Overview
NPU virtualization abstracts a physical NPU (Ascend AI product) into multiple virtual NPUs (vNPUs) so that it can be shared among containers. It enables flexible partitioning and dynamic management of hardware resources. NPU virtualization offers the following benefits:
- Efficient resource utilization: A single server's NPUs can be divided into multiple vNPUs for different users, reducing computing costs.
- Strong resource isolation: Containerization technologies enable vNPUs for different users to be completely isolated, preventing computing interference or data leak.
- Unified management: The allocation and reclamation of resources of different specifications are streamlined, facilitating multi-tenant management.
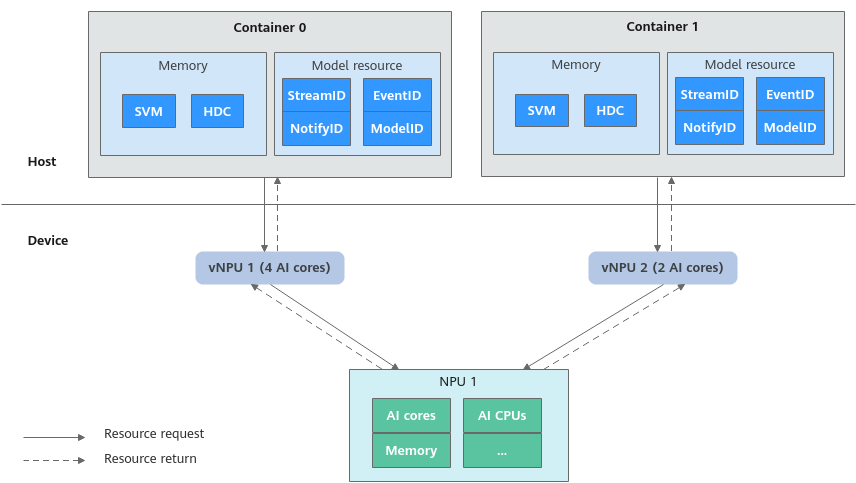
Basic Rules of NPU Virtualization
The Ascend NPU hardware provides core computing resources, including AI cores, AI CPUs, and memory. Leveraging virtualization technologies, CCE can flexibly divide physical NPUs into multiple vNPUs based on your needs. Each vNPU contains a specific number of AI cores, AI CPUs, and memory. For example, if one container requests four AI cores and another requests two AI cores, CCE will allocate two vNPUs to meet these requests. For details, see Figure 1.
Supported NPU Chip Types
CCE has only verified the virtualization of Ascend Snt3P3. .
To check the hardware data of a chip, log in to the target node and run the npu-smi info -t info-vnpu -i <id> -c <chip_id> command. Obtain the id and chip_id as follows:
- id: The device ID or NPU ID, which can be obtained by running the npu-smi info -l command.
- chip_id: The chip ID, which can be obtained by running the npu-smi info -m command.
NPU Virtualization Templates
|
Chip Type |
Template |
AI Cores |
Memory |
AI CPU |
VPC |
VDEC |
JPEGD |
VENC |
JPEGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ascend Snt3P3 |
vir04 |
4 |
12 GiB |
4 |
6 |
6 |
8 |
2 |
4 |
|
vir04_3c |
4 |
12 GiB |
3 |
6 |
6 |
8 |
1 |
4 |
|
|
vir02 |
2 |
6 GiB |
2 |
3 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
vir02_1c |
2 |
6 GiB |
1 |
3 |
3 |
4 |
0 |
2 |
|
|
vir01 |
1 |
3 GiB |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
vir04_3c_ndvpp |
4 |
12 GiB |
3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
vir04_4c_dvpp |
4 |
12 GiB |
4 |
12 |
12 |
16 |
3 |
8 |

NPU virtualization supports flexible combinations of virtual instances. An NPU chip can be virtualized into multiple vNPUs using various virtualization templates, with the total resources used by each vNPU not exceeding the physical limits of the NPU. Recommended specifications are provided for flexible combination as needed. For details, see Virtual Instance Specifications.
NPU Virtualization Modes
CCE provides two NPU virtualization modes to choose from based on service needs.
- Automatic NPU Virtualization (Computing Segmentation): NPUs are virtualized by node pool. You can split NPUs to vNPUs in batches through the UI. This mode supports only fixed virtualization template combinations and is suitable for large-scale unified resource management.
- Manual NPU Virtualization: NPUs are virtualized by node. You can manually control the resource allocation of each NPU. This mode is more flexible but complex and is ideal for scenarios requiring fine-grained resource management.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot