Topology-aware Affinity Scheduling on Hypernodes
In large-scale AI training and inference scenarios, as computing resources are distributed, network communication between pods often faces bandwidth bottlenecks and high latency. Especially, when highly associated pods on different nodes communicate with each other, the system performance and response speed decrease significantly. To solve this problem, Volcano Scheduler provides hypernode topology-aware affinity scheduling. A hypernode can have 48 nodes. The NPUs on a hypernode form a hyperplane network through a specific network connection. This configuration enables faster data transmission rates. Topology-aware affinity scheduling on hypernodes schedules pods with high interdependence onto the same hypernode. By doing so, it minimizes cross-node communication, reduces network latency, and speeds up data transmission.
Overview
Volcano Scheduler provides hyperjobs, a new workload API. You can use hyperjobs to schedule and manage related jobs in a unified manner. For details, see Use Case. Hypernode topology-aware affinity scheduling complies with the following principles:
- Affinity scheduling: Volcano Scheduler creates Volcano jobs based on the hyperjob template. Each Volcano job is an affinity group. During scheduling, the pods for the Volcano jobs are scheduled onto the nodes with the volcano.sh/hypernode label (which indicates that the nodes are on hypernodes). At the same time, pods in the same affinity group are scheduled onto the nodes with the same volcano.sh/hypernode label (which indicates that the nodes are on the same hypernode).
Figure 1 Affinity scheduling flowchart

- Gang scheduling: A hyperjob is only scheduled when the number of running Volcano jobs reaches the value of minAvailable (or the sum of the replicatedJobs.replicas values if minAvailable is not specified). In addition, each Volcano job in a hyperjob also supports gang scheduling.
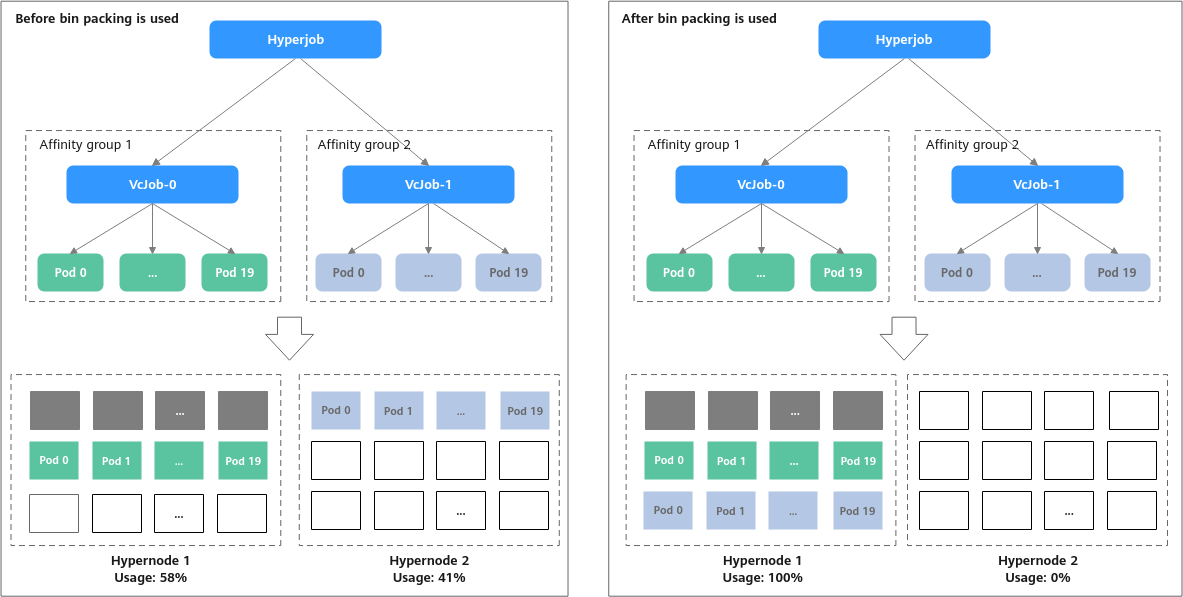
- Bin packing: When hypernodes are on an equivalent network, Volcano Scheduler preferentially allocates hyperjobs to a hypernode with the fewest resource fragments to improve resource utilization. In Figure 2, there are two hypernodes (hypernode 1 and hypernode 2) in the cluster, and eight nodes on hypernode 1 have been allocated for executing other jobs. A hyperjob that contains two Volcano jobs is delivered. Each Volcano job requires 20 pods, and each pod requests to exclusively occupy a node.
- If bin packing is not used, VcJob-0 may be scheduled to hypernode 1 and vcjob-1 to hypernode 2. In this case, the usage of hypernode 1 is 58% (28/48 × 100% = 58%), and that of hypernode 2 is 41% (20/48 × 100% = 41%).
- If bin packing is used, vcjob-0 and vcjob-1 are preferentially scheduled to hypernode 1, and its usage is 100%. The usage of hypernode 2 is 0%, so that hypernode 2 is idle and can be used to handle other jobs.
Prerequisites
- A CCE standard or Turbo cluster of v1.23 or later is available. For details about how to create a cluster, see Buying a CCE Standard/Turbo Cluster.
- There are hypernodes in the cluster. Hypernodes cannot be purchased for CCE standard or Turbo clusters. You can purchase hypernodes (Ascend instances) in ModelArts in advance. After the purchase, CCE automatically accepts and manages the nodes. For details, see Creating a Standard Dedicated Resource Pool.
In a CCE standard or Turbo cluster, you can use the volcano.sh/hypernode label to check if a node is a hypernode or which hypernode that it belongs to.
