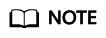After creating a TaurusDB instance, you can create a proxy instance. With the proxy address, write requests are automatically forwarded to the primary node, and read requests are forwarded to each node based on the routing policy of the proxy instance, offloading the read load from the primary node.
This section describes how to create a proxy instance for read/write splitting.
Step 1: Create a Proxy Instance
Step 2: Perform User Authentication
Step 3: Check Security Group Rules
Step 4: Use the Proxy Address to Connect to Your TaurusDB Instance
Step 5: Verify Read/Write Splitting
Constraints
Before creating a proxy instance, you need to ensure that:
- You have purchased a TaurusDB instance.
- You have understood the precautions. For details, see Precautions.
Procedure
Step 1: Create a Proxy Instance
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose Database Proxy.
- Click Create Proxy Instance.
- On the displayed page, set required parameters and click Next.
Figure 1 Creating a proxy instance
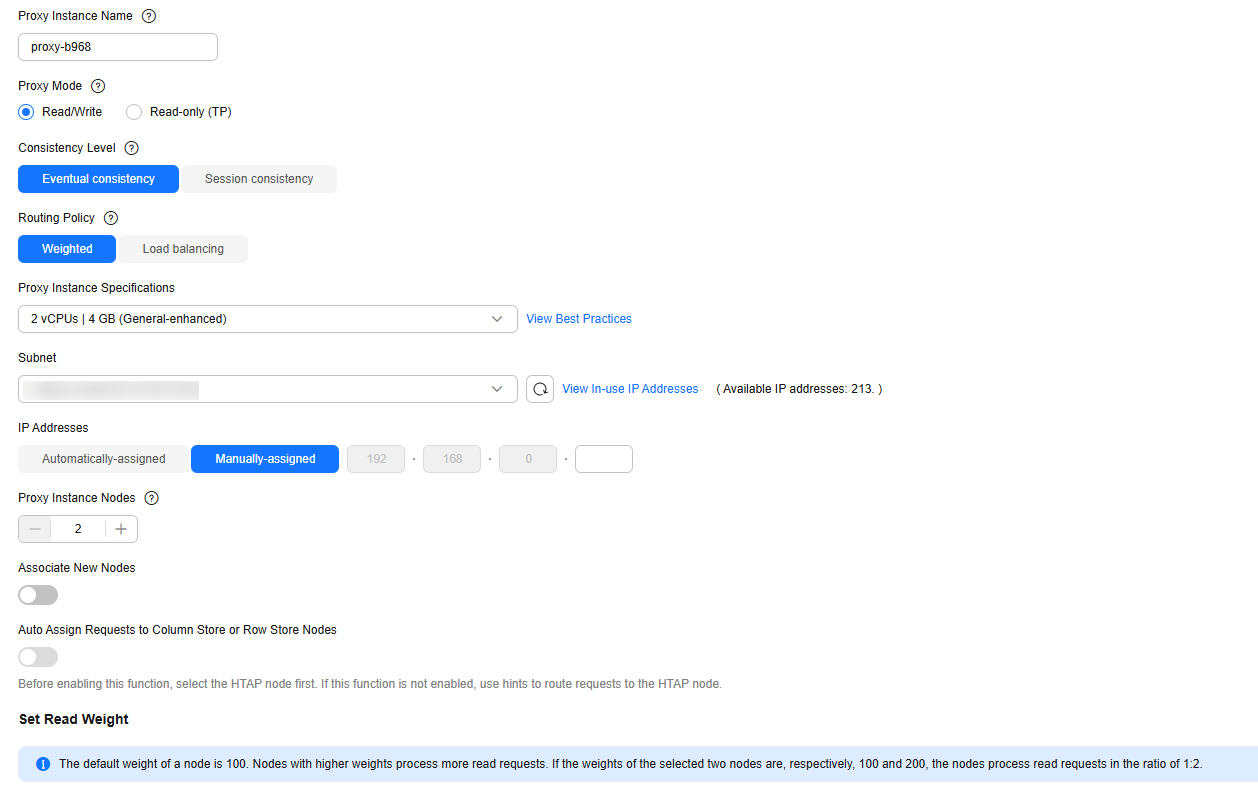
Table 1 Parameter description
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Proxy Instance Name |
The name can consist of 4 to 64 characters and must start with a letter. Only letters (case-sensitive), digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_) are allowed. |
|
Proxy Mode |
You can select Read/Write, Read-only (TP), or Read-only (AP) as needed.
- Read/Write: All write requests are forwarded only to the primary node, and all read requests are forwarded to the selected nodes based on the read weights or active connections. The default read weight of a node is 100.
- Read-only (TP): Write requests are not forwarded to any node. All read requests are forwarded to the selected read replicas based on the read weights or active connections. The read requests are not forwarded to the primary node, even if the primary node is selected.
- Only read requests are supported in the read-only (TP) mode. If write requests are forwarded to any node, an error message is displayed.
- DDL, DML, and temporary table operations are not supported in the read-only (TP) mode.
- Read-only (AP): Write requests are not forwarded to any node. All read requests are forwarded to the selected nodes based on the read weights. This mode is in the OBT phase. To use it, submit a service ticket.
- Only the weighted routing policy is supported in the read-only (AP) mode. The weights of AP nodes cannot be all 0.
- Binlog pull is not supported.
- Session consistency is not supported. Only eventual consistency is supported.
- Transaction splitting is not supported.
- The feature for assigning requests to row and column store nodes is not supported.
- Session-level connection pooling is not supported.
- ALT is not supported.
- New nodes cannot be automatically associated with a proxy instance.
- Multi-primary instances do not support the read-only (AP) mode.
|
|
Consistency Level |
The consistency level can only be configured when the kernel version of your TaurusDB instance is 2.0.28.1 or later. For details about how to check the kernel version, see How Can I Check the Version of a TaurusDB Instance?
Value:
- Eventual consistency
After a proxy instance is created, requests for SELECT operations are routed to different nodes based on their read weights. Because there is a replication latency between the primary node and each read replica and the replication latency varies for different read replicas, the result returned by each SELECT statement may be different when you repeatedly execute a SELECT statement within a session. In this case, only eventual consistency is ensured.
To offload read requests from the primary node to read replicas, you can select eventual consistency.
- Session consistency
To eliminate data inconsistencies caused by eventual consistency, session consistency is provided. Session consistency ensures the result returned by each SELECT statement in a session is the data that was updated after the last write request.
To use session consistency, the kernel version of your proxy instance must be 2.7.4.0 or later.
- Global consistency
Global consistency ensures data consistency in different sessions. It means that once data is written, you can immediately query the updated data.
You can select global consistency when there are more read operations than write operations.
Global consistency is only available when the TaurusDB instance kernel is 2.0.57.240900 or later and the proxy instance kernel is 2.25.06.000 or later.
For more information about consistency levels, see Changing the Consistency Level of a Proxy Instance.
|
|
Routing Policy |
Value:
For more information about routing policies, see Changing the Routing Policy of a Proxy Instance. |
|
Proxy Instance Specifications |
You can select the proxy instance specifications as needed.
- Kunpeng general computing-plus: 2 vCPUs | 4 GB, 4 vCPUs | 8 GB, and 8 vCPUs | 16 GB
- General-enhanced: 2 vCPUs | 4 GB, 4 vCPUs | 8 GB, and 8 vCPUs | 16 GB
|
|
Subnet |
This function is in the OBT phase. To use it, submit a service ticket.
When creating a proxy instance, you can specify a subnet for the proxy instance. If the subnet where the TaurusDB instance is associated with is a secondary CIDR block, you can only select the same subnet as the TaurusDB instance for the proxy instance. |
|
IP Addresses |
IPv4 addresses can be automatically or manually assigned.
- Automatically-assigned: When you create a proxy instance, TaurusDB automatically assigns an IPv4 proxy address.
- Manually-assigned: You can enter an idle IPv4 address within the subnet CIDR block as the proxy address of the TaurusDB instance. You can click View In-use IP Addresses to view the IP addresses that have been used.
|
|
Proxy Instance Nodes |
You can enter an integer from 2 to 16. The default value is 2.
Number of recommended proxy instance nodes = (Number of vCPUs of the primary node + Total number of vCPUs of all read replicas)/(4 x Number of vCPUs of the proxy instance), rounded up. |
|
Associate New Nodes |
After Associate New Nodes is enabled, new read replicas will be automatically associated with the proxy instance. |
|
New Node Weight |
If Routing Policy is Weighted, you need to configure read weights for the new nodes. The default weight of a node is 100. Nodes with higher weights process more read requests. |
|
Auto Assign Requests to Column Store or Row Store Nodes (OBT) |
After this function is enabled, a proxy instance distributes requests based on the actual execution cost of a SQL statement to maximize the query performance. For details about the usage and constraints, see Enabling Request Distribution Among Row Store and Column Store Nodes for Complex OLAP Queries.
This function is in the OBT phase. To use it, submit a service ticket. |
|
Database Nodes |
Select nodes to be associated with the proxy instance for processing read requests. The nodes displayed in the list include TaurusDB nodes (the primary node and read replicas) and HTAP nodes (BE nodes and FE nodes).
- If Routing Policy is Load balancing, you do not need to configure read weights for selected nodes. Read requests are forwarded to nodes with fewer active connections.
- If Routing Policy is Weighted, you need to configure read weights of the primary node and read replicas. Read requests are forwarded to nodes based on the weights you specify.
For example, read weights assigned to one primary node and two read replicas are 100, 200, and 200, respectively.
In the read/write mode, the primary node and two read replicas process read requests in the ratio of 1:2:2. The primary node processes 20% of read requests, and each read replica processes 40% of read requests. Write requests are automatically routed to the primary node.
In the read-only mode, the read weight of the primary node does not take effect, and the two read replicas process 50% of read requests, respectively.
|
- View the proxy instance and associated nodes.
After the proxy instance creation is complete, you can view the created proxy instance on the Database Proxy page.
Figure 2 Viewing the created proxy instance

Click Basic Information in the navigation pane. Click  in the upper right corner of the page and select View Instance Topology. In the instance topology, you can view the database nodes associated with the proxy instance. You can move the pointer to a node name to view its details.
in the upper right corner of the page and select View Instance Topology. In the instance topology, you can view the database nodes associated with the proxy instance. You can move the pointer to a node name to view its details.
Figure 3 Viewing information about nodes associated with a proxy instance

Step 2: Perform User Authentication
Before using a proxy instance to connect to your TaurusDB instance, ensure that the current database account has the permissions to access the proxy address, or the proxy instance cannot connect to your TaurusDB instance.
You can perform the following steps to check the permissions and grant the account the permissions to access the proxy address.
- Connect to your TaurusDB instance through DAS (recommended).
- On the Instances page, locate the target instance and click Log In in the Operation column.
Alternatively, on the Instances page, click the instance name. On the displayed Basic Information page, click Log In in the upper right corner.
- Enter the login username and password and click Test Connection.
For details about other connection methods, see Connection Methods.
- Run the following SQL statement to check whether host of your account contains a proxy address.
To obtain the proxy address, click the target TaurusDB instance. In the navigation pane, choose Database Proxy. In the proxy instance list, view the proxy address.
SELECT user,host FROM mysql.user;

If the address is %, the host contains all CIDR blocks.
- If the host does not contain the CIDR block where the proxy instance is associated with, assign the remote access permissions to the host.
For example, if you want to connect to the TaurusDB instance using 192.168.0 as user root, set Host to 192.168.% on the DAS user management page. For details, see Editing a User.
Figure 4 Configuring a host IP address

Step 3: Check Security Group Rules
You need to ensure that the inbound and outbound rules allow access from the proxy address. The default port number is 3306.
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, click the instance name to go to the Basic Information page.
- In the Network Information area, click the security group name in the Security Group field.
- On the Inbound Rules tab, check whether access through port 3306 is allowed by default.
Figure 5 Allowing access through port 3306
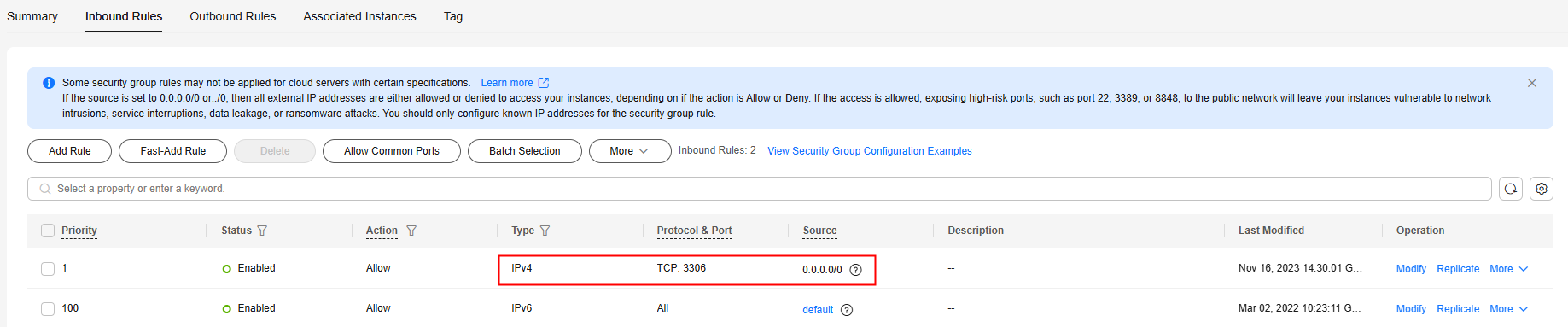
If there is no such a rule, click Fast-Add Rule. In the displayed dialog box, select MySQL (3306) and click OK.
Figure 6 Fast adding port 3306
Step 4: Use the Proxy Address to Connect to Your TaurusDB Instance
- View the proxy address and port on the TaurusDB console.
Click the TaurusDB instance name. In the navigation pane, choose Database Proxy. In the proxy instance list, view the proxy address and port.
Figure 7 Viewing a proxy address and port

- Log in to an ECS.
For details, see Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
- Run the following command to connect to the TaurusDB instance through the proxy address:
mysql -h host -P port -u userName -p
Example:
mysql -h 192.168.0.61 -P 3306 -u root -p
Enter the password of the database account if the following information is displayed:
Enter password:
Table 2 Parameter description
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
host |
Proxy address obtained in 1. |
|
port |
Port obtained in 1. |
|
userName |
Username, that is, the TaurusDB database administrator account. The default value is root. |
Step 5: Verify Read/Write Splitting
You can run the show last route command to check the routing result after you perform a read operation.
The following is an example.
- After connecting to your TaurusDB instance through the proxy address, perform a read operation.
Example:
select 1;
Figure 8 Performing a read operation

- Run the following command to view the routing result of the read operation in 1:
show last route;
Figure 9 Viewing a query result

The IP address in the command output is the IP address of the node to which the read operation is routed. Read operations are routed to the primary node or read replicas based on the specified routing policy.
Do not include show last route in service code or multi-statement requests.