Using DNS Resolver to Enable Communication Between On-premises Servers and the Cloud
Background
For security purposes of data management and information, data is stored both on-premises and cloud. Instead, a hybrid networking that spans Huawei Cloud and on-premises data centers is used.
This hybrid networking safeguards your sensitive data on one hand, and on the other hand, it retains flexible deployment and cost control of Huawei Cloud.
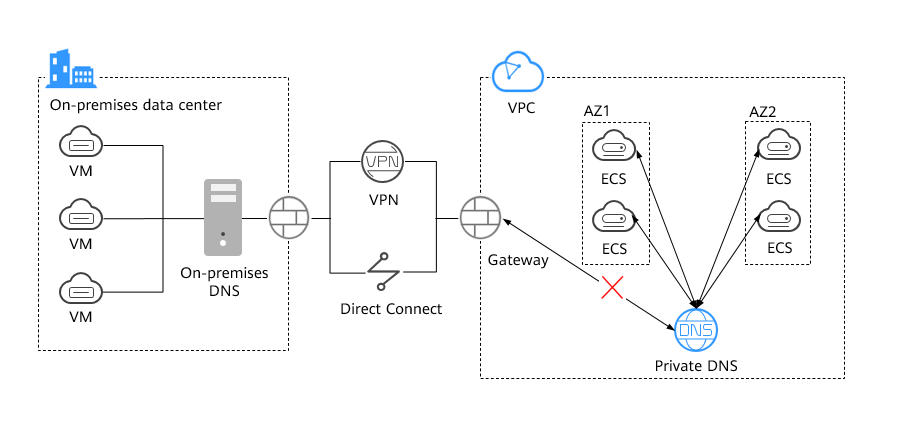
Generally, on-premises data centers can access cloud resources over a Direct Connect or VPN connection so that servers in on-premises data centers can communicate with Huawei Cloud servers.
However, for security purposes, on-premises servers are not allowed to directly access the IP address starting with 100 of Huawei Cloud private DNS, but servers on Huawei Cloud can. Both Huawei Cloud DNS and on-premises DNS servers have independent domain names. This causes the following problems:
- On-premises servers can only use on-premises DNS to resolve on-premises domain names. They cannot resolve domain names of Huawei Cloud services, such as OBS and SFS.
- Huawei Cloud servers can only use the DNS service on Huawei Cloud to resolve private domain names, cloud service domain names, and Internet domain names, instead of on-premises domain names.
Solution
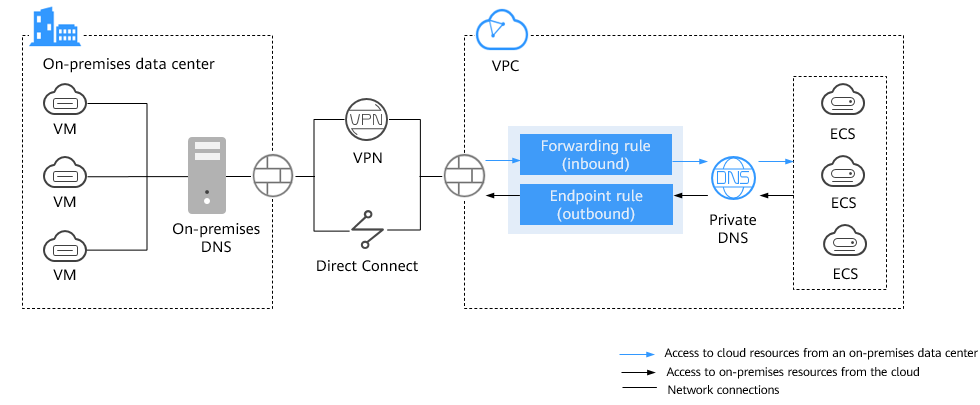
To address the issues mentioned above, Huawei Cloud DNS provides a hybrid DNS solution, as shown in Figure 2.
With Huawei Cloud DNS Resolver, you can create inbound and outbound endpoints to enable communication between on-premises and cloud DNS servers.
- Access to cloud resources from an on-premises data center
With forwarding rules, on-premises DNS servers can forward the DNS queries for the Huawei Cloud service domain names (most suffixed with myhuaweicloud.com) and their subdomains or for private domain names to the inbound endpoints so that these queries can be handled by cloud DNS.
- Access to on-premises resources from the cloud
To allow cloud servers to access on-premises domain names, you can create an outbound endpoint and configure endpoint rules to specify the on-premises domain name to be accessed as well as the IP addresses of the on-premises DNS servers. Huawei Cloud private DNS then forwards the DNS queries for the on-premises domain name to the on-premises DNS servers based on the endpoint rules.
Procedure
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
With inbound endpoints, on-premises DNS queries for cloud domain names can be forwarded to Huawei Cloud private DNS. |
|
|
With outbound endpoints, Huawei Cloud private DNS can forward the DNS queries for on-premises domain names to on-premises DNS servers. |
|
|
You need to configure endpoint rules for outbound endpoints and forwarding rules on on-premises DNS. |
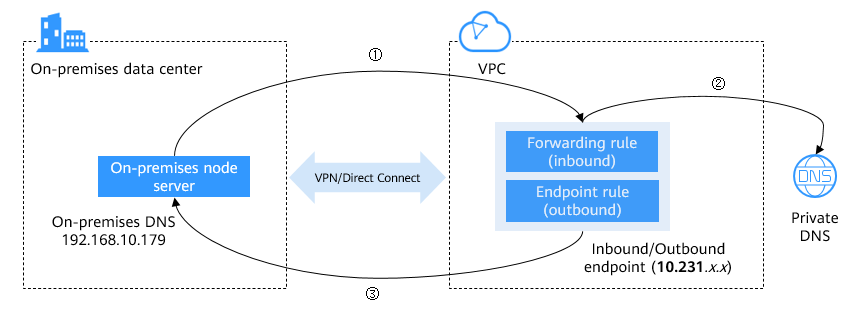
Once the preceding configurations have been completed, an on-premises data center and cloud resources can communicate with each other, as shown in Figure 3.
As shown in Figure 3, the access path between an on-premises data center and cloud resources is as follows:
1. On-premises DNS server forwards the DNS queries for a cloud service domain name (example.huaweicloud.com, for example) to the IP address (10.231.x.x) specified in an inbound endpoint.
2. The inbound endpoint (10.231.x.x) forwards the DNS queries for the cloud service domain name to the Huawei Cloud private DNS.
3. Based on an endpoint rule (10.231.x.x), Huawei Cloud private DNS forwards the DNS queries for an on-premises domain name (example.com, for example) to the on-premises DNS server (192.168.10.179).
The prerequisite for the communication is that you have configured endpoint rules for the outbound endpoint and forwarding rules on the on-premises DNS server as follows:
- Outbound endpoint: With the outbound endpoints, Huawei Cloud private DNS can forward the DNS queries for the on-premises domain name (example.com, for example) to on-premises DNS.
- On-premises DNS:
- With forwarding rules, on-premises DNS servers can forward the DNS queries for a cloud service domain name to the IP address specified in an inbound endpoint.
- Record sets for the on-premises domain name (example.com, for example) need to be configured.
Step 1: Configure an Inbound Endpoint
With inbound endpoints, on-premises DNS queries for cloud domain names can be forwarded to Huawei Cloud private DNS.
- Go to the Resolvers page.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project. - In the upper right corner of the page, click Create Endpoint.
- Configure parameters as prompted.
Pay attention to the following parameters:
- Endpoint Type: Select Inbound.
- VPC: Select the VPC that the cloud resources to be accessed belong to.
- IP Addresses: Specify an IP address, for example, 10.231.x.x.
- Click Create Now.
Step 2: Configure an Outbound Endpoint
With outbound endpoints, Huawei Cloud private DNS can forward the DNS queries for on-premises domain names to on-premises DNS servers.
- In the upper right corner of the page, click Create Endpoint.
- Configure parameters as prompted.
Pay attention to the following parameters:
- Endpoint Type: Select Outbound.
- VPC: Select the VPC that the cloud resources to be accessed belong to.
- IP Addresses: Specify an IP address, for example, 10.231.x.x.
- Click Create Now.
Step 3: Configure Endpoint Rules and Forwarding Rules
Configuring endpoint rules for an outbound endpoint
- Go to the Resolvers page.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project. - On the Outbound Endpoint tab, locate the target outbound endpoint, Click Add Endpoint Rule in the Operation column.
- On the Add Endpoint Rule page, configure parameters as instructed.
Pay attention to the following parameters:
- Domain Name: Enter an on-premises domain name, for example, example.com.
- VPC: Select the VPC that the cloud resources to be accessed belong to.
- IP Addresses: Enter the IP address of an on-premises DNS server, for example, 192.168.10.179.
- Click OK.
Configuring forwarding rules on on-premises DNS
- Log in to a DNS server (IP address: 192.168.10.179) in the on-premises data center.
- Run the following command to install BIND and configure DNS for the server:
- After installation, run the command below to configure forwarding rules for the DNS server. This tells the DNS server to forward queries it cannot resolve itself to inbound endpoints.
Pay attention to the following parameters:
- Add the listening IP address 192.168.10.179.
- Add the forwarders directive and specify the IP addresses of the inbound endpoint.
Figure 4 Example of an on-premises DNS file with forwarders
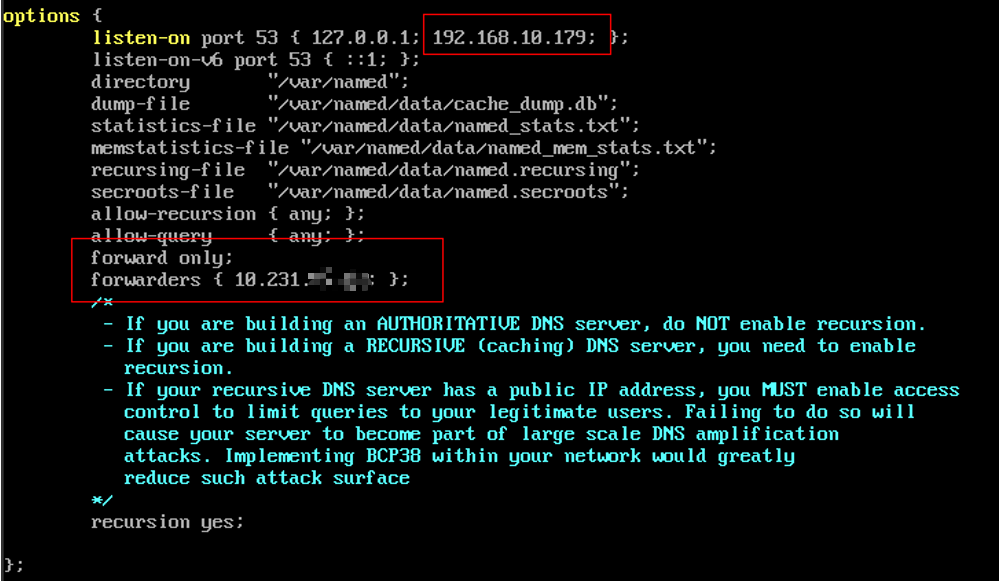
10.231.x.x is the IP address configured for the inbound endpoint.
- Create a domain name example.com in the on-premises DNS. The DNS zone file for example.com is /opt/dns/zones/example.com.z.
zone "example.com" IN { type master; file "/opt/dns/zones/example.com.z"; };
- Run the following command to configure record sets for the domain name example.com:
vim /opt/dns/zones/example.com.z
example.com. 172800 IN NS ns1.test.net. example.com. 172800 IN NS ns1.test.com. example.com. 300 IN SOA ns1.test.net. ns1.test.com. (1 7200 900 1209600 300) example.com. 300 IN A 192.168.10.179
After the configuration is complete, communication between an on-premises data center and cloud resources has been established.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot