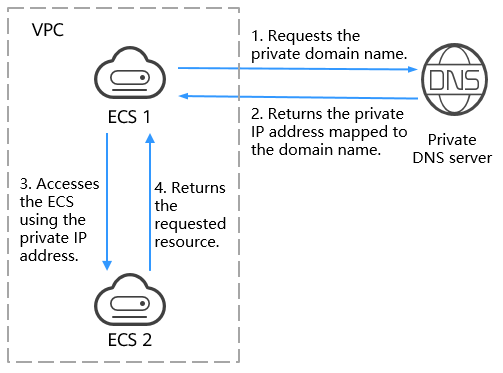
Figure 1 shows the resolution process.
When an ECS in the VPC requests to access a private domain name, the private DNS server directly returns a private IP address mapped to the domain name.
Scenarios
Private domain name resolution is applicable to the scenarios below.
You can plan host names based on the locations, usages, and account information of ECSs, and map the host names to private IP addresses. This helps you manage ECSs more easily.
For example, if you have deployed 20 ECSs in an AZ, 10 used for website A and 10 for website B, you can plan their host names and private zones as follows:
- ECSs for website A: weba01.region1.az1.com – weba10.region1.az1.com
- ECSs for website B: webb01.region1.az1.com – webb10.region1.az1.com
After configuring the preceding private zones, you will be able to quickly determine the locations and usages of ECSs during routine management and maintenance.
For detailed operations, see Configuring Private Domain Name Resolution for ECSs.
Related Operations
|
Category |
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Private zones |
Create a private zone for your domain name. |
|
|
Modify, delete, batch delete, and view private zones. Constraints
|
||
|
Share a private zone across accounts. |
||
|
Apply a private zone in multiple VPCs. Constraints
|
||
|
Disassociate a private zone from a VPC. |
||
|
DNS rules |
Learn about types, scenarios, and configuration rules of record sets supported by private zones. |
|
|
Learn about record set conflicts of private zones and how to handle the conflicts. |
||
|
Record sets |
Configure record sets for private zones. |
|
|
Set a recursive resolution proxy for subdomains in a private zone. |
||
|
Modify a record set, delete a record set, batch delete record sets in a single zone, and view record set details. |
||
|
Disable or enable record sets for a domain name. SOA and NS record sets are automatically generated and cannot be disabled. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot