Suggestions on TaurusDB Metric Alarm Configuration
You can set alarm rules on Cloud Eye to customize the monitored objects and notification policies and keep track of the instance status. This section describes how to configure TaurusDB metric alarm rules.
Creating a Metric Alarm Rule
- Log in to the Cloud Eye console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and project. - In the navigation pane, choose Alarm Management > Alarm Rules. On the displayed page, click Create Alarm Rule in the upper right corner.
- On the displayed page, set parameters as prompted.
Figure 1 Setting alarm rule parameters
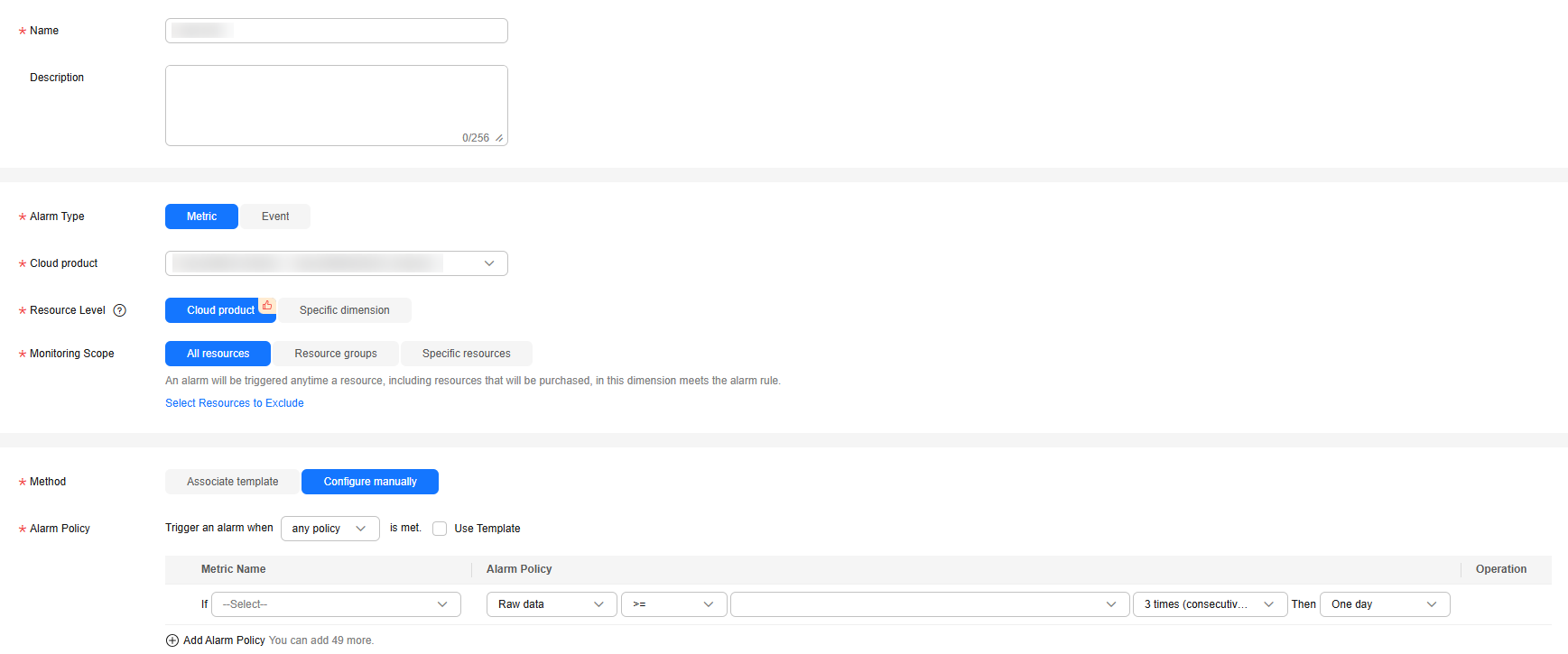
Table 1 Alarm rule parameters Parameter
Description
Name
Name of the alarm rule. The system generates a random name, but you can change it if needed.
Description
Description of the alarm rule.
Alarm Type
Select Metric.
Cloud product
Select TaurusDB.
Resource Level
Cloud product is recommended.
Monitoring Scope
- All resources: An alarm will be triggered if any resource of the current cloud product meets the alarm policy. To exclude resources that do not require monitoring, click Select Resources to Exclude.
- Resource groups: An alarm will be triggered if any resource in the selected resource group meets the alarm policy.
- Specific resources: Click Select Specific Resources to select resources.
Method
- Associate template: After an associated template is modified, the policies contained in this alarm rule to be created will be modified accordingly.
You are advised to select Use existing template. The existing templates already contain three common alarm metrics: CPU usage, memory usage, and storage space usage.
- Configure manually: Configure alarm policies manually.
Template
If you select Associate template for Method, you need to select a template.
