Collecting GPU Pod Monitoring Metrics and Setting Up a Grafana Dashboard
Application Scenarios
Monitoring metrics for GPU pods, such as gpu_pod_core_percentage_total, gpu_pod_core_percentage_used, gpu_pod_memory_total, and gpu_pod_memory_used, have been added to CCE AI Suite (NVIDIA GPU) of versions 2.1.30, 2.7.46, and later. These metrics allow for comprehensive monitoring of the resource usage of a GPU card and the compute and memory usage of the GPU workloads that run on a GPU. By using these metrics, you can create monitoring dashboards at different levels (for example, by pod or node) to stay informed about cluster information in real-time. For details about GPU metrics, see GPU Metrics.
The Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on does not automatically collect these metrics. To view them on Grafana dashboards, you must manually configure the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on for data collection and set up a dashboard. This section provides an example using pod monitoring to explain how to collect GPU pod monitoring metrics and establish a dashboard.
Prerequisites
- A NVIDIA GPU node is running properly in the cluster.
- The CCE AI Suite (NVIDIA GPU) add-on has been installed in the cluster and its version is 2.1.30, 2.7.46, or later. For details about how to install the add-on, see CCE AI Suite (NVIDIA GPU).
- The Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on and Grafana add-on have been installed in the cluster, and public access has been enabled for Grafana. For details about how to install these add-ons, see Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring and Grafana.
- To use AOM data sources (Configuring an AOM Data Source), enable Report Monitoring Data to AOM in the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on and Interconnect with AOM in the Grafana add-on. In addition, make sure to use the same AOM instances for both add-ons.
- To use Prometheus data sources (Configuring a Prometheus Data Source), enable Local Data Storage in the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on.
Process
|
Procedure |
Description |
Billing |
|---|---|---|
|
The Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on does not automatically collect GPU pod monitoring metrics. To view these metrics in the monitoring center, you need to manually configure the add-on for data collection. |
If Report Monitoring Data to AOM is enabled for the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on, uploading GPU pod monitoring data to AOM will incur fees. For details, see Product Pricing Details. |
|
|
When setting up a GPU pod monitoring dashboard on the Grafana GUI, make sure to choose either the AOM or Prometheus data sources that can be properly connected to Grafana. |
N/A |
|
|
Pod monitoring is used as an example to explain how to establish a GPU pod monitoring dashboard. |
N/A |
Step 1: Collect GPU Pod Monitoring Metrics
The Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on does not automatically collect GPU pod monitoring metrics. To view these metrics in the monitoring center, you need to manually configure the add-on for data collection.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Cluster > Settings. In the right pane, click the Monitoring tab. In the Monitoring Settings area, locate Preset Policies under Collection Settings and click Enable. In the dialog box displayed, click OK. If you have already enabled Preset Policies, skip this step.

The Preset Policies feature is used to configure preset collection policies for the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on. Enabling this feature will result in the deletion of preset ServiceMonitor and PodMonitor policies. Any manually created collection configurations will remain unaffected. Once this feature is enabled, customizing preset collection tasks becomes effortless.
Figure 1 Enabling the Preset Policies feature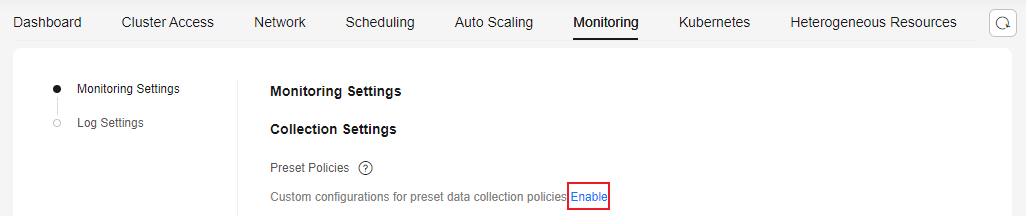
- In the Monitoring Settings area, locate Metric Settings and click Refresh to obtain data. After you enabled Preset Policies, the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on will be automatically upgraded. Then, choose Monitoring Settings > Collection Settings > Preset Policies and click Manage.
On the Collection Settings page, click the search box, select Task Name, and choose nvidia-gpu-device-plugin from the drop-down list. In the Collection Metric column, click Edit Trustlist.Figure 2 Editing trustlist
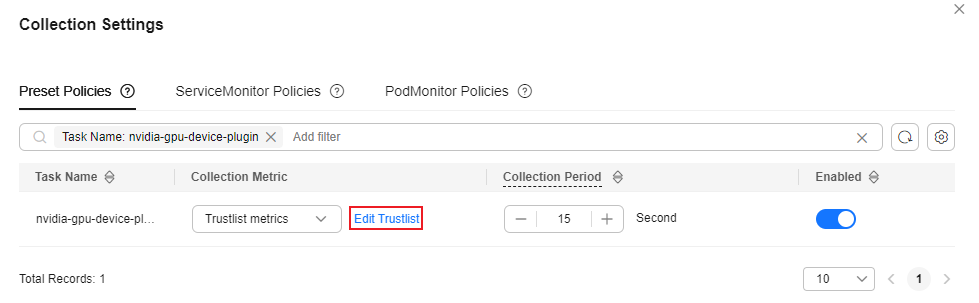
- In the upper left corner of the Trustlist metrics page, click Add Metric and add the gpu_pod_core_percentage_total, gpu_pod_core_percentage_used, gpu_pod_memory_total, and gpu_pod_memory_used metrics. After completing the operation, close the current page.
Step 2: Configure a Data Source for Grafana
Grafana supports:
- AOM data sources: Grafana creates the prometheus-aom data source automatically. Make sure this data source can be properly connected to Grafana.
- Prometheus data sources: You can use the prometheus data source preset in Grafana. Make sure this data source can be properly connected to Grafana.
To use an AOM data source, ensure that Report Monitoring Data to AOM has been enabled for the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on, Interconnect with AOM has been enabled for the Grafana add-on, and the two add-ons are connected to the same AOM instance. After you enabled Interconnect with AOM for the Grafana add-on, the prometheus-aom data source is automatically generated on the Grafana GUI. Ensure that the data source can be properly connected. After the connectivity test has been passed, you can start using the AOM data source.
- In the navigation pane, choose Cluster > Add-ons. In the right pane, find the Grafana add-on and click Access to go to the Grafana GUI.
- Enter the username and password when you access the Grafana GUI for the first time. The default username and password are both admin. After entering the username and password, reset the password following instructions.
- In the upper left corner, click
 , click
, click  on the left of Connections, and click Data sources to access the Data sources page.
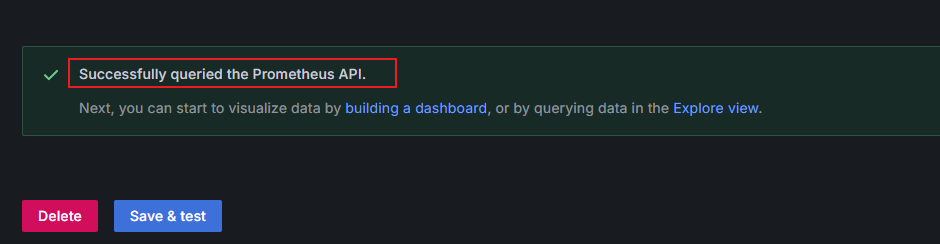
on the left of Connections, and click Data sources to access the Data sources page. - In the data source list, click prometheus-aom. Click Save & test at the bottom of the prometheus-aom data source page to check the data source connectivity. If "Successfully queried the Prometheus API" is displayed, the connectivity test has been passed.
Figure 3 Connectivity test passed
Before using a Prometheus data source, ensure that Local Data Storage has been enabled for the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on. The Grafana prometheus data source can connect directly to the local Prometheus data source after Local Data Storage is enabled. Ensure that the data source can be properly connected. After the connectivity test has been passed, you can start using the Prometheus data source.
- In the navigation pane, choose Cluster > Add-ons. In the right pane, find the Grafana add-on and click Access to go to the Grafana GUI.
- Enter the username and password when you access the Grafana GUI for the first time. The default username and password are both admin. After entering the username and password, reset the password following instructions.
- In the upper left corner, click
 , click
, click  on the left of Connections, and click Data sources to access the Data sources page.
on the left of Connections, and click Data sources to access the Data sources page. - In the data source list, click prometheus. Click Save & test at the bottom of the prometheus data source page to check the data source connectivity. If "Successfully queried the Prometheus API" is displayed, the connectivity test has been passed.
Figure 4 Connectivity test passed
Step 3: Configure a Grafana Dashboard
Grafana dashboards are essential for centralized monitoring and visualizing data from various data sources. They provide real-time insights into system statuses and service metrics using charts, graphs, and alarms. Grafana can generate monitoring dashboards based on GPU pod metrics, categorizing them by pod, GPU, node, and cluster. This section focuses on configuring a Grafana dashboard for pods as an example. Additional PromQL statements for different monitoring panels are available in PromQL Statement. You can perform the following operations to set up related dashboards.
- Create a Grafana dashboard to show GPU pod monitoring metrics.
- On the Grafana GUI, click
 to open the menu bar on the left and click Dashboards. In the upper right corner of the Dashboards page, click New and choose New dashboard from the drop-down list.
Figure 5 Creating a dashboard
to open the menu bar on the left and click Dashboards. In the upper right corner of the Dashboards page, click New and choose New dashboard from the drop-down list.
Figure 5 Creating a dashboard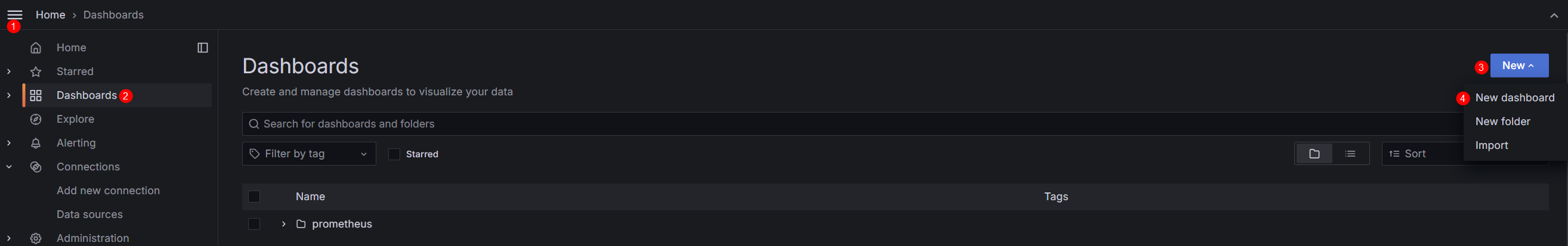
- In the upper right corner of the New dashboard page, click
 to name the dashboard. Enter GPU Pod Dashboard for Title and click Save dashboard in the upper right corner. On the Save dashboard page displayed, click Save. In this example, the dashboard is named GPU Pod Dashboard. You can use another name.
Figure 6 Renaming a dashboard
to name the dashboard. Enter GPU Pod Dashboard for Title and click Save dashboard in the upper right corner. On the Save dashboard page displayed, click Save. In this example, the dashboard is named GPU Pod Dashboard. You can use another name.
Figure 6 Renaming a dashboard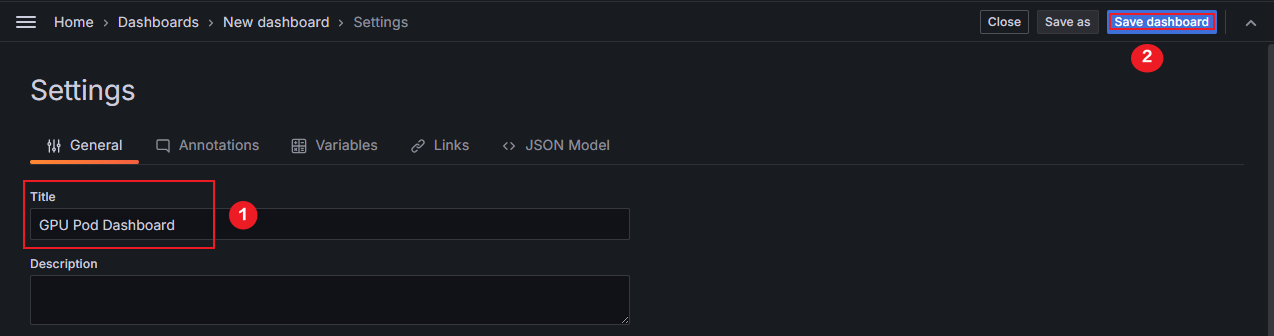
- On the Grafana GUI, click
- Configure variables on the Grafana dashboard.
Grafana variables allow you to create dynamic, customizable, templated dashboards. By changing variable values within the dashboard, you can modify the queries and panels. There is no need to create separate dashboards for each service or metric. Table 1 outlines the variables to configure in this example. Using instance as an example, this step demonstrates how to configure variables on a Grafana dashboard. You can refer to the instance example to add the variables listed in Table 1 in order.
Table 1 Variables Variable
Description
PromQL Statement
instance
Pod name of dp. It is used to obtain GPU nodes.
label_values(up{job=~".*nvidia-gpu-device-plugin.*"},instance)
gpu_index
GPU card number, for example, 0, 1, or 2
label_values(cce_gpu_temperature{instance=~"$instance"}, gpu_index)
namespace
Namespace where the GPU workload is in
label_values(gpu_pod_memory_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index"}, namespace)
pod
Pod name of a GPU workload
label_values(gpu_pod_memory_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace"}, pod)
- In the upper right corner of the New dashboard page, click
 . On the Settings page, click the Variables tab and click Add variable.
Figure 7 Adding a variable
. On the Settings page, click the Variables tab and click Add variable.
Figure 7 Adding a variable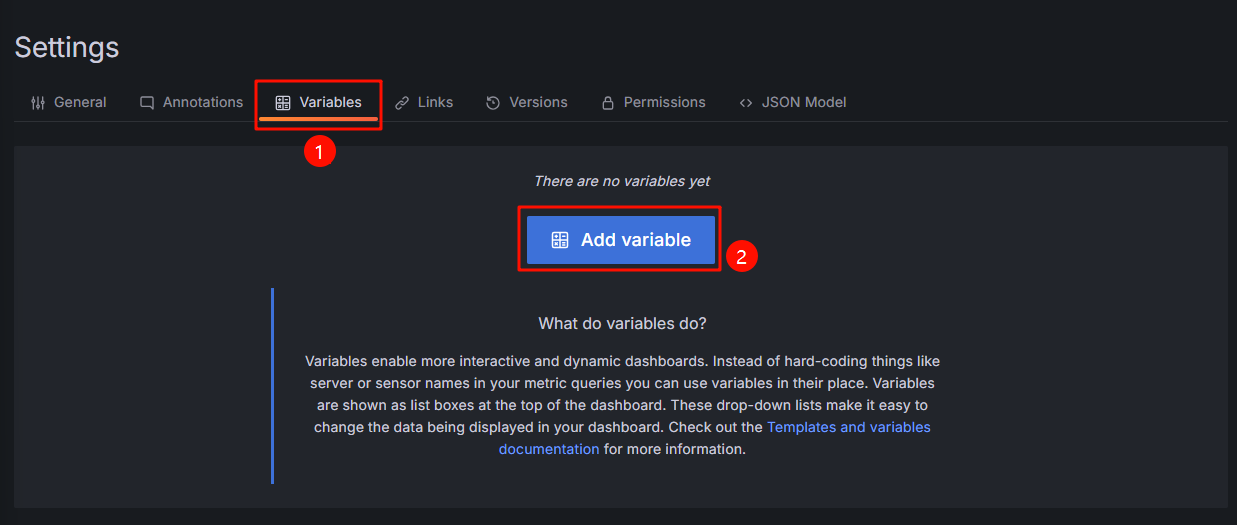
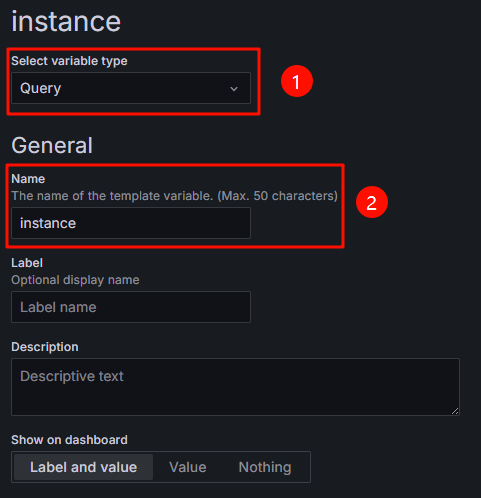
- Configure Select variable type and General. For details, see Figure 8 and Table 2.
Table 2 Configuration example for Select variable type and General Parameter
Example Value
Description
Select variable type
Query
Choose a variable type and select Query to obtain the values of variables in Table 1 from data source queries.
Name
instance
Configure a variable name.
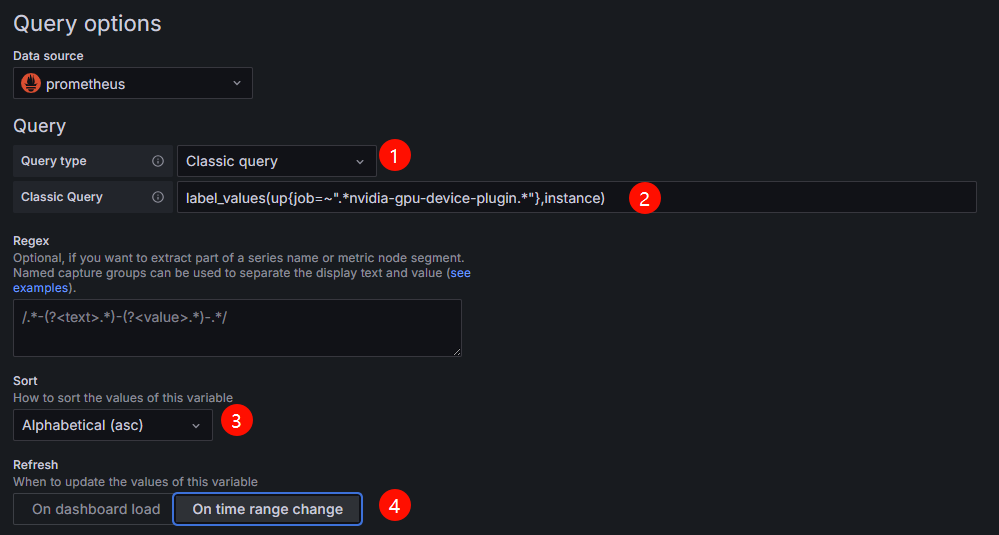
- Configure Query options. For details, see Figure 9 and Table 3.
Table 3 Configuration example for Query options Parameter
Example Value
Description
Query type
Classic query
Select the data query mode and display mode.
In this example, select Classic query, which is a text-based query mode where you can write query statements (such as PromQL) directly to retrieve data.
Classic Query
label_values(up{job=~".*nvidia-gpu-device-plugin.*"},instance)
Enter a Prometheus query statement.
The query statement in this example is used to get the up metrics whose job labels contain nvidia-gpu-device-plugin from Prometheus and extract the instance label values of these metrics.
Sort
Alphabetical (asc)
Select the sorting mode of variable values. You can select a value as needed.
In this example, Alphabetical (asc) is selected, which means the records are sorted in ascending alphabetical order.
Refresh
On time range change
Manage the update timing of variable values to specify when they are retrieved and refreshed from the data source. You can select a value as needed.
In this example, On time range change is selected, meaning variable values are fetched from the data source again when the dashboard's time window changes.
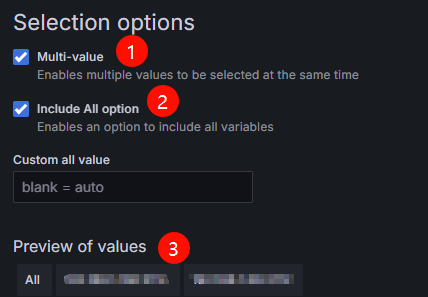
- Configure Selection options. For details, see Figure 10 and Table 4.
Table 4 Configuration example for Selection options Parameter
Example Value
Description
Multi-value
Selected
After this function is enabled, you can select multiple values of a variable.
Include All option
Selected
After this function is enabled, the All option is added to the variable drop-down list, allowing you to select all values with just one click.
Preview of values
-
Variable value of instance. It is the pod name of dp.
Repeat the preceding steps to add variables listed in Table 1 in order. After the variables are configured,
 appears on the right of the variables, showing a message that indicates the variables are not being referenced. These variables will be referenced when you configure the monitoring panel.
appears on the right of the variables, showing a message that indicates the variables are not being referenced. These variables will be referenced when you configure the monitoring panel. - Click Save dashboard in the upper right corner. On the Save dashboard page displayed, click Save to save the variables.
- In the upper right corner of the New dashboard page, click
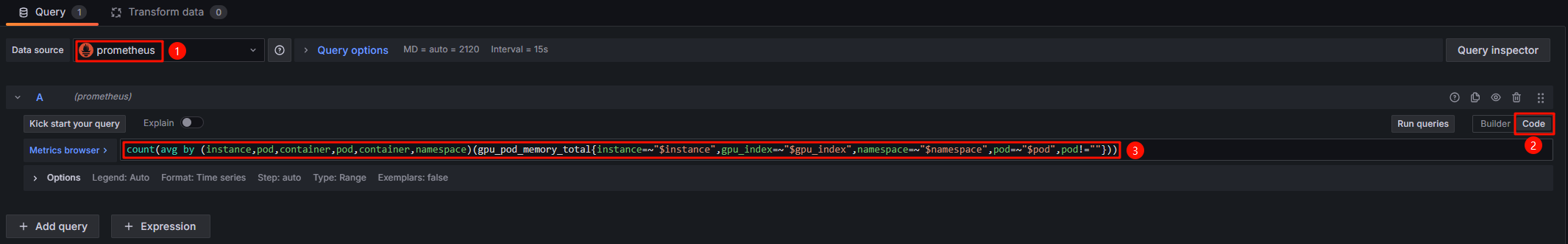
- Configure the Grafana monitoring panels.
The following uses the monitoring panels listed in the below table as examples to describe how to create different types of monitoring panels. For details, see Table 5. You can set up different monitoring panels as needed. For details, see Table 6.
Table 5 Monitoring panels Panel Name
Description
Panel Type
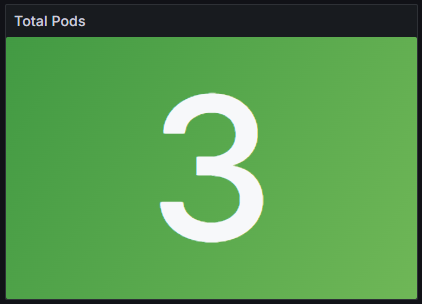
Total Pods
Total number of GPU pods running on non-sharable GPUs
Stat
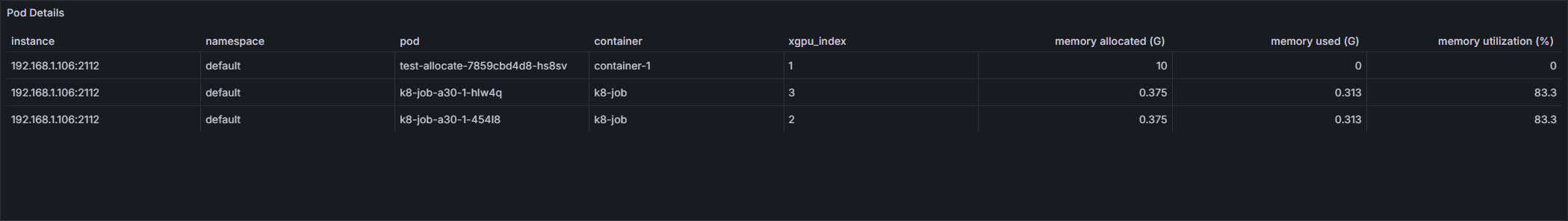
Pod Details
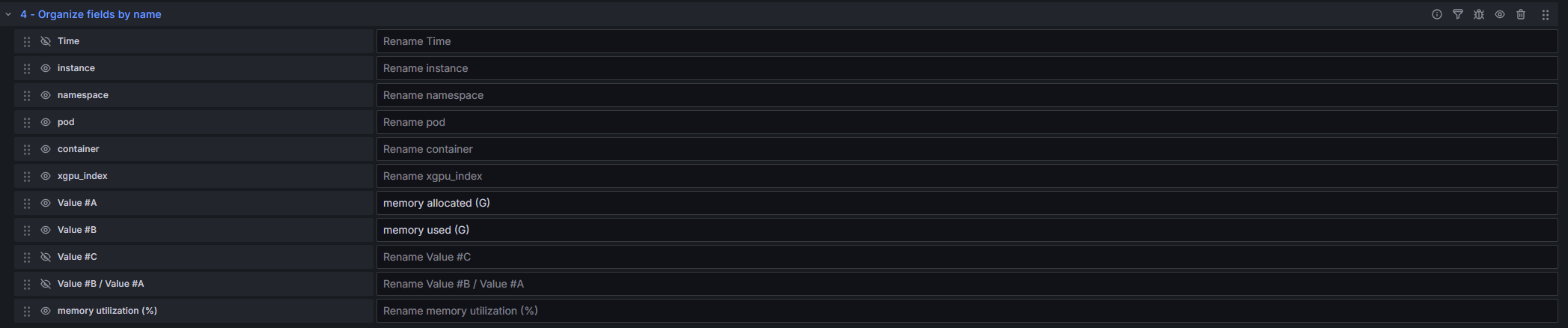
Summary of information such as the pod names, allocated GPU memory, and used GPU memory in a table
Table
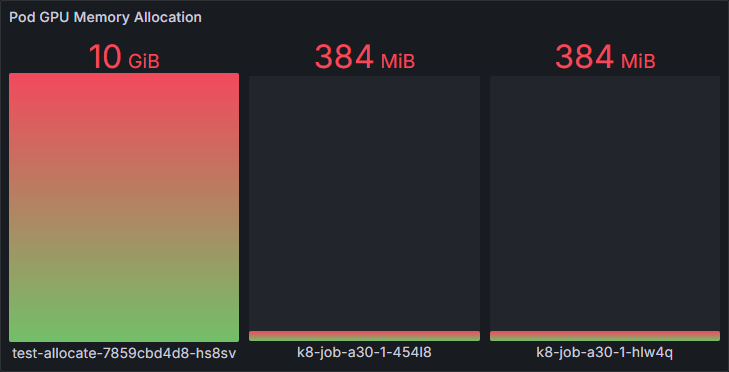
Pod GPU Memory Allocation
Amount of GPU memory allocated to pods of the GPU workloads
Bar gauge
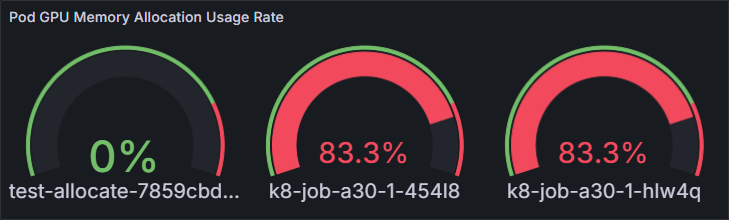
Pod GPU Memory Allocation Usage Rate
Usage of GPU memory allocated to pods of the GPU workloads
Gauge
PromQL Statement
This section provides PromQL statements for each monitoring panel in different dimensions. You can use these statements to create Grafana dashboards in various dimensions.

If the allocated GPU memory or compute is 0, calculating their utilization is meaningless. The PromQL statements here exclude cases where GPU memory or compute allocation is 0 when calculating their utilization.
|
Panel Name |
PromQL Statement |
|---|---|
|
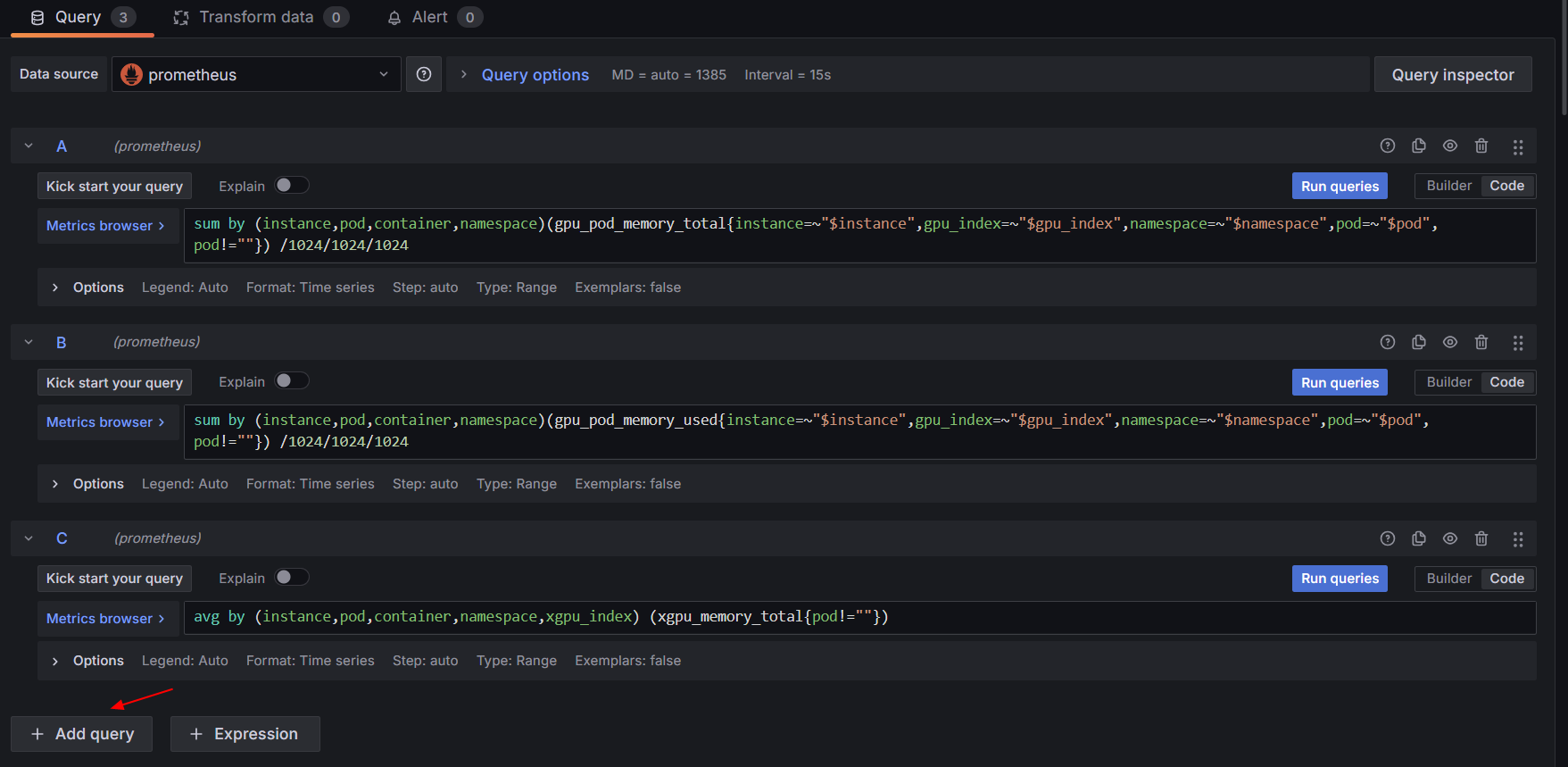
Total Pods |
count(avg by (instance,pod,container,pod,container,namespace)(gpu_pod_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""})) |
|
Pod Details |
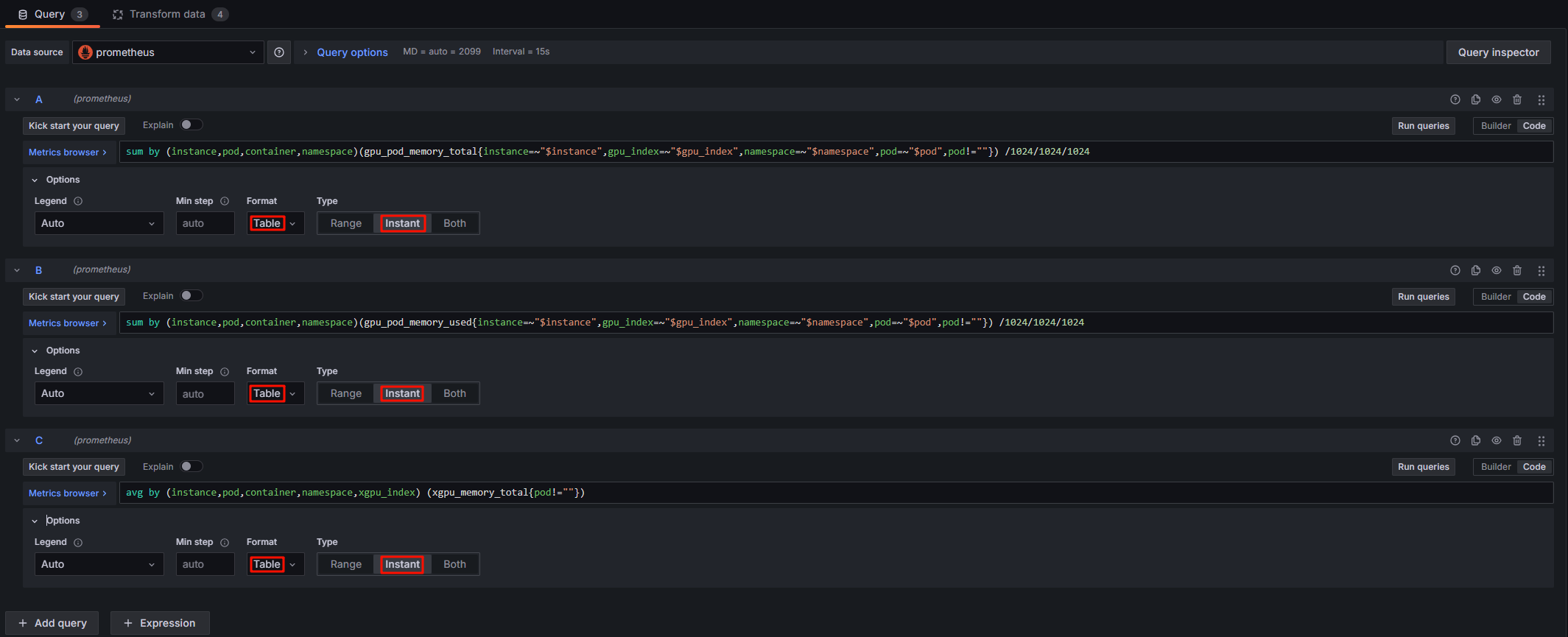
sum by (instance,pod,container,namespace)(gpu_pod_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) /1024/1024/1024 |
|
sum by (instance,pod,container,namespace)(gpu_pod_memory_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) /1024/1024/1024 |
|
|
avg by (instance,pod,container,namespace,xgpu_index) (xgpu_memory_total{pod!=""}) |
|
|
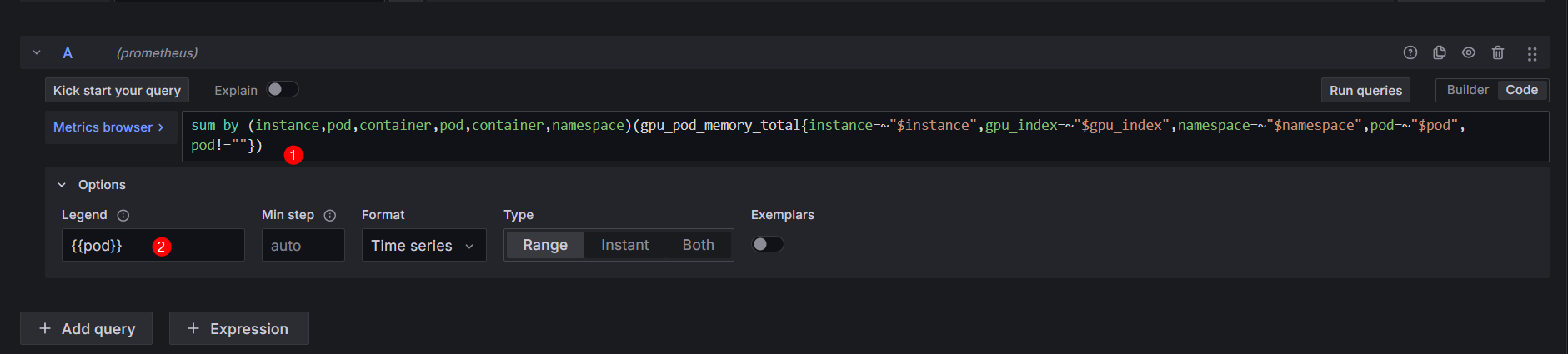
Pod GPU Memory Allocation |
sum by (instance,pod,container,pod,container,namespace)(gpu_pod_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
Used GPU Memory of Pods |
sum by (instance,pod,container,pod,container)(gpu_pod_memory_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
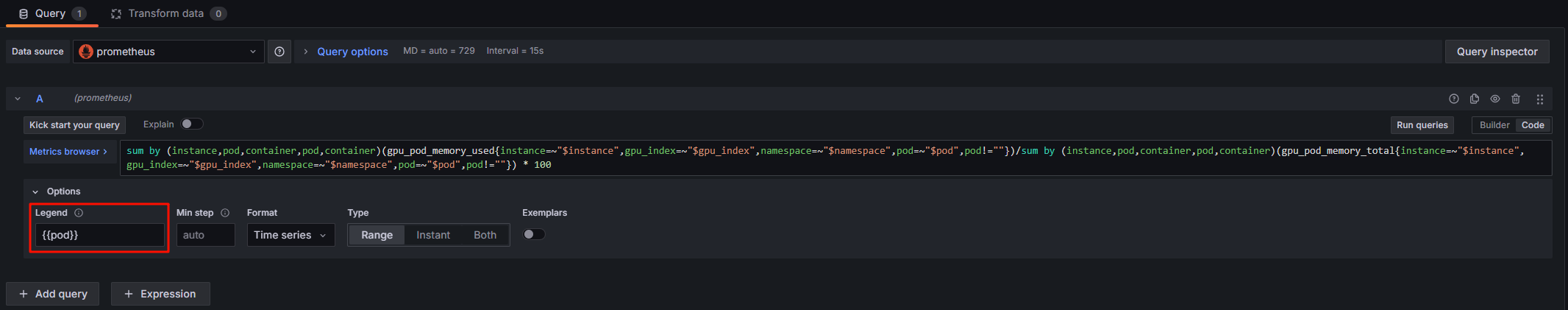
Pod GPU Memory Allocation Usage Rate |
sum by (instance,pod,container,pod,container)(gpu_pod_memory_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""})/sum by (instance,pod,container,pod,container)(gpu_pod_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}!=0) * 100 |
|
GPU Compute Allocated to Pods |
sum by (instance,pod,container,pod,container)(gpu_pod_core_percentage_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
Used GPU Compute of Pods |
sum by (instance,pod,container,pod,container)(gpu_pod_core_percentage_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
Usage of GPU Compute Allocated to Pods |
sum by (instance,pod,container,pod,container)(gpu_pod_core_percentage_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""})/sum by (instance,pod,container,pod,container)(gpu_pod_core_percentage_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}!=0) * 100 |
|
Panel Name |
PromQL Statement |
|---|---|
|
Total GPUs |
count(avg by (instance,gpu_index)(cce_gpu_temperature{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod"})) |
|
GPU Details |
avg by (instance,gpu_index,gpu_id,modelName)(cce_gpu_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod"}) /1024/1024/1024 |
|
sum by (instance,gpu_index,gpu_id,modelName)(gpu_pod_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) /1024/1024/1024 |
|
|
Allocated GPU Memory |
sum by (instance,gpu_index)(gpu_pod_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
Used GPU Memory |
sum by (instance,gpu_index)(gpu_pod_memory_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
Usage of Allocated GPU Memory |
sum by (instance,gpu_index)(gpu_pod_memory_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""})/sum by (instance,gpu_index)(gpu_pod_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}!=0) * 100 |
|
Total GPU Memory |
avg by (instance,gpu_index)(cce_gpu_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod"}) |
|
Allocated GPU Compute |
sum by (instance,gpu_index)(gpu_pod_core_percentage_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
Used GPU Compute |
sum by (instance,gpu_index)(gpu_pod_core_percentage_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
Usage of Allocated GPU Compute |
sum by (instance,gpu_index)(gpu_pod_core_percentage_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""})/sum by (instance,gpu_index)(gpu_pod_core_percentage_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}!=0) * 100 |
|
Total GPU Compute |
count by (instance, gpu_index) (avg by (instance,gpu_index)(cce_gpu_temperature{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod"})) * 100 |
|
Panel Name |
PromQL Statement |
|---|---|
|
Total GPU Nodes |
count(avg by (instance)(cce_gpu_temperature{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod"})) |
|
GPU Node Details |
avg by (instance)(cce_gpu_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod"}) /1024/1024/1024 |
|
sum by (instance)(gpu_pod_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) /1024/1024/1024 |
|
|
GPU Memory Allocated to Nodes |
sum by (instance)(gpu_pod_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
Used GPU Memory of Nodes |
sum by (instance)(gpu_pod_memory_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
Usage of GPU Memory Allocated to Nodes |
sum by (instance)(gpu_pod_memory_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""})/sum by (instance)(gpu_pod_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}!=0) * 100 |
|
Total GPU Memory of Nodes |
sum by (instance) (avg by (instance,gpu_index)(cce_gpu_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod"})) |
|
GPU Compute Allocated to Nodes |
sum by (instance)(gpu_pod_core_percentage_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
Used GPU Compute of Nodes |
sum by (instance)(gpu_pod_core_percentage_used{pod!=""}) |
|
Usage of GPU Compute Allocated to Nodes |
sum by (instance)(gpu_pod_core_percentage_used{pod!=""})/sum by (instance)(gpu_pod_core_percentage_total{pod!=""}!=0) * 100 |
|
Total GPU Compute of Nodes |
count by (instance) (avg by (instance,gpu_index)(cce_gpu_temperature)) * 100 |
|
Panel Name |
PromQL Statement |
|---|---|
|
GPU Memory Allocated to Clusters |
sum (gpu_pod_memory_total{pod!=""}) |
|
Used GPU Memory of Clusters |
sum (gpu_pod_memory_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
Usage of GPU Memory Allocated to Clusters |
sum (gpu_pod_memory_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""})/sum (gpu_pod_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) * 100 |
|
Total GPU Memory of Clusters |
sum (avg by (instance,gpu_index)(cce_gpu_memory_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod"})) |
|
GPU Compute Allocated to Clusters |
sum (gpu_pod_core_percentage_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
Used GPU Compute of Clusters |
sum (gpu_pod_core_percentage_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) |
|
Usage of GPU Compute Allocated to Clusters |
sum (gpu_pod_core_percentage_used{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""})/sum (gpu_pod_core_percentage_total{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod",pod!=""}) * 100 |
|
Total GPU Compute of Clusters |
count(avg by (instance,gpu_index)(cce_gpu_temperature{instance=~"$instance",gpu_index=~"$gpu_index",namespace=~"$namespace",pod=~"$pod"})) * 100 |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot