Setting Up an FTP Site (Ubuntu)
Scenarios
This section guides you through the setup of an FTP site on a Linux ECS using vsftpd. vsftpd is an FTP server software that is widely used in Linux releases. Ubuntu 22.04 (64-bit) is used as an example in this section.
Solution Architecture
Advantages
- A website with a simple networking architecture can be quickly set up.
- The website is secure and easy to use.
Resource Planning
|
Resource |
Description |
Cost |
|---|---|---|
|
VPC |
VPC CIDR block: 192.168.0.0/16 |
Free |
|
VPC subnet |
|
Free |
|
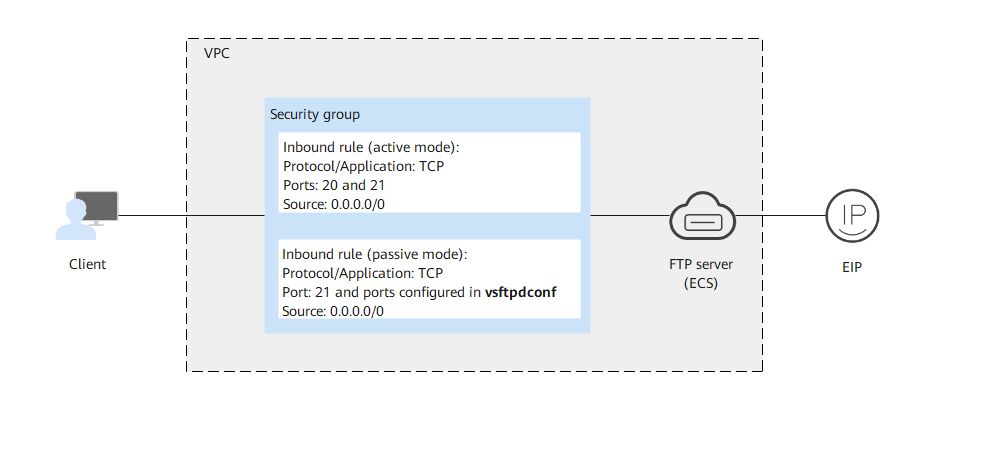
Security group |
Inbound rule (active mode):
Inbound rule (passive mode):
|
Free |
|
ECS |
|
The following resources generate costs:
For billing details, see Billing Modes. |
|
vsftpd |
A free, open-source FTP software. |
Free |
Process
Procedure
- Log in to the ECS.
- Install vsftp.
- Run the following commands to install vsftpd:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install vsftpd
If Do you want to continue? [Y/n] is displayed, enter y or Y to continue the installation.
- Run the following command to back up the original configuration file:
sudo cp /etc/vsftpd.conf /etc/vsftpd.conf.bak
- Run the following commands to install vsftpd:
- Configure vsftp.
- Modify the vsftpd.conf configuration file.
- Run the following command to open the vsftpd.conf file:
sudo vim /etc/vsftpd.conf
- Press i to enter insert mode.
- Modify the vsftpd.conf file.
Set FTP to active or passive mode based on site requirements. If other Huawei Cloud ECSs need to use EIPs to access the FTP server that is set up on a Huawei Cloud ECS, set FTP to passive mode.
- Parameters for configuring the active FTP mode:
#No anonymous login to the FTP server is allowed. Local users are allowed to log in to the FTP server with their local file directories specified. anonymous_enable=NO #Anonymous login to the FTP server is not allowed. local_enable=YES #Local users are allowed to log in to the FTP server. write_enable=YES #File upload is enabled. #The following parameters only allow login users to visit their own home directories: chroot_local_user=YES #The directory access rule applies to all users. chroot_list_enable=YES #The directory access rule does not apply to exclusive users. chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list #Exclusive users. #Add the following parameters to configure the FTP directory. local_root=/home/ftp allow_writeable_chroot=YES
- The passive FTP mode requires not only all the parameters configured for the active FTP mode, but also include the following parameter settings:
#Set the following parameters to enable the passive mode and specify the range of ports opened for the FTP server. pasv_min_port=35000 #Minimum port number in passive FTP mode pasv_max_port=40000 #Maximum port number in passive FTP mode
- Parameters for configuring the active FTP mode:
- Press Esc to exit insert mode. Then, enter :wq to save the settings and exit.
- Run the following command to open the vsftpd.conf file:
- Run the following command to restart vsftpd to apply the setting:
sudo systemctl restart vsftpd
- Modify the vsftpd.conf configuration file.
- Configure the user directory.
- After FTP is installed, a user named ftp is created by default. The user does not have a password. Run the following command to reset the password of ftp:
sudo passwd ftp
- Run the following command to add the user to the list of allowed FTP users:
echo "ftp" | sudo tee -a /etc/vsftpd.userlist
- Run the following commands to create an FTP file directory and grant permissions to the user:
sudo mkdir /home/ftp sudo chmod 777 /home/ftp
- After FTP is installed, a user named ftp is created by default. The user does not have a password. Run the following command to reset the password of ftp:
- Configure a security group.
After setting up the FTP site, add an inbound rule to the security group to allow packets to pass through the FTP port. For details, see Adding a Security Group Rule.
Table 2 Security group rules Priority
Action
Type
Protocol & Port
Source
1
Allow
IPv4
Protocols/TCP (Custom): 21
0.0.0.0/0
1
Allow
IPv4
Protocols/TCP (Custom): 1024-65535 (for example, 35000-40000)
0.0.0.0/0
- Verify the configuration on the client.
On the computer with the client installed, enter ftp://<server-IP-address>:<FTP-port-number> in the address bar. If you do not specify the port number, port 21 is used by default. If a dialog box is displayed for you to enter the username and password, the configuration is correct. After entering the username and password, you can perform operations on the FTP folder with assigned permissions.

- If active FTP mode is selected, use this method to configure the Internet Explorer browser. Otherwise, the FTP folder will be inaccessible. To configure the Internet Explorer browser, choose Tools > Internet Options > Advanced, select Enable FTP folder view, and deselect Use Passive FTP.
- If an error occurs when you use a browser to access the FTP server, clear the browser caches and try again.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





