Scaling Out/Up an Elasticsearch Cluster
If an Elasticsearch cluster struggles to maintain performance in the face of rapid data growth or sustained high memory usage, you may scale it horizontally by adding more nodes and more node types, or do so vertically by increasing the storage capacity of existing nodes.
|
Type |
Scenario |
Change Process |
|---|---|---|
|
Adding new nodes |
If a cluster experiences rapid data growth or sustained high memory usage, you may add more nodes to it to improve cluster availability. |
Procedure for adding data nodes or cold data nodes:
Adding master or client nodes does not trigger data migration. During the capacity expansion, the system ensures that each shard has at least one available replica to ensure service continuity. |
|
Adding master nodes |
As your cluster's data volume grows, you can improve its stability and reliability by adding dedicated master nodes for more effective cluster node management. |
Procedure for adding a new node type: Add new nodes and modify cluster configuration. Adding master nodes does not trigger data migration, and therefore does not interrupt services. |
|
Adding client nodes |
To handle increased query and write loads as your cluster's data volume grows, you can add dedicated client nodes. This offloads request processing from your data nodes, improving overall cluster scalability. |
Procedure for adding a new node type: Add new nodes and modify cluster configuration. Adding client nodes does not trigger data migration, and therefore does not interrupt services. However, when client nodes are added, the cluster's address changes from the data node address to the client node address. You must update the client configuration to use this new address. Otherwise, the client nodes cannot function. |
|
Adding cold data nodes |
As your cluster's data volume keeps growing, you may have large quantities of historical data that is infrequently accessed but still useful for analytical purposes. To optimize both storage costs and query performance, you can add cold data nodes to store such data. |
Procedure for adding a new node type: Add new nodes and modify cluster configuration. Adding cold data nodes does not trigger data migration, and therefore does not interrupt services. |
|
Increasing node storage capacity |
|
The disk capacity expansion will not interrupt ongoing services. |
Impact on Billing
For a pay-per-use cluster, you can see its new price when confirming the scale-out or scale-up on the console. After the change is complete, the cluster will be billed based on the new price. For details, see Cloud Search Service Price Calculator.
For a yearly/monthly cluster, a new order will be placed after you confirm the scale-out or scale-up. Then you can check the new price.
Constraints
- The node storage capacity of a cluster can only be increased—not decreased. Select an appropriate node storage capacity based on the data volume and projected data growth.
- For a yearly/monthly cluster, you cannot increase the number of nodes and node storage capacity at the same time. For a pay-per-use cluster, however, you can do that.
- The storage capacity of the master and client nodes in a cluster cannot be expanded.
- The storage capacity of data nodes that use local disks cannot be expanded.
- For the range of node quantities supported by each node type, see Table 2.
Change Impact
Before the change, learn about possible impacts and operation suggestions, and develop a plan to minimize these impacts.
Expanding the storage capacity of cluster nodes (vertical scaling) does not impact services, whereas adding new nodes or new node types (horizontal scaling) may have the following impacts:
- Impact on performance
Adding new nodes does not interrupt services. However, after new nodes are added, data shards need to be redistributed to these nodes to balance the load, and this process will consume I/O performance. This is why you are advised to perform the operation during off-peak hours.
To minimize this impact, it is advisable to adjust the data migration rate based on the cluster's traffic cycle: increase the data migration rate during off-peak hours to shorten the task duration, and decrease it before peak hours arrive to ensure optimal cluster performance. The data migration rate is determined by the indices.recovery.max_bytes_per_sec parameter. The default value of this parameter is the number of vCPUs multiplied by 8 MB. For example, for four vCPUs, the data migration rate is 32 MB. You can adjust it based on the service requirements.PUT /_cluster/settings { "transient": { "indices.recovery.max_bytes_per_sec": "128MB" } } - Characteristics of this process
Once started, a scaling task cannot be stopped until it succeeds or fails.
Duration
- It takes 10 to 30 minutes to add new nodes or new node types (horizontal scaling), depending on the cluster's scheduling capabilities.
- It takes 10 to 15 minutes to expand the storage capacity of cluster nodes (vertical scaling).
Prerequisites
- The cluster status is Available, and there are no ongoing tasks.
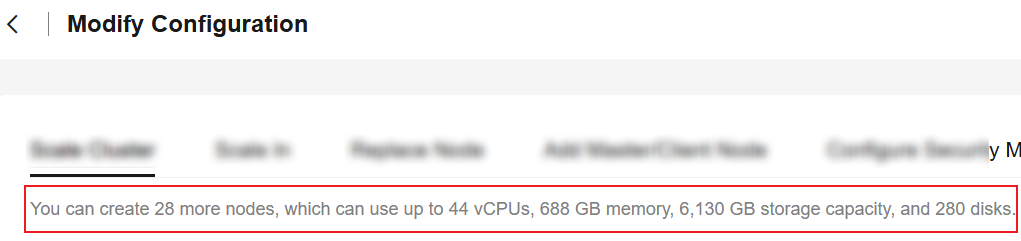
- Your CSS resource quotas are sufficient for the capacity expansion you are about to perform. You can check available resources on the Modify Configuration page.
Figure 1 Checking available resources
Adding More Nodes or Increasing Node Storage Capacity
If a cluster experiences rapid data growth or sustained high memory usage, you may add more nodes to it or increase the cluster nodes' storage capacity. This helps to improve service and data availability and durability.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > Elasticsearch.
- In the cluster list, find the target cluster, and choose More > Modify Configuration in the Operation column. The Modify Configuration page is displayed.
- Click the Scale Cluster tab.
- Set the necessary parameters.
Table 3 Adding more nodes or increasing node storage capacity Parameter
Description
Action
Select Scale out.
Resources
Quantities of resources added.
Nodes
Increase the number of nodes and node storage capacity in the Nodes and Node Storage Type columns. You can change multiple node types at the same time.
- For the range of node quantities supported by each node type, see Constraints.
- The value range of node storage capacity is determined by the node flavor you select. The value must be divisible by 20.
NOTE:For a yearly/monthly cluster, you cannot increase the number of nodes and node storage capacity at the same time. For a pay-per-use cluster, however, you can do that.
Figure 2 Scaling out a cluster
- Click Next.
- Confirm the information and click Submit.
- Click Back to Cluster List to go back to the Clusters page. The Task Status is Scaling out. When Cluster Status changes to Available, the cluster has been successfully scaled out.
Adding New Node Types
For a cluster that has no dedicated master, client, or cold data nodes, as the load on its data plane increases, you may dynamically add such nodes to it to share the load of the data nodes.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > Elasticsearch.
- In the cluster list, find the target cluster, and choose More > Modify Configuration in the Operation column. The Modify Configuration page is displayed.
- Click the Add Node Types tab.
If a cluster already has dedicated master, client, and cold data nodes, the Add Node Types tab is unavailable.
- On the Add Node Types tab, configure the nodes.
Table 4 Adding new node types Parameter
Description
Node types
Select the type of nodes you want to add.
- Only the node types that the cluster does not already have are displayed. For example, if the cluster already has dedicated master nodes, only Client Node and Cold Data Node are displayed.
- Only one node type can be added at a time. For example, if you need to add both master and client nodes, you need to perform this task twice.
Node Specifications
Select node specifications based on site requirements.
Nodes
Set the number of nodes to add. For the value range, see Constraints.
Node Storage Type
Set the node storage type.
The storage capacity per master or client node is fixed to 40 GB.
Figure 3 Adding new node types
- Click Next.
- Confirm the information and click Submit.
Return to the cluster list page. The Task Status of the cluster is Scaling out. When Cluster Status changes to Available, nodes have been added successfully.
- When adding master nodes for a cluster whose version is earlier than 7.x, restart data nodes and cold data nodes after Cluster Status changes to Available to make the configuration of the new master nodes take effect. Otherwise, the cluster status may be displayed as unavailable due to delayed status synchronization (when in fact the cluster services are available).
- When adding client nodes, you can choose whether to restart data nodes and cold data nodes and bring the Cerebro and Kibana processes offline after Cluster Status changes to Available. This helps avoid conflicts.
- When adding cold data nodes, you must restart data nodes to activate the hot tag after Cluster Status changes to Available. This ensures that the cold data nodes function properly. After cold data nodes are added, manually migrate historical data to them. For details, see Switching Between Hot and Cold Storage for an Elasticsearch Cluster.
For details about the restart operation, see Restarting an Elasticsearch Cluster.
Related Documents
- You can also upgrade the node specifications and change the EVS disk type of an Elasticsearch cluster. For details, see Changing the Node Specifications and Storage Type of an Elasticsearch Cluster.
- During a capacity expansion, if the resources in an AZ become insufficient, you can migrate the nodes in this AZ to another that has sufficient resources, and then perform the capacity expansion in the new AZ. For details, see Switching AZs for an Elasticsearch Cluster.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





