Modifying a Configuration File
This action aims to modify the specified content in a file by identifying specific identifiers. The following table describes the configuration parameters.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Action Name |
Custom action name. Enter 1 to 128 characters. Do not start or end with a space. Use letters, digits, spaces, and these special characters: -_,;:./() |
|
Environment |
Deployment object. Select an environment whose resource type is host cluster. |
|
Absolute Path |
Absolute path of the configuration file to modify.
|
|
Prefix and Suffix |
Parameter reference flag. If no prefix or suffix is matched, the configuration file remains unchanged and no error is reported in logs. |
|
Action Control |
You can configure whether to enable the settings.
|
Configuration Example
To change the service port, perform the following steps:
- Open the configuration file and view the content.
Figure 1 Checking the configuration file
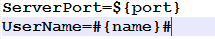
- Change the prefix and suffix. For example, change the prefix to ${ and the suffix to }.
- On the Parameters tab, set Name and Default Value.

- Save the configuration and deploy the application.
- After the deployment is complete, open the configuration file again.
The value of ${port} is changed to 8080.Figure 2 Checking the configuration file
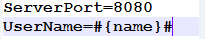
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot