Using DNS Resolver to Access a Specific Domain Name Across Regions
Scenarios
An enterprise deploys VPCs and ECSs in multiple regions and uses Cloud Connect to enable cross-region VPC communication. The enterprise needs to flexibly control the traffic paths of different domain names for refined management.
For example, when an ECS in a VPC in a region of the Chinese mainland requests to access a specific Internet domain name (for example, www.example.com) outside the Chinese mainland, the request needs to be resolved over the Internet egress in the region outside the Chinese mainland. In addition, the service access to the domain name is also forwarded through the Internet egress. The requests for other Internet domain name are still forwarded through the Internet egress in the region where the VPC is located.
Solution Overview
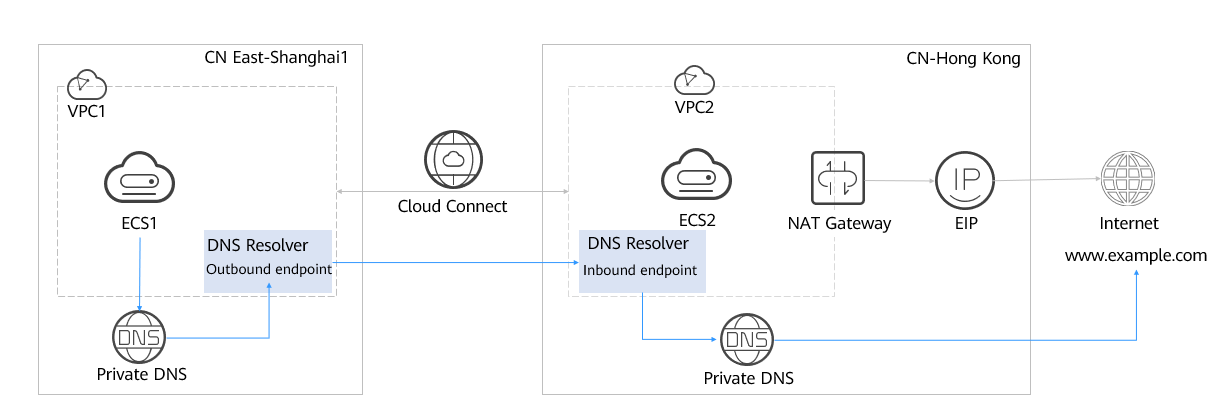
The outbound and inbound endpoints of Huawei Cloud DNS Resolver work with Cloud Connect to allow access to specific domain names across regions.
Resource and Cost Planning
The following table lists the resources required for access to specific domain names across regions.
|
Resource |
Resource Name |
Description |
Quantity |
Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
DNS Resolver |
Inbound endpoint |
|
2 |
Free |
|
Outbound endpoint |
|
|||
|
ECS |
ECS 1 |
|
2 |
For details, see ECS Pricing Details. |
|
ECS 2 |
|
|||
|
EIP |
You can specify the resource name. |
|
1 |
For details, see EIP Pricing Details. |
|
NAT gateway |
You can specify the resource name. |
In the CN-Hong Kong region, purchase a public NAT gateway, add a DNAT rule for the gateway, and bind the EIP to the DNAT rule. In this way, multiple ECSs in different AZs in a VPC can share the EIP. |
1 |
For details, see NAT Gateway Pricing Details. |
|
VPC |
VPC 1 |
|
2 |
Free |
|
VPC 2 |
|
- CN East-Shanghai1: VPC 1 and ECS 1 (associated with VPC 1)
- CN-Hong Kong: VPC 2, ECS 2 (associated with VPC 2), EIP, and public NAT gateway
Process
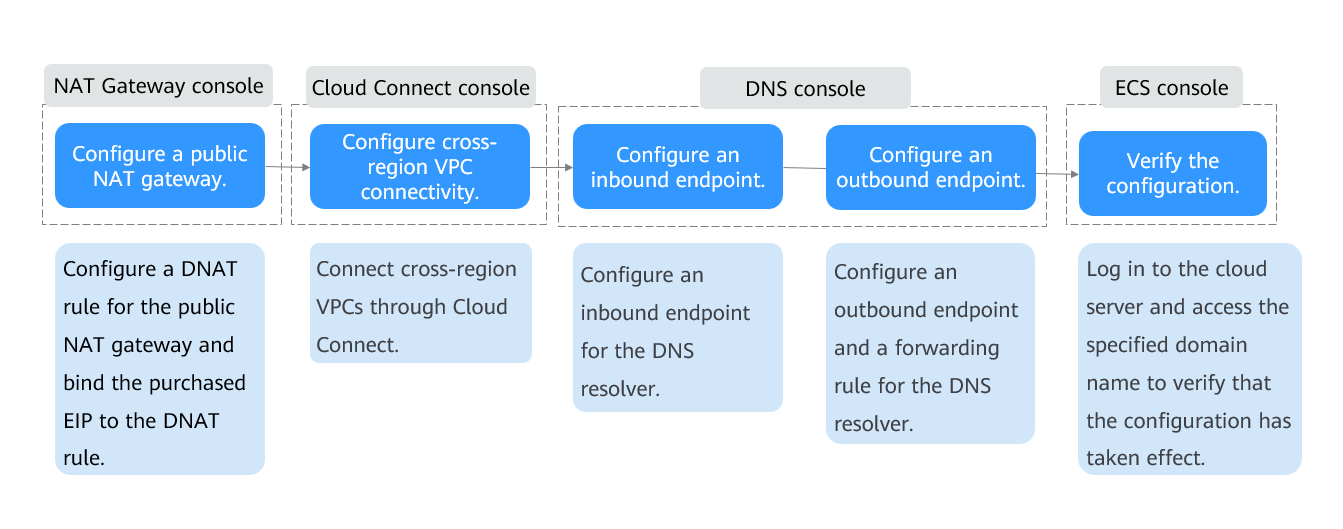
Procedure
- Configure a public NAT gateway.
Add a DNAT rule for the public NAT gateway and associate the DNAT rule with the purchased EIP. For details, see Adding a DNAT Rule.
- Connect VPCs in different regions.
Create a cloud connection and load network instances VPC 1 and VPC 2 to enable communication between two VPCs. For details, see Using a Cloud Connection to Connect VPCs in the Same Account But Different Regions.
- Configure an inbound endpoint for DNS Resolver.
- Go to the Resolvers page.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
Select the CN-Hong Kong region.
- In the upper right corner of the page, click Create Endpoint.
- Configure the parameters based on Table 2.
Figure 1 Creating an inbound endpoint
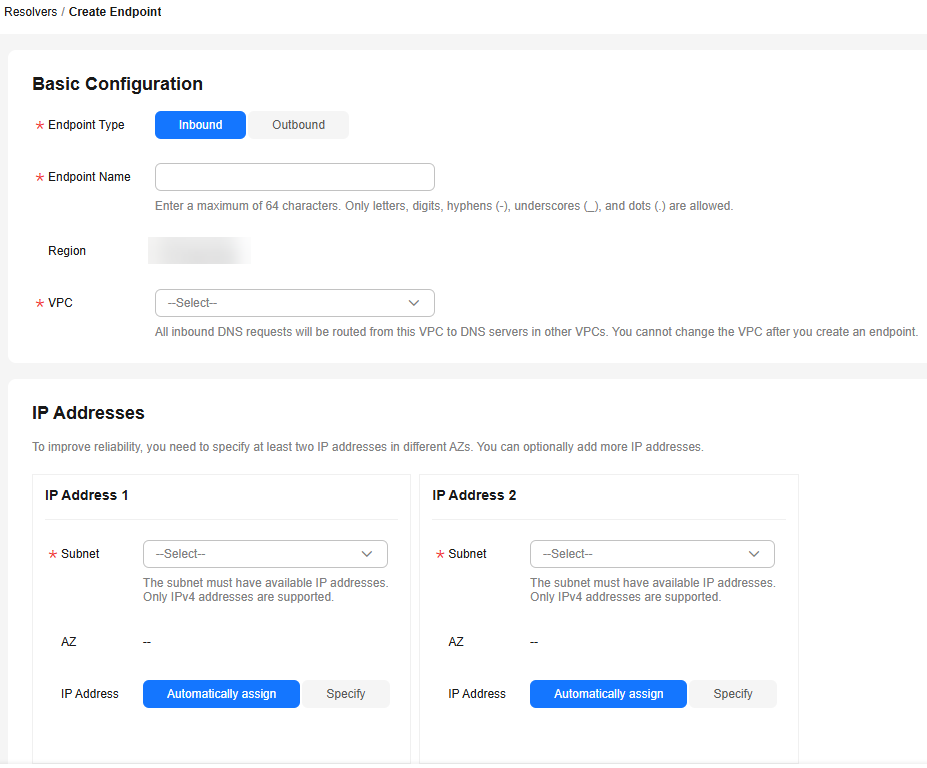
Table 2 Parameters for creating an inbound endpoint Parameter
Description
Endpoint Type
Type of the endpoint. There are two options: Inbound and Outbound.
Select Inbound.
Endpoint Name
Name of the endpoint. The name can:
- Contain only letters, digits, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.).
- Contain 1 to 64 characters.
Region
Region where the inbound endpoint works.
Select CN-Hong Kong.
VPC
The VPC over which all inbound DNS queries are forwarded to cloud DNS servers.
Select VPC 2.
CAUTION:The VPC cannot be changed after an endpoint is created.
Subnet
The subnet must have available IP addresses. Only IPv4 addresses are supported.
IP Addresses
There are two options: Automatically assign or Specify.
Select Specify and enter the following IP addresses:
172.16.5.5
172.16.6.6
- Click Create Now.
- Configure an outbound endpoint and a forwarding rule for DNS Resolver.
- Create an outbound endpoint.
- Go to the Resolvers page.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
Select CN East-Shanghai1 in this step.
- In the upper right corner of the page, click Create Endpoint.
- Configure the parameters based on Table 3.
Figure 2 Creating an outbound endpoint
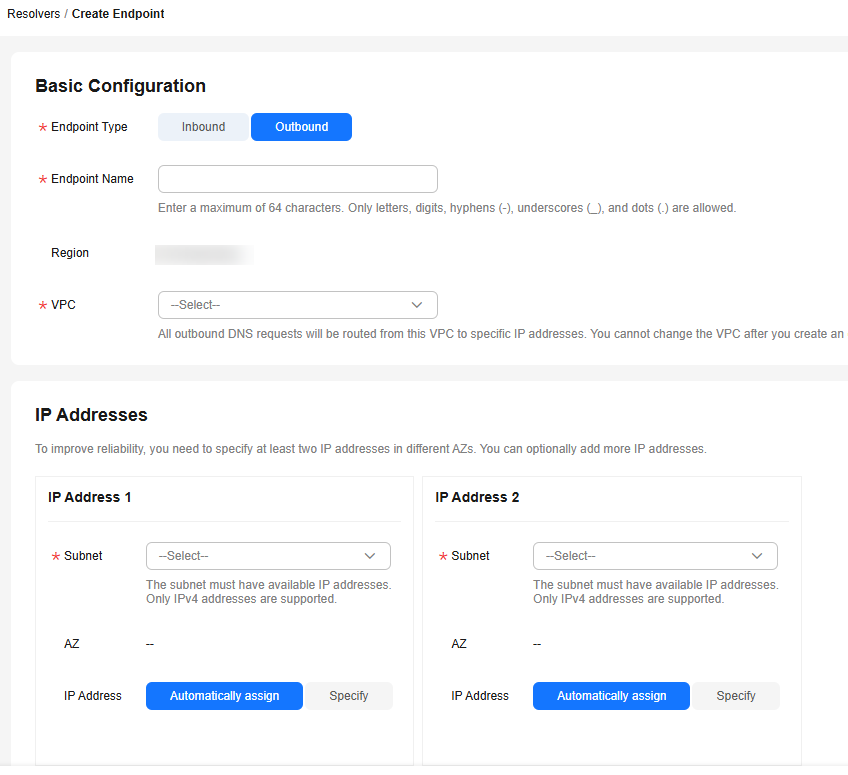
Table 3 Parameters for creating an outbound endpoint Parameter
Description
Endpoint Type
Type of the endpoint. There are two options: Inbound and Outbound.
Select Outbound.
Endpoint Name
Name of the endpoint. The name can:
- Contain only letters, digits, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.).
- Contain 1 to 64 characters.
Region
Region where the outbound endpoint works.
Select CN East-Shanghai1.
VPC
The VPC over which all outbound DNS queries are forwarded to the IP addresses specified in the endpoint rules.
Select VPC 1.
CAUTION:The VPC cannot be changed after an endpoint is created.
Subnet
The subnet must have available IP addresses. Only IPv4 addresses are supported.
IP Addresses
There are two options: Automatically assign or Specify.
Select Specify and enter the following IP addresses:
192.168.2.2
192.168.3.3
- Click Create Now.
- Create an endpoint rule.
- On the Resolvers page, click the Endpoint Rules tab.
- In the upper left corner above the rule list, click Add Endpoint Rule.
- Configure the parameters based on Table 4.
Figure 3 Adding a rule
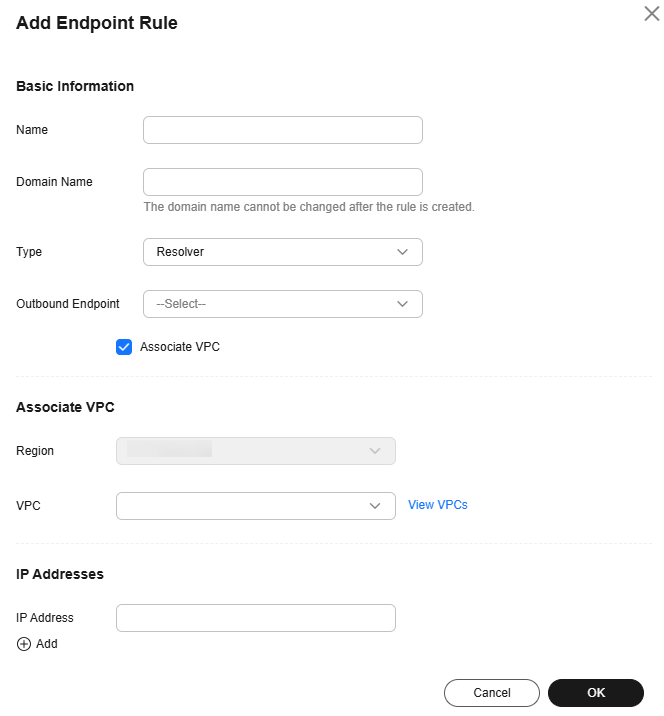
Table 4 Parameters for adding an endpoint rule Parameter
Description
Name
Name of the endpoint rule added to an outbound endpoint.
Domain Name
Enter the domain name to be accessed.
Type
By default, Resolver is selected.
Outbound Endpoint
Select the outbound endpoint that you want to add this endpoint rule to.
Select the outbound endpoint created in step 4.a.
Associate VPC
Whether to associate VPCs with the endpoint rule.
If this option is selected, you need to select one or more VPCs.
Select this option.
Region
Region that the VPCs belong to.
This parameter is displayed after Associate VPC is selected.
Select CN East-Shanghai1.
VPC
Select the VPCs to be associated with the endpoint rule.
This parameter is displayed after Associate VPC is selected.
Select VPC 1.
IP Addresses
IP address of a DNS server in the on-premises data center.
You can add one or more IP addresses.
Enter the IP addresses specified in the inbound endpoint associated with VPC 2 in the CN-Hong Kong region.
172.16.5.5
172.16.6.6

After an endpoint rule is added, the domain name, type, and outbound endpoint cannot be changed.
- Click OK.
- Create an outbound endpoint.
Verification
- Ensure that the public NAT gateway takes effect and the cross-region VPCs are connected through Cloud Connect.
- Verify the access to the specific domain name across regions.
Log in to ECS 1 and run the ping Domain name to be accessed command.
Example: ping www.example.com
If the command output displays the IP address mapped to domain name www.example.com, the access to the specific domain name is successful.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





