Database Proxy is a network proxy service that sits between TaurusDB and applications. It is used to handle all requests from the applications to access TaurusDB instances.
Read/write splitting means that read and write requests are automatically forwarded through database proxy addresses. After creating a TaurusDB instance, you can create a proxy instance. With the proxy address, write requests are automatically forwarded to the primary node and read requests are forwarded to each node based on the routing policy of the proxy instance, offloading the read load from the primary node.
Proxy instances are free.
Basic Concepts
Proxy Address
After buying a proxy instance, you can view the proxy address on the Database Proxy page. The proxy instance sends write requests to the primary node and read requests to read replicas through this address.
Proxy Mode
There are read/write, read-only (TP), and read-only (AP) proxy modes. The read/write attribute processing logic varies depending on the proxy mode. For details, see Table 1.
- Read/Write: All write requests are routed only to the primary node, and all read requests are routed to the selected nodes based on the read weights or active connections.
- Read-only (TP): All read requests are routed to the selected read replicas based on the read weights or active connections. The read requests will not be routed to the primary node.
- Read-only (AP): All read requests are routed to the selected read replicas and HTAP nodes based on the read weights.
Table 1 Read/Write attribute processing logic
|
Proxy Mode |
Routing Policy |
Weight of Primary Node |
Normal Case |
All Read Replicas Are Faulty |
|
Read-only (TP) |
Weighted
Load balancing |
Not configurable |
The primary node does not process read-only requests.
Proxy address: readable but not writable |
The primary node does not process read-only requests.
Proxy address: connection error |
|
Read-only (AP) |
Weighted |
Not configurable |
The primary node does not process read-only requests.
Proxy address: readable but not writable |
The primary node does not process read-only requests.
Proxy address: connection error |
|
Read/Write |
Load balancing |
Assigned by system |
Primary node: readable and writable
Proxy address: readable and writable |
Primary node: readable and writable
Proxy address: readable and writable |
|
Weighted |
> 0 |
Primary node: readable and writable
Proxy address: readable and writable |
Primary node: readable and writable
Proxy address: readable and writable |
|
= 0 |
Primary node: not readable but writable
Proxy address: readable and writable |
Primary node: readable and writable
Proxy address: readable and writable |
Transaction Splitting
With transaction splitting enabled for a proxy instance, the proxy instance can route read requests prior to write operations in a transaction to read replicas, reducing the load on the primary node.
For more information about transaction splitting, see Enabling Transaction Splitting for a Proxy Instance.
Connection Pool
Proxy instances provide session-level connection pools, which help reduce the database load caused by frequent establishment of short connections.
For more information about connection pools, see Enabling the Connection Pool for a Proxy Instance.
Routing Policy
Proxy instances support weighted and load balancing routing policies.
- Weighted: Read requests are assigned to nodes based on the weights you specify.
- Load balancing: Read requests are assigned to nodes with fewer active connections. In the load balancing policy, you do not need to configure the weights of nodes.
For more information about routing policies, see Changing the Routing Policy of a Proxy Instance.
How Read/Write Splitting Works
You can create one or more proxy instances for your TaurusDB instance to enable read/write splitting.
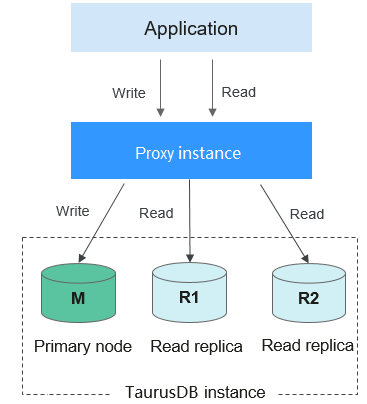
If your TaurusDB instance has only one proxy instance, applications connect to the proxy instance through the proxy address. Write requests are forwarded to the primary node and read requests to the primary node or read replicas based on the routing policy you specify.
Figure 1 Read/write splitting with only one proxy instance
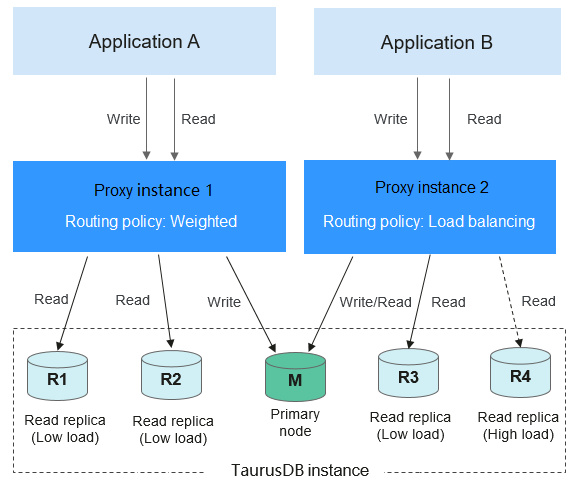
To isolate workloads from one another, you can create up to four proxy instances for a TaurusDB instance. Different applications can connect to different proxy instances as required. The associated read replicas of the proxy instances process read requests from different applications for workload isolation.
Figure 2 Read/write splitting with multiple proxy instances
Read/Write Splitting Advantages
- Compared with manual read/write splitting in applications, the read/write splitting using proxy addresses features flexible scale-out and low maintenance costs.
- Read requests are distributed to your read replicas based on weights to balance your database traffic and improve resource utilization.
- A proxy instance routes read requests of an application only to its associated read replicas to isolate workloads.
- By default, proxy instances provide overload protection to prevent server OOM (out of memory) due to heavy pressure when you perform operations on large result sets. This function is enabled by default and does not need to be configured separately. The pressure caused by the slow kernel depends on flow control.
Request Routing Rules
Write Requests Sent Only to the Primary Node
- INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE
- All DDL operations (such as table/database creation, table/database deletion, table structure change, and permission change)
- All requests in transactions (But if transaction splitting is enabled, some read requests in transactions may be sent to read replicas. For details, see Enabling Transaction Splitting for a Proxy Instance.)
- User-defined functions
- Stored procedures
- EXECUTE statements
- Multi-statement requests
- Requests that use temporary tables
- All changes to user variables
- KILL in SQL statements (not the kill command)
- set names command in prepared statements
Read Requests Sent Only to the Primary Node
- If query statements are in transactions, the transaction requests are routed to the primary node. If set autocommit=0 is added before a query statement, the query statement is routed to the primary node as a transaction.
- If all read replicas are abnormal or the read weights allocated to the read replicas are 0, requests will be routed to the primary node. You can set read weights for the primary node and read replicas after read/write splitting is enabled.
- When running SQL statements:
- If multi-statements (for example, insert xxx;select xxx) are executed, all subsequent requests will be routed to the primary node. To restore read/write splitting, disconnect your application from your instance and then connect it back again.
- Read operations with locks (for example, SELECT for UPDATE) will be routed to the primary node.
- When /*FORCE_MASTER*/ is used, requests will be routed to the primary node.
- If the HANDLER statement is executed, all subsequent requests will be routed to the primary node. To restore read/write splitting, disconnect your application from your instance and then connect it back again.
- SELECT last_insert_id()
- All queries of user variables
Requests Sent Either to the Primary Node or a Read Replica
- SELECT not in a transaction
- The COM_STMT_EXECUTE command
Requests Always Sent to All Nodes
- Changes to all system variables
- The USE command
Precautions
Table 2 Precautions for proxy instances
|
Category |
Precaution |
|
Version constraints |
- If the kernel version of your TaurusDB instance is one of the following, proxy instances cannot be created:
- From 2.0.26.2 to 2.0.28.3
- 2.0.29.1
- If the kernel version of your TaurusDB instance is earlier than 2.0.42.230601, only one proxy instance can be created.
- If the kernel version of your TaurusDB instance is 2.0.42.230601 or later, up to four proxy instances can be created.
For details about how to check the kernel version, see How Can I Check the Version of a TaurusDB Instance? |
|
Unsupported functions |
- Proxy instances do not support compression protocols.
- Proxy instances do not support the READ-UNCOMMITTED transaction isolation level.
- Proxy instances only support permission verification at the database level, not at the individual table level.
|
|
Usage constraints |
- Read/write splitting can be enabled only when at least one read replica is created.
- After read/write splitting is enabled, the database port of your TaurusDB instance cannot be changed.
- If multi-statements are executed, all subsequent requests will be routed to the primary node. To restore the read/write splitting function, disconnect the connection from your applications and establish a connection again.
- When a proxy address is used, all transaction requests are routed to the primary node (you can use transaction splitting to route read requests prior to write operations in a transaction to read replicas). The non-transaction read consistency is not ensured. To ensure read consistency, encapsulate the read requests into a transaction.
- When a proxy address is used, you can run show processlist command on the proxy instance or TaurusDB instance. If show processlist is executed on a proxy instance, only the services delivered through proxy nodes are displayed.
- If a proxy node is abnormal, running show processlist or Kill on the proxy instance may take a long time, but services are not affected.
- After a proxy node is deleted, services on the deleted proxy node may be displayed when show processlist is executed on the proxy instance.
- If Kill is executed on the proxy instance, error information such as timeout may be displayed occasionally. You can run show processlist again to check whether the services are killed successfully.
- If a proxy node is abnormal, there may be frame freezing for 2 seconds when you run show processlist on the proxy instance. The results will still be returned.
- To prevent a proxy instance from consuming too many resources to parse SQL statements, a maximum of 100 SQL statements can be committed and executed in a batch, and the size of a concatenate SQL statement cannot exceed 100 MB.
|
|
HTAP analysis |
- Consistency levels and connection pools are not supported.
- Only the weighted routing policy is supported.
- Only the read/write proxy mode is supported.
|