Automatic NPU Virtualization (Computing Segmentation)
In CCE, the ascend-vnpu-manager component of the CCE AI Suite (Ascend NPU) add-on enables NPUs to be virtualized into vNPUs by node pool, enhancing resource utilization. After NPU virtualization is enabled, CCE automatically splits NPUs in the node pool based on the specified template, enabling standardized and batch virtualization deployment.
Prerequisites
- The CCE AI Suite (Ascend NPU) add-on of a version later than 2.1.63 has been installed in the cluster. For details, see CCE AI Suite (Ascend NPU).
- An NPU driver has been installed on the NPU nodes, and the driver version is 23.0.1 or later. To upgrade a driver, perform the following operations:

- To upgrade a driver, ensure that the NPU firmware is available on the node. Reinstalling the driver will restart the node. You are advised to drain the node before installing the driver. For details, see Draining a Node. VMs do not support firmware upgrade.
- To install a driver for all users in the OS during a driver upgrade, use the --install-for-all parameter together. You can use, for example, ./Ascend-hdk-310p-npu-driver_x.x.x_linux-{arch}.run --full --install-for-all.
- If a driver upgrade fails, see "What Can I Do If an NPU Driver Fails to Be Upgraded?" in FAQs > "Chart and Add-on".
- Uninstall the original NPU driver. For details, see Uninstalling the NPU Driver.
- Go to Firmware and Drivers, select the corresponding product model, and download the driver installation package (in .run format) of 23.0.1 or later.
- Check the NPU installation prerequisites and restrictions in Before You Start, and install the NPU by referring to Installing the Driver (.run).
Notes and Constraints
Only Snt3P3 and Snt9B3 chips can be virtualized using ascend-vnpu-manager.

Snt9B3 virtualization is in the experimental phase, with ongoing improvements to model operator coverage. To ensure smooth execution of model operators, verify task compatibility before deployment. Once confirmed, tasks that support execution on the vNPUs of Snt9B3 can leverage the CCE compute segmentation to apply, modify, or remove NPU virtualization configurations.
Configuring NPU Virtualization
Before enabling NPU virtualization, evict NPU workload pods from the node pool. For details, see Draining a Node.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console. In the navigation pane, choose Settings.
- Switch to the Heterogeneous Resources tab and enable NPU Virtualization (node pool scope only).
- In the NPU Virtualization Settings area, click Add and configure parameters. After the parameter are set, CCE automatically splits NPUs in the node pool based on the Virtual Instance Specifications.

Deleting a configuration does not trigger management actions on the target node. Management actions are triggered only when virtual instance specifications are added or modified. After a configuration is deleted, the vNPU resource configuration of the node pool remains. To delete the vNPU configuration of the node, set the node pool's Virtual Instance Specifications to all-disabled.
Table 1 NPU virtualization settings Parameter
Description
Node Pool
Choose a non-default node pool for virtualization.
Chip Type
Select a chip type for virtualization. Only Ascend Snt3P3 and Snt9B3 chips can be virtualized.
Virtual Instance Specifications
CCE offers various NPU virtualization templates to select from based on service needs. Before modifying the virtual instance specifications of a node pool, clear all NPU and vNPU workloads in the node pool.
Hover over a specification name to view the template name and number of vNPUs. For example, all-disabled indicates NPU virtualization is disabled, while all-7vir01 indicates that each NPU of the specified type in the node pool is split into seven vNPUs using the vir01 template. For more details, see NPU Virtualization Templates.
To configure NPU virtualization for multiple node pools and NPU chips, click Add.
- After configuring these parameters, click Confirm Settings in the lower right corner. In the Confirm Settings dialog box, click Save. After the settings are saved, the ascend-vnpu-manager component of the CCE AI Suite (Ascend NPU) add-on is automatically deployed on eligible nodes. This component monitors changes to the ConfigMap global-vnpu-configs and triggers vNPU management actions accordingly.
- After NPU virtualization configuration is complete, you can verify it by viewing the ascend-vnpu-manager logs.
In the navigation pane, choose Add-ons. On the right of the page, find the CCE AI Suite (Ascend NPU) add-on and click View Details. Switch to the Pods tab and find the ascend-vnpu-manager pod of the target node. In the Operation column, choose More > View Log.
- NPU virtualization configuration is successful if the following information is displayed in the logs.
Figure 1 Verifying NPU virtualization
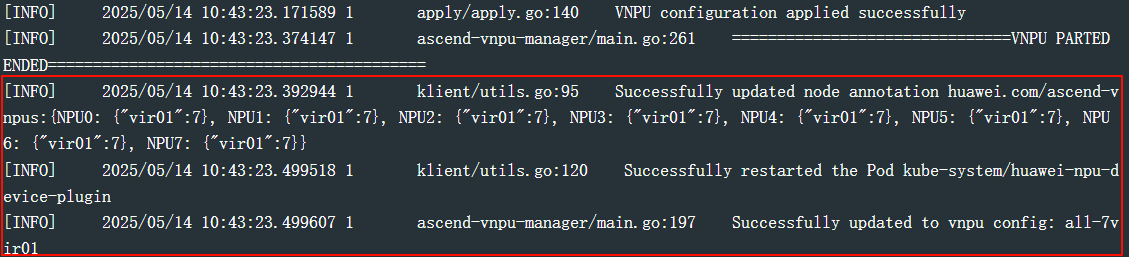
- If logs display messages like "Error: error applying VNPU configuration: failed to apply func on device1, err: NPU1 has VNPU in use ...", NPU or vNPU workloads are running on the node, preventing NPU virtualization configuration. To resolve this issue, do as follows:
Delete the NPU or vNPU workloads on the node, and then delete the ascend-vnpu-manager pod. NPU virtualization will function correctly on the node after the pod is restarted and runs properly.
- NPU virtualization configuration is successful if the following information is displayed in the logs.
Using vNPUs
You can allocate vNPU resources to containers using either the console or kubectl.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console. In the navigation pane, choose Workloads. In the upper right corner of the displayed page, click Create Workload.
- In the Container Settings area, choose Basic Info. Split compute power for NPU Quota and choose the required virtualization template. The virtualization template is named in the format of "Ascend-Chip type-Virtual instance template". For example, Ascend-310-vir01 indicates that the Ascend Snt3 vNPUs are obtained based on the vir01 template. After the template is selected, CCE allocates vNPU resources to containers based on the specified template.
Table 2 Virtualization templates Parameter
Description
Virtualization Template
The following templates are available:
- Configured: The virtualization templates that are configured on the Heterogeneous Resources tab in Settings can be used.
- Not configured: The virtualization templates that are not configured on the Heterogeneous Resources tab in Settings cannot be used. If you select an unconfigured template, workload creation will fail due to insufficient resources. In this case, configure the template in NPU Virtualization Settings. For details, see Configuring NPU Virtualization. After the configuration is complete, the workload is automatically scheduled.
- Configure other parameters by referring to Creating a Workload. Then, click Create Workload in the lower right corner. When the workload changes to the Running state, it is created.
After vNPUs are created, you can use YAML to specify the vNPU resources for workloads to efficiently manage and flexibly configure resources. If you need to use the Volcano Scheduler, its version must be 1.12.1 or later.
- Create a workload and request vNPU resources using the vir02 template.
- Create a YAML file named vnpu-worker.
vim vnpu-worker.yamlContainers can request NPU or vNPU resources. The two types of resources cannot be used concurrently.

Before using a vNPU, ensure that it has been created. If a vNPU is not created, an error is reported, for example, "0/2 nodes are available: 2 Insufficient huawei.com/ascend-310-2c".
kind: Deployment apiVersion: apps/v1 metadata: name: vnpu-test namespace: default spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: vnpu-test template: metadata: labels: app: vnpu-test spec: schedulerName: kube-scheduler # If the workload requires Volcano Scheduler, install the add-on and ensure that the add-on version is v1.12.1 or later. containers: - name: container-0 image: nginx:latest resources: limits: cpu: 250m huawei.com/ascend-310-2c: '1' # The number of vNPUs to be requested. The value is fixed at 1. memory: 512Mi requests: cpu: 250m huawei.com/ascend-310-2c: '1' # The value is fixed at 1. memory: 512Mi
- The container only requests one vNPU, meaning that the number of vNPUs in both requests and limits is fixed at 1.
- The vNPU must be created on the node in advance, and there must be sufficient resources. If the vNPU resources are insufficient, an error message similar to "0/2 nodes are available: 2 Insufficient huawei.com/ascend-310-2c." is displayed.
- huawei.com/ascend-310-2c indicates the name of the requested vNPU. The vNPU name varies depending on the product and template. You can refer to the table below to see the mapping between the products and names.
Table 3 vNPU names in different products Product Type
Virtualization Template
vNPU Name
Atlas inference series (eight AI Cores)
vir01
huawei.com/ascend-310-1c
vir02
huawei.com/ascend-310-2c
vir02_1c
huawei.com/ascend-310-2c.1cpu
vir04
huawei.com/ascend-310-4c
vir04_3c
huawei.com/ascend-310-4c.3cpu
vir04_3c_ndvpp
huawei.com/ascend-310-4c.3cpu.ndvpp
vir04_4c_dvpp
huawei.com/ascend-310-4c.4cpu.dvpp
Ascend training series (30 or 32 AI Cores)
vir16
huawei.com/ascend-1980-16c
vir08
huawei.com/ascend-1980-8c
vir04
huawei.com/ascend-1980-4c
vir02
huawei.com/ascend-1980-2c
vir10_3c_32g
huawei.com/ascend-1980-10c.3cpu.32g
vir05_1c_16g
huawei.com/ascend-1980-5c.1cpu.16g
- Create the workload.
kubectl apply -f vnpu-worker.yamlInformation similar to the following is displayed:
deployment/vnpu-test created
- Check whether the pod is running.
kubectl get pod | grep vnpu-testIf the following information is displayed, the workload pod is running properly:
vnpu-test-6658cd795b-rx76t 1/1 Running 0 59m
- Create a YAML file named vnpu-worker.
- Access the container.
kubectl -n default exec -it vnpu-test-6658cd795b-rx76t -c container-0 -- /bin/bash - Check whether the vNPU is mounted to the container.
- Configure an environment variable to specify the search path of the dynamic link library (DLL), which ensures that CCE can properly load the required DLL file when running NPU-related applications.
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/HiAI/driver/lib64:/usr/local/Ascend/driver/lib64/common:/usr/local/Ascend/driver/lib64/driver:/usr/local/Ascend/driver/lib64
- View the vNPU mounted to the container.
npu-smi info
The command output indicates that the vNPU whose ID is 104 has been mounted to the container. The virtualization template is vir02.
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | npu-smi 24.1.rc2.3 Version: 24.1.rc2.3 | +-------------------------------+-----------------+------------------------------------------------------+ | NPU Name | Health | Power(W) Temp(C) Hugepages-Usage(page) | | Chip Device | Bus-Id | AICore(%) Memory-Usage(MB) | +===============================+=================+======================================================+ | 104 xxx | OK | NA 54 0 / 0 | | 0 0 | 0000:00:0D.0 | 0 445 / 5381 | +===============================+=================+======================================================+ +-------------------------------+-----------------+------------------------------------------------------+ | NPU Chip | Process id | Process name | Process memory(MB) | +===============================+=================+======================================================+ | No running processes found in NPU 104 | +===============================+=================+======================================================+
- Configure an environment variable to specify the search path of the dynamic link library (DLL), which ensures that CCE can properly load the required DLL file when running NPU-related applications.
Disabling NPU Virtualization
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console. In the navigation pane, choose Settings. Then, click the Heterogeneous Resources tab.
- Evict vNPU loads on nodes with NPU virtualization enabled. For details, see Draining a Node.
- In NPU Virtualization Settings, set Virtual Instance Specifications of all node pools to all-disabled, and click Confirm Settings in the lower right corner. In the Confirm Settings dialog box, click Save. CCE will clear the NPU virtualization instances on the node.
- On the Heterogeneous Resources tab page, disable NPU virtualization. In the displayed dialog box, click OK. In the lower right corner, click Confirm Settings. In the Confirm Settings dialog box, click Save. CCE will clear the existing virtualization settings and automatically delete the ascend-vnpu-manager pod.
Helpful Links
To monitor NPU metrics, see NPU Monitoring.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