You can select a default alarm template or create a custom template.
Alarm Policy
If you select Configure manually for Method, you need to configure alarm policies.
An alarm is triggered when the metric configured for this alarm reaches the preset threshold in consecutive periods. For example, Cloud Eye triggers an alarm every 5 minutes if the average CPU usage of the monitored object is 80% or more for three consecutive 5-minute periods.
Alarm Severity
The alarm severity can be Critical, Major, Minor, or Warning.
Figure 2 Setting alarm notification parameters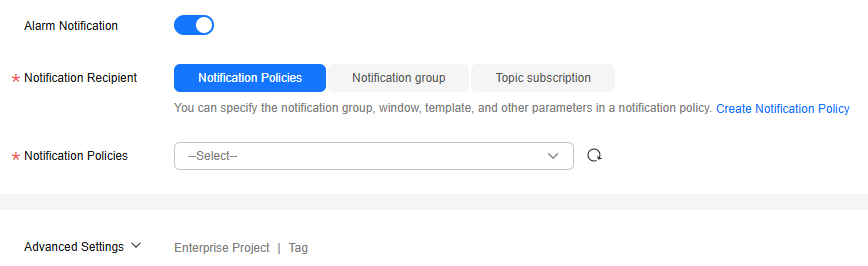
Table 2 Alarm notification parameters Parameter
Description
Alarm Notification
Whether to notify users when alarms are triggered. Notifications can be sent by email, text message, or HTTP/HTTPS message.
Notification Recipient
You can select a notification group or topic subscription as required.
Notification Group
Notification group the alarm notification is to be sent to.
Notification Object
Object the alarm notification is to be sent to. You can select the account contact or a topic. This parameter is only available if you select Topic subscription for Notification Recipient.
- The account contact is the mobile phone number and email address of the registered account.
- A topic is used to publish messages and subscribe to notifications.
Notification Window
Time window during which Cloud Eye sends notifications.
If Notification Window is set to 08:00-20:00, Cloud Eye sends notifications only within this window.
Trigger Condition
Condition for triggering an alarm notification. You can select Generated alarm (when an alarm is generated), Cleared alarm (when an alarm is cleared), or both.
Enterprise Project
Enterprise project that the alarm rule belongs to. Only users with the enterprise project permissions can view and manage the alarm rule.
Tag
Key-value pairs that you can use to easily categorize and search for cloud resources.
- Click Create.
For details about how to create alarm rules, see Creating an Alarm Rule in Cloud Eye User Guide.
Metric Alarm Configuration Suggestions
|
Metric ID |
Metric Name |
Metric Description |
Threshold in Best Practices |
Alarm Severity in Best Practices |
Handling Suggestion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
gaussdb_mysql001_cpu_util |
CPU Usage |
CPU usage of the monitored object |
Raw data > 80% for three consecutive periods |
Major |
|
|
gaussdb_mysql002_mem_util |
Memory Usage |
Memory usage of the monitored object |
Raw data > 90% for three consecutive periods |
Major |
|
|
gaussdb_mysql072_conn_usage |
Connection Usage |
Percent of used TaurusDB connections to the total number of connections |
Raw data > 80% for three consecutive periods |
Major |
Identify why there are too many connections and optimize related workloads. For details about the risks and optimization solutions, see Are There Any Risks If There Are Too Many Connections to a TaurusDB Instance? and What Do I Do If There Are Too Many Database Connections? |
|
gaussdb_mysql077_replication_delay |
Replication Delay |
Delay between the primary node and read replicas
NOTE:
This metric is used only for read replicas. |
Raw data > 1s for three consecutive periods |
Major |
This issue is usually caused by a large number of DDL operations performed on or UPDATE statements written to the primary node. If read replicas are sensitive to data timeliness, perform DDL operations during off-peak hours or optimize workloads to reduce the sudden spike in data writes. |
|
gaussdb_mysql104_dfv_write_delay |
Storage Write Delay |
Average delay of writing data to the storage layer in a specified period |
Raw data > 50 ms for three consecutive periods |
Major |
Check whether the instance has performance bottlenecks in CPU, memory, and connections and solve the bottlenecks based on the corresponding suggestions. |
|
gaussdb_mysql105_dfv_read_delay |
Storage Read Delay |
Average delay of reading data from the storage layer in a specified period |
Raw data > 50 ms for three consecutive periods |
Major |
Check whether the instance has performance bottlenecks in CPU, memory, and connections and solve the bottlenecks based on the corresponding suggestions. |
|
gaussdb_mysql119_disk_used_ratio |
Disk Usage |
Disk usage of the monitored object |
Raw data > 80% for three consecutive periods |
Major |
|
|
gaussdb_mysql128_long_trx_count |
Long-Running Transactions |
Number of long transactions that are not closed |
Raw data > 1 for three consecutive periods |
Major |
Optimize the workloads related to long transactions. For details, see: |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





