Interconnecting LakeFormation with a DLI Cluster
You can create databases and tables on the management console or using SQL statements.
For details about how to create a database and table using SQL statements, see Creating a Database, Creating an OBS Table, and Creating a DLI Table.
This section describes how to create a data catalog, database, and table on the management console.
- Views can be created only by using SQL statements, not through the Create Table page.
- For Hudi tables created using SQL statements, you need to configure Hive synchronization parameters before they can be checked in the databases and tables on the DLI management console.
Precautions
When creating a data catalog, database, or table, you have required permissions by default. You need to grant permissions to other users so that they can view the created data catalog, database, or table.
Creating a Data Catalog
The DLI management console provides the DLI data catalog by default. You can also follow this section's instructions to create a connection to a LakeFormation catalog on the DLI management console. Once created, the LakeFormation catalog will be displayed under the data catalog list on the DLI management console.
- Before creating a connection to a LakeFormation catalog on DLI, ensure that a data catalog has been created on the LakeFormation management console.
- Log in to the LakeFormation management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Metadata > Catalog.
- On the displayed page, click Create.
Set catalog instance parameters as needed.
For parameter settings and descriptions, see Creating a Catalog.
- Once created, you can view information about the created catalog on the Catalog page.
DLI can only connect to the default LakeFormation instance. Set the instance in LakeFormation as the default to ensure successful connection.
- Create a data catalog on the DLI management console.
On the DLI management console, you need to create a connection to a LakeFormation catalog to enable access to the catalog stored within a LakeFormation instance when submitting jobs on DLI.
You can create data catalog connections on three pages of the DLI management console, and the created data catalog connections will be visible under the Catalog tab of the SQL Editor page.
- On the Catalog tab of the SQL Editor page, click
 to create a connection to a LakeFormation catalog.
to create a connection to a LakeFormation catalog. - On the Flink job editing page, click
 next to Catalog Name to create a connection to a LakeFormation catalog. (Only Flink 1.17 or later supports configuring data catalogs.)
next to Catalog Name to create a connection to a LakeFormation catalog. (Only Flink 1.17 or later supports configuring data catalogs.) - On the Spark job editing page, click
 next to Catalog Name to create a connection to a LakeFormation catalog. (Only Spark 3.3.1 supports configuring data catalogs.)
next to Catalog Name to create a connection to a LakeFormation catalog. (Only Spark 3.3.1 supports configuring data catalogs.)
You can only create one mapping for each data catalog in LakeFormation.
For example, a user creates a mapping named catalogMapping1 in DLI, which corresponds to the data catalog catalogA in LakeFormation. Once created, you cannot create a mapping to catalogA in the same project space.
Take creating a data catalog connection on the Catalog tab of the SQL Editor page as an example:- Log in to the DLI management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose SQL Editor.
- On the SQL editor page, select a data catalog under Catalog.
- Click
 to create a data catalog.
to create a data catalog. - In the Create Catalog dialog box, set data catalog parameters.
Table 1 Data catalog parameters Parameter
Mandatory
Description
External Catalog Name
Yes
Catalog name of the default LakeFormation instance.
Type
Yes
Currently, the only available option is LakeFormation.
This option is fixed and does not need to be selected.
Catalog Name
Yes
Catalog mapping name used in DLI. When running SQL statements, you need to specify the catalog mapping to identify the external metadata to be accessed. You are advised to set this parameter to the same value as External Catalog Name.
Currently, DLI can only connect to the data catalog of the default LakeFormation instance.
Description
No
Description of the data catalog.
- Click OK.
- After the data catalog is created, the connection status of the data catalog is displayed in the data catalog list.
- Blinking
 indicates that the data catalog is being created.
indicates that the data catalog is being created.  indicates that the data catalog has been created and the data catalog connection has been activated.
indicates that the data catalog has been created and the data catalog connection has been activated. indicates that the data catalog fails to be created. In this case, it is advised to delete the current data connection and create a data catalog again.
indicates that the data catalog fails to be created. In this case, it is advised to delete the current data connection and create a data catalog again.
- Blinking
- On the Catalog tab of the SQL Editor page, click
Creating a Database
- You can create a database on either the Data Management page or the SQL Editor page.
- To create a database on the Data Management page:
- On the left of the management console, choose Data Management > Databases and Tables.
- In the upper right corner of the Databases and Tables page, click Create Database to create a database.
- To create a database on the SQL Editor page:
- On the left of the management console, click SQL Editor.
- In the navigation pane on the left, click
 next to Databases.
next to Databases.
- To create a database on the Data Management page:
- In the displayed Create Database dialog box, specify Name and Description by referring to Table 2.
Figure 1 Creating a database
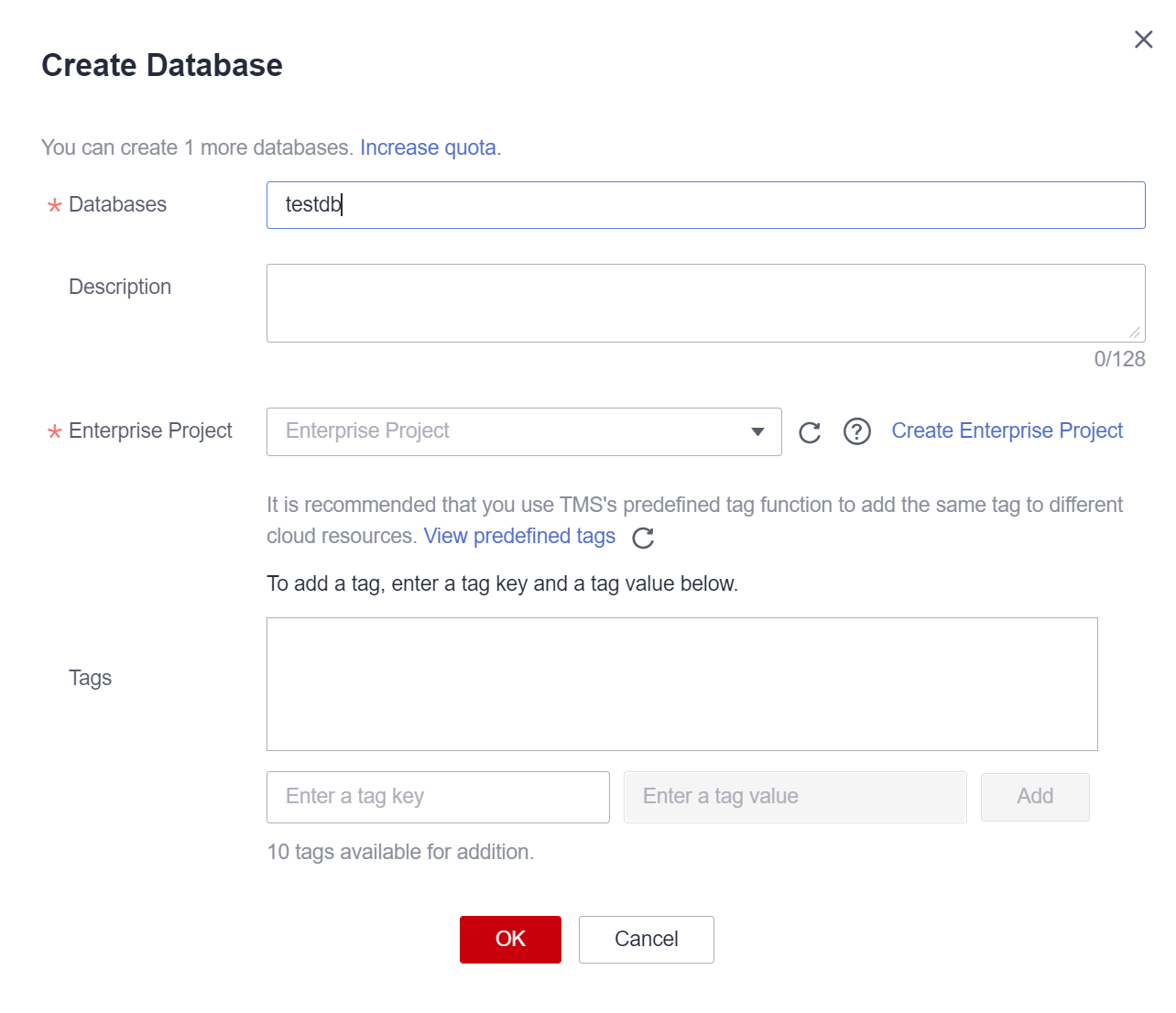
Table 2 Description Parameter
Description
Database Name
- Only numbers, letters, and underscores (_) are allowed. The value cannot contain only numbers or start with an underscore (_).
- The database name is case insensitive and cannot be left blank.
- The value can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
NOTE:The default database is a built-in database. You cannot create the default. database.
Enterprise Project
If the created queue belongs to an enterprise project, you can select the corresponding enterprise project.
Enterprise projects let you manage cloud resources and users by project.
For how to set enterprise projects, see Enterprise Management User Guide.
NOTE:This parameter is displayed only for users who have enabled the Enterprise Management Service.
Description
Description of a database.
Tags
Tags used to identify cloud resources. A tag includes the tag key and tag value. If you want to use the same tag to identify multiple cloud resources, that is, to select the same tag from the drop-down list box for all services, you are advised to create predefined tags on the Tag Management Service (TMS).
If your organization has configured tag policies for DLI, add tags to resources based on the policies. If a tag does not comply with the tag policies, resource creation may fail. Contact your organization administrator to learn more about tag policies.
For details, see Tag Management Service User Guide.
NOTE:- A maximum of 20 tags can be added.
- Only one tag value can be added to a tag key.
- The key name in each resource must be unique.
- Tag key: Enter a tag key name in the text box.
NOTE:
A tag key can contain a maximum of 128 characters. Only letters, numbers, spaces, and special characters (_.:+-@) are allowed, but the value cannot start or end with a space or start with _sys_.
- Tag value: Enter a tag value in the text box.
NOTE:
A tag value can contain a maximum of 255 characters. Only letters, numbers, spaces, and special characters (_.:+-@) are allowed.
- Click OK.
After a database is created, you can view and select the database for use on the Databases and Tables page or SQL Editor page.
Creating a Table
Before creating a table, ensure that a database has been created.
- You can create a table on either the Databases and Tables page or the SQL Editor page.
Datasource connection tables, such as View tables, HBase (CloudTable/MRS) tables, OpenTSDB (CloudTable/MRS) tables, GaussDB(DWS) tables, RDS tables, and CSS tables, cannot be created. You can use SQL to create views and datasource connection tables. For details, see Data Lake Insight SQL Syntax Reference.
- To create a table on the Data Management page:
- On the left of the management console, choose Data Management > Databases and Tables.
- On the Databases and Tables page, select the database for which you want to create a table. In the Operation column, click More > Create Table to create a table in the current database.
- To create a table on the SQL Editor page:
- On the left of the management console, click SQL Editor.
- In the navigation pane of the displayed SQL Editor page, click Databases. You can create a table in either of the following ways:
- Click a database name. In the Tables area, click
 on the right to create a table in the current database.
on the right to create a table in the current database. - Click
 on the right of the database and choose Create Table from the shortcut menu to create a table in the current database.
on the right of the database and choose Create Table from the shortcut menu to create a table in the current database.
- Click a database name. In the Tables area, click
- To create a table on the Data Management page:
- In the displayed Create Table dialog box, set parameters as required.
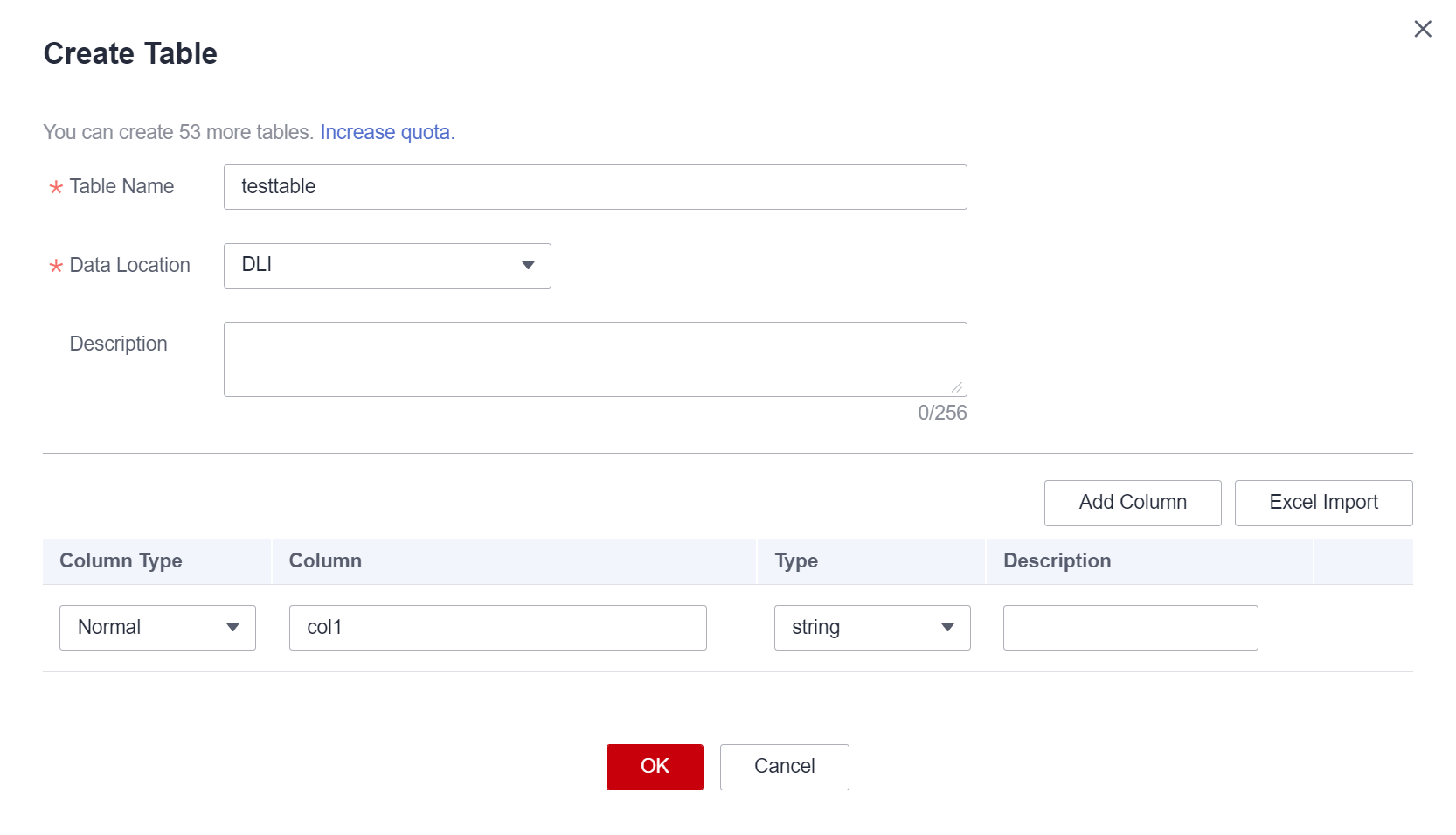
- If you set Data Location to DLI, set related parameters by referring to Table 3.
Figure 2 Creating a DLI table
- If you set Data Location to OBS, set related parameters by referring to Table 3 and Table 4.
When there are both a folder and a file with the same name in the OBS directory, creating an OBS table pointing to that path will prioritize the file over the folder.
Figure 3 Creating an OBS table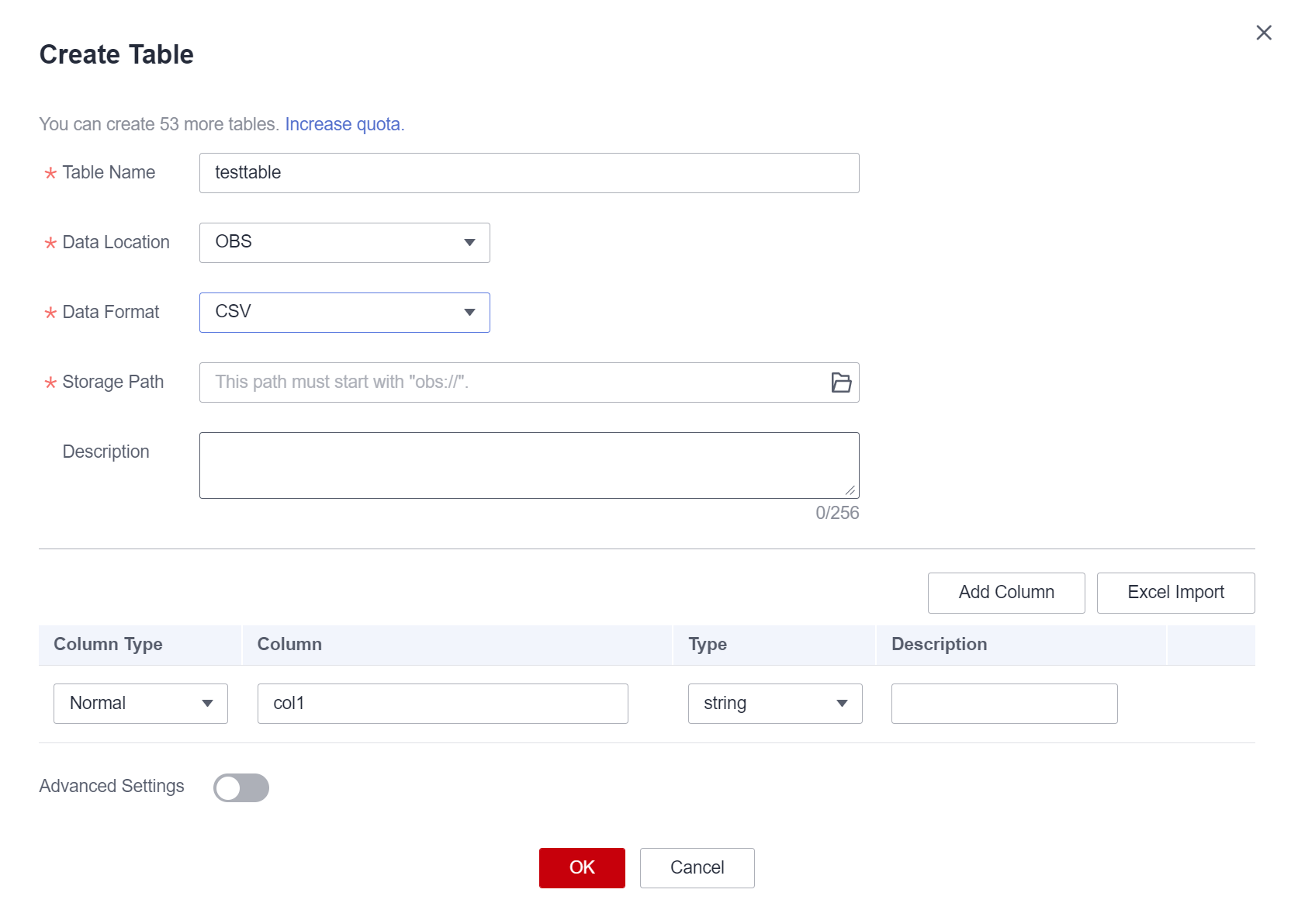
Table 3 Common parameters Parameter
Description
Example
Table Name
- Only numbers, letters, and underscores (_) are allowed. The value cannot contain only numbers or start with an underscore (_).
- The table name is case insensitive and cannot be left unspecified.
- The table name can contain the dollar sign ($). An example value is $test.
- The value can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
table01
Data Location
Data storage location. Currently, DLI and OBS are supported.
DLI
Description
Description of the table.
-
Column Type
Available values: Normal or Partition
Normal
Column
Name of a column in a table. The column name must contain at least one letter and can contain underscores (_). It cannot contain only numbers.
You can select Normal or Partition. Partition columns are dedicated to partition tables. User data is partitioned to improve query efficiency.
NOTE:The column name is case-insensitive and must be unique.
name
Type
Data type of a column. This parameter corresponds to Column Name.
- string: The data is of the string type.
- int: Each integer is stored on four bytes.
- date: The value ranges from 0000-01-01 to 9999-12-31.
- double: Each number is stored on eight bytes.
- boolean: Each value is stored on one byte.
- decimal: The valid bits are positive integers between 1 to 38, including 1 and 38. The decimal digits are integers less than 10.
- smallint/short: The number is stored on two bytes.
- bigint/long: The number is stored on eight bytes.
- timestamp: The data indicates a date and time. The value can be accurate to six decimal points.
- float: Each number is stored on four bytes.
- tinyint: Each number is stored on one byte. Only OBS tables support this data type.
string
Column Description
Description of a column.
-
Operation
- Add Column
- Delete
NOTE:
If the table to be created includes a great number of columns, you are advised to use SQL statements to create the table or import column information from the local EXCEL file.
-
Table 4 Parameter description when Data Location is set to OBS Parameter
Description
Example
Data Format
DLI supports the following data formats:
- Parquet: DLI can read non-compressed data or data that is compressed using Snappy and gzip.
- CSV: DLI can read non-compressed data or data that is compressed using gzip.
- ORC: DLI can read non-compressed data or data that is compressed using Snappy.
- JSON: DLI can read non-compressed data or data that is compressed using gzip.
- Avro: DLI can read uncompressed Avro data.
CSV
Storage Path
Enter or select an OBS path. The path can be a file or folder.
- When creating an OBS table, you must specify a folder as the path. If a file is specified, data cannot be imported.
- When there are both a folder and a file with the same name in the OBS directory, importing data pointing to that path will prioritize the file over the folder.
obs://obs1/sampledata.csv
Table Header: No/Yes
This parameter is valid only when Data Format is set to CSV. Whether the data source to be imported contains the table header.
Click Advanced Settings and select the checkbox next to Table Header: No. If the checkbox is selected, the table header is displayed. If the checkbox is deselected, no table header is displayed.
-
User-defined Delimiter
This parameter is valid only when Data Format is set to CSV and you select User-defined Delimiter.
The following delimiters are supported:
- Comma (,)
- Vertical bar (|)
- Tab character (\t)
- Others: Enter a user-defined delimiter.
Comma (,)
User-defined Quotation Character
This parameter is valid only when Data Format is set to CSV and you select User-defined Quotation Character.
The following quotation characters are supported:
- Single quotation mark (')
- Double quotation marks (")
- Others: Enter a user-defined quotation character.
Single quotation mark (')
User-defined Escape Character
This parameter is valid only when Data Format is set to CSV and you select User-defined Escape Character.
The following escape characters are supported:
- Backslash (\)
- Others: Enter a user-defined escape character.
Backslash (\)
Date Format
This parameter is valid only when Data Format is set to CSV or JSON.
This parameter specifies the format of the date in the table and is valid only Advanced Settings is selected. The default value is yyyy-MM-dd. For definition of characters involved in the date pattern, see Table 3 in Importing Data to the Table.
2000-01-01
Timestamp Format
This parameter is valid only when Data Format is set to CSV or JSON.
This parameter specifies the format of the timestamp in the table and is valid only Advanced Settings is selected. The default value is yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss. For definition of characters involved in the time pattern, see Table 3 in Importing Data to the Table.
2000-01-01 09:00:00
- If you set Data Location to DLI, set related parameters by referring to Table 3.
- Click OK.
After a table is created, you can view and select the table for use on the Data Management page or SQL Editor page.
Related Operations
After a table is created, you can import data from other OBS buckets to the table.
For details about how to import data, see Importing OBS Data to a DLI Table.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