- The Volcano Scheduler add-on of v1.15.8 or later has been installed. For details, see Volcano Scheduler.
- The CCE AI Suite (Ascend NPU) add-on of v2.1.23 or later has been installed in the cluster. For details, see CCE AI Suite (Ascend NPU).
Notes and Constraints
In a single pod, only one container can request NPU resources, and init containers cannot request NPU resources. Otherwise, the pod cannot be scheduled.
Enabling Topology-aware Scheduling on Hypernodes
After topology-aware scheduling is enabled, you can manually divide affinity groups based on the data transmission requirements between training jobs. Volcano Scheduler schedules jobs in the same affinity group onto the same hypernode, improving network transmission efficiency.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console. In the navigation pane, choose Overview. In the navigation pane, choose Settings. Then click the Scheduling tab.
- In Volcano Scheduler configuration, topology-aware scheduling on hypernodes is disabled by default. You need to modify the configuration to enable this function.
- Set Default Cluster Scheduler to Volcano and click Expert mode > Try Now.
Figure 3 Expert mode > Try Now
- In the YAML file, add the following parameters to enable topology-aware scheduling on hypernodes for efficient data transmission between different jobs in the same affinity group:
... tiers: - plugins: - name: priority - enableJobStarving: false enablePreemptable: false name: gang - name: conformance - plugins: - enablePreemptable: false name: drf - name: predicates - name: nodeorder - plugins: - name: cce-gpu-topology-predicate - name: cce-gpu-topology-priority - name: xgpu - plugins: - name: nodelocalvolume - name: nodeemptydirvolume - name: nodeCSIscheduling - name: networkresource - plugins: # Enable topology-aware scheduling. - name: hypernode-topology-aware ... - Click Save in the lower right corner.
- Set Default Cluster Scheduler to Volcano and click Expert mode > Try Now.
- In the lower right corner of the tab, click Confirm Settings. In the displayed dialog box, confirm the modification and click Save.
Use Case
- Create a hyperjob and define two affinity groups (Volcano jobs) in the hyperjob.
- Create a YAML file for the hyperjob.
vim hyper-job.yamlBelow is the file content (Only one container in a pod can request NPU resources. Init containers cannot request NPUs. Otherwise, the pod cannot be scheduled):apiVersion: batch.volcano.sh/v1alpha1 kind: HyperJob metadata: name: hyperjob-test spec: replicatedJobs: - replicas: 2 # The number of Volcano jobs name: vcjob-test # The name of the Volcano jobs template: tasks: - replicas: 2 # The number of pods name: worker # The name of the pods template: spec: containers: # Define containers. - name: test image: busybox command: ['sh', '-c', 'echo "Hello, Kubernetes!" && sleep 3600'] imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent resources: requests: cpu: 1 "huawei.com/ascend-1980": 8 # The number of requested NPUs, which must be the same as the value of limits. The system determines whether each pod exclusively occupies a node based on the number of requested NPUs. limits: cpu: 1 "huawei.com/ascend-1980": 8
- requests."huawei.com/ascend-1980" indicates the number of NPUs requested by a pod. The value must be the same as the value of limits. The system determines whether each pod exclusively occupies a node based on the value of this parameter and the number of NPUs on the node.
- Create the hyperjob.
kubectl apply -f hyper-job.yamlInformation similar to the following is displayed:
hyperjob.batch.volcano.sh/hyperjob-test created
- Check whether the hyperjob is created.
kubectl get hyperjob
If the following information is displayed, the hyperjob has been created:NAME MINAVAILABLE AGE hyperjob-test 2 68s
- Check whether the Volcano jobs are executed.
kubectl get vcjob
If the following information is displayed, the two Volcano jobs have been executed and all the pods have been scheduled:
NAME STATUS MINAVAILABLE RUNNINGS AGE hyperjob-test-vcjob-test-0 Running 2 2 2m30s hyperjob-test-vcjob-test-1 Running 2 2 2m30s
- Create a YAML file for the hyperjob.
- Check the IP address of the node where each pod is located.
kubectl get pod -o wide
The command output is as follows (the NODE column indicates the IP address of the node where the pod is located):
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES hyperjob-test-vcjob-test-0-worker-0 1/1 Running 0 2m56s 192.168.9.35 192.168.9.104 <none> <none> hyperjob-test-vcjob-test-0-worker-1 1/1 Running 0 2m55s 192.168.9.105 192.168.9.37 <none> <none> hyperjob-test-vcjob-test-1-worker-0 1/1 Running 0 2m56s 192.168.9.32 192.168.9.100 <none> <none> hyperjob-test-vcjob-test-1-worker-1 1/1 Running 0 2m55s 192.168.9.202 192.168.9.75 <none> <none>
- View the value of the volcano.sh/hypernode label of the node where each pod is located to check whether the pods in the same affinity group (Volcano job) are scheduled onto the same hypernode. Only the nodes on a hypernode have the volcano.sh/hypernode label. If the label values are the same, these nodes belong to the same hypernode.
kubectl describe node 192.168.9.104 | grep volcano.sh/hypernode kubectl describe node 192.168.9.37 | grep volcano.sh/hypernode kubectl describe node 192.168.9.100 | grep volcano.sh/hypernode kubectl describe node 192.168.9.75 | grep volcano.sh/hypernode
Information similar to the following is displayed:
volcano.sh/hypernode=hypernode-1 volcano.sh/hypernode=hypernode-1 volcano.sh/hypernode=hypernode-2 volcano.sh/hypernode=hypernode-2
The pods for hyperjob-test-vcjob-test-0 are scheduled to hypernode-1 and the pods for hyperjob-test-vcjob-test-1 are scheduled to hypernode-2.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot