Managing Slow Query Logs of a DB Instance
Scenarios
Slow query logs record statements that exceed the long_query_time value (10s by default). The lock wait time is not calculated into the query time. You can check log details and statistics to identify statements that are executing slowly and then optimize the statements.
You can set log_queries_not_using_indexes to determine whether to record queries without indexes. The default value is OFF, indicating that queries without indexes are not recorded. If this parameter is set to ON, all queries without indexes are recorded and this setting is not affected by the long_query_time value.
If you need to record the number of statements without indexes per minute, you can set log_throttle_queries_not_using_indexes. The default value is 0.
Constraints
- You can view the slow query log records of a specified statement or a specific time period.
- Only SELECT statements return the number of result rows. The number of result rows for the INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and CREATE statements is 0 by default.
- You can view slow query logs of a specified database name (which cannot contain any special characters). The database name supports only exact search.
- Slow query logs only record executed statements whose execution duration exceeds the threshold.
- The long_query_time parameter determines when a slow query log is recorded. However, changes to this parameter do not affect already recorded logs. If long_query_time is changed from 1s to 0.1s, TaurusDB starts recording statements that meet the new threshold and still displays the previously recorded logs that do not meet the new threshold. For example, a 1.5s SQL statement that was recorded when the threshold was 1s will not be deleted now that the new threshold is 2s.
- If the length of a single line of a SQL statement exceeds 16 KB, the statement will be truncated. When you view slow query log details, the SQL statement may be incomplete after special processing and is for reference only.
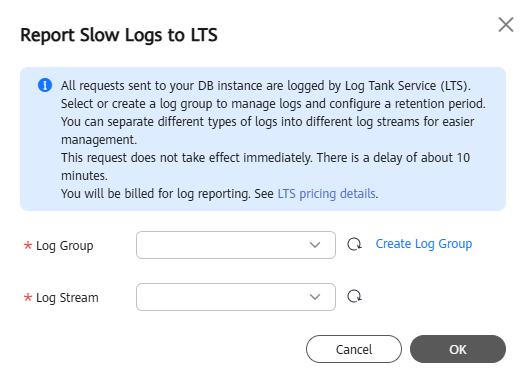
Reporting Slow Query Logs to LTS
After log groups and log streams are configured, slow query logs are stored in LTS. You can view the reported slow query logs in LTS.
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose Logs.
- On the Slow Query Logs tab, click
 next to Report Slow Logs to LTS.
next to Report Slow Logs to LTS. - In the displayed dialog box, specify Log Group and Log Stream and click OK.
Figure 1 Reporting slow query logs to LTS
Viewing, Analyzing, and Downloading Slow Query Logs
You can view and analyze slow query logs on the console. By default, SQL statements are anonymized. If Show Original Log is enabled, SQL statements in the logs will be displayed in plaintext. Logs displayed in plaintext will be automatically deleted 30 days later. If a DB instance is deleted, its related logs will also be deleted.
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose Logs.
- On the Slow Query Logs tab, view the slow query log details.
- Enabling Show Original Log
To show slow query logs in plaintext, click
 next to Show Original Log. In the displayed dialog box, click OK.
next to Show Original Log. In the displayed dialog box, click OK. - Viewing slow query logs
View slow query logs of different nodes and SQL statements in a given database.
Supported SQL statements include SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, ALTER, and DROP.
Click
 and specify a time period.
and specify a time period.
Figure 2 Viewing log details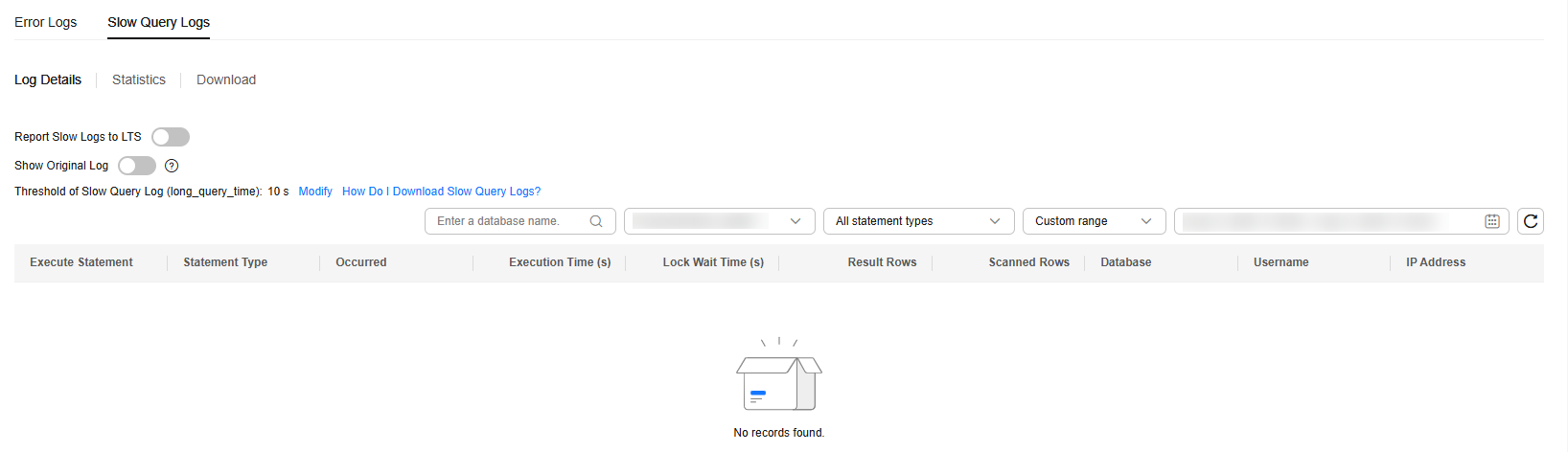
- Enabling Show Original Log
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose Logs. On the Slow Query Logs tab, click Statistics to view details.
Figure 3 Viewing statistics

- On the Statistics page, only one of the SQL statements of the same type is displayed as an example. For example, if two select sleep(N) statements, select sleep(1) and select sleep(2), are executed in sequence, only select sleep(N) will be displayed.
- However, if Show Original Log is enabled, all of the slow SQL statements are displayed. For example, if select sleep(1) and select sleep(2) are executed in sequence, both of them will be displayed.
- No. and Ratio of SQL Executions indicates the ratio of the slow executions to the total executions of the SQL statement.
- On the Statistics page, only the latest 5,000 slow SQL statements within a specified period are analyzed.
- You can filter slow log statistics by database name (which cannot contain any special characters), statement, or time period. The database name supports only exact search.
- If any database name in the slow log statistics contains special characters such as < > ', the special characters will be escaped.
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose Logs.
- On the Slow Query Logs tab, click Download. Locate a log whose status is Preparation completed and click Download in the Operation column.
Figure 4 Downloading a slow query log

- The system automatically loads the download preparation tasks. The loading duration is determined by the log file size and network environment.
- When the log is being prepared for download, the log status is Preparing.
- When the log is ready for download, the log status is Preparation completed.
- If the preparation for download fails, the log status is Abnormal.
Logs in the Preparing or Abnormal state cannot be downloaded.
- Only logs no more than 40 MB can be downloaded directly from this page. The time range is calculated from the time you download the logs back to the time when the accumulated file size reaches 40 MB.
- The download link is valid for 5 minutes. After the download link expires, a message is displayed indicating that the download link has expired. If you need to download the log, click OK.
- You can select the logs to be downloaded by node.
- The system automatically loads the download preparation tasks. The loading duration is determined by the log file size and network environment.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





