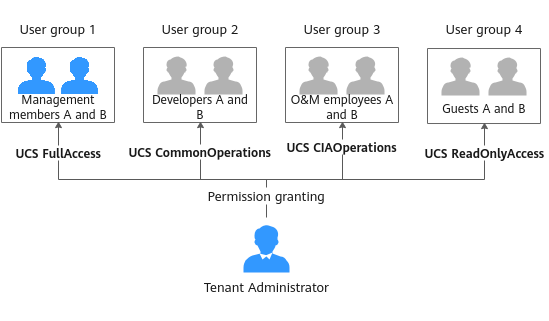
Example: Designing and Configuring Permissions for Users in a Company
A company uses UCS on Huawei Cloud to manage multiple clusters. The company has multiple functional teams responsible for permission granting, resource management, application creation, traffic distribution, and O&M, respectively. You can use IAM and RBAC for fine-grained authorization.
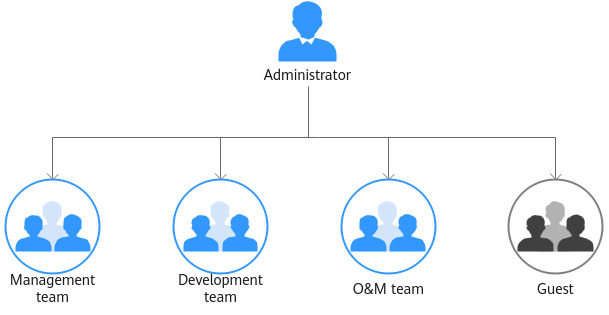
- Management team: manages all resources of the company.
- Development team: develops services.
- O&M team: views and monitors the usage of all resources.
- Guest: a reserved read-only team that has only the permission for viewing resources.
Grant required permissions to different functional teams in the company according to Table 1.
|
Functional Team |
Policy to Be Granted |
Permissions Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Management team |
UCS FullAccess |
Administrator permissions for UCS. Users with these permissions can perform all operations on UCS resources, for example, creating permission policies and security policies. |
|
Development team |
UCS CommonOperations |
Common operation permissions for UCS. Users with these permissions can create workloads, distribute traffic, and perform other operations. |
|
O&M team |
UCS CIAOperations |
Administrator permissions for UCS Container Intelligent Analysis |
|
Guest |
UCS ReadOnlyAccess |
Read-only permissions for UCS services (except for Container Intelligent Analysis) |
Permission Design
The following figure shows the operations that can be performed by different functional teams on UCS resources.
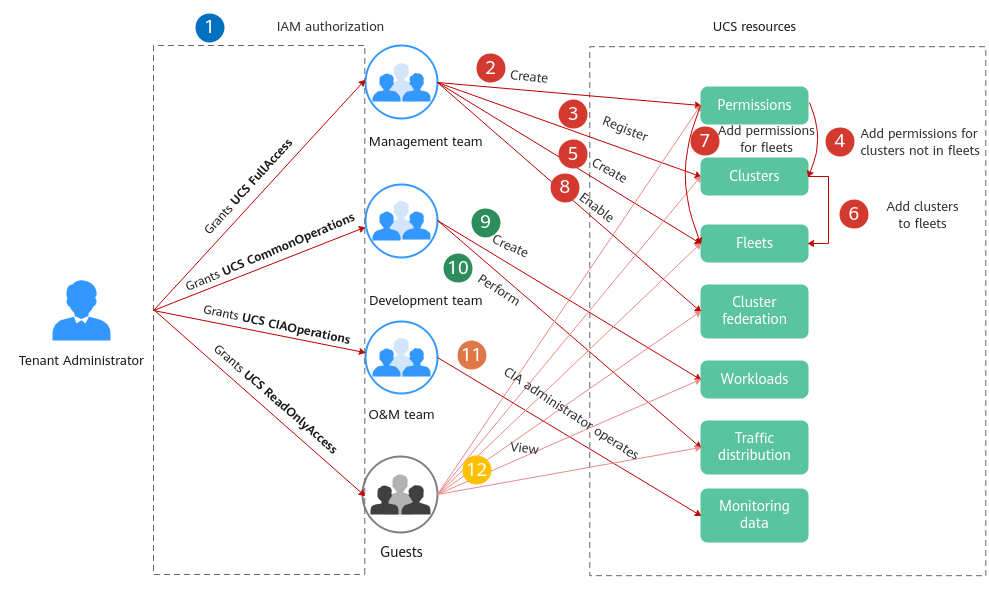
 : The administrator with the Tenant Administrator role grants permissions to each functional team.
: The administrator with the Tenant Administrator role grants permissions to each functional team. to
to  : The management team with the UCS FullAccess permissions is responsible for creating fleets, registering clusters, adding clusters to fleets, enabling cluster federation, and building the multi-cluster federation infrastructure. The management team can add permissions for clusters or fleets by user or user group and namespace so that different users have corresponding operation permissions on specific Kubernetes resources.
: The management team with the UCS FullAccess permissions is responsible for creating fleets, registering clusters, adding clusters to fleets, enabling cluster federation, and building the multi-cluster federation infrastructure. The management team can add permissions for clusters or fleets by user or user group and namespace so that different users have corresponding operation permissions on specific Kubernetes resources. and
and  : The development team with the UCS CommonOperations permissions performs operations such as creating workloads and distributing traffic.
: The development team with the UCS CommonOperations permissions performs operations such as creating workloads and distributing traffic. : The O&M team with the UCS CIAOperations permissions performs monitoring and O&M.
: The O&M team with the UCS CIAOperations permissions performs monitoring and O&M. : Guests with the UCS ReadOnlyAccess permissions can view resources such as clusters, fleets, and workloads.
: Guests with the UCS ReadOnlyAccess permissions can view resources such as clusters, fleets, and workloads.
Administrator: Performing IAM Authorization
The administrator with the Tenant Administrator role performs IAM authorization for each functional team by creating four user groups, granting the UCS FullAccess, UCS CommonOperations, UCS CIAOperations, and UCS ReadOnlyAccess permissions to these user groups, and adding users to the user groups, as shown in Figure 3.
For example, create the dev user group for the development team, grant the UCS CommonOperations permissions to the user group, and add the devuser1 and devuser2 users.
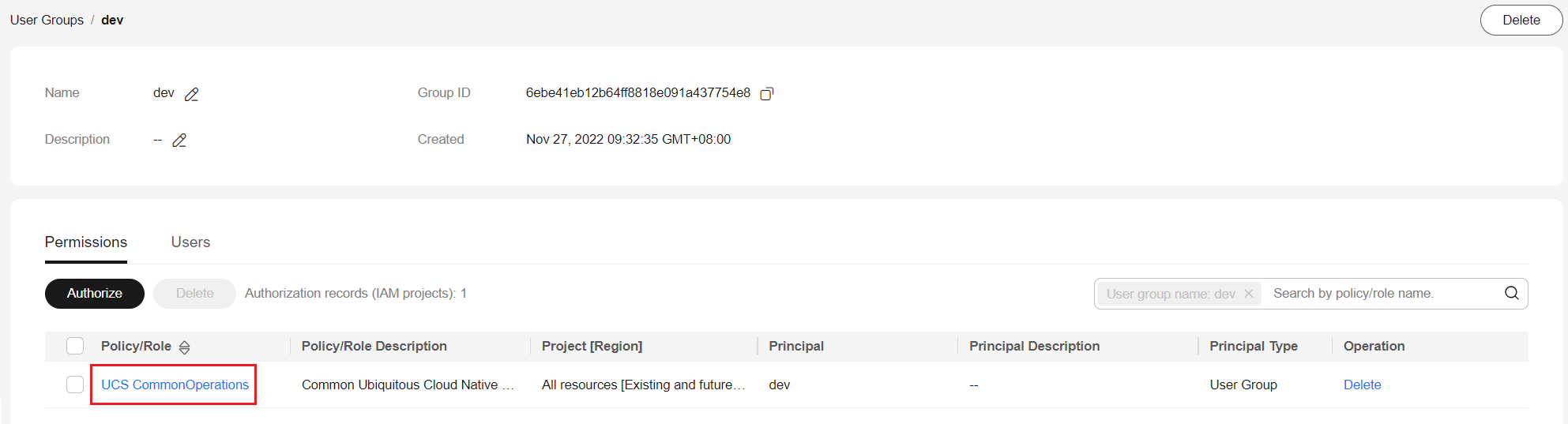
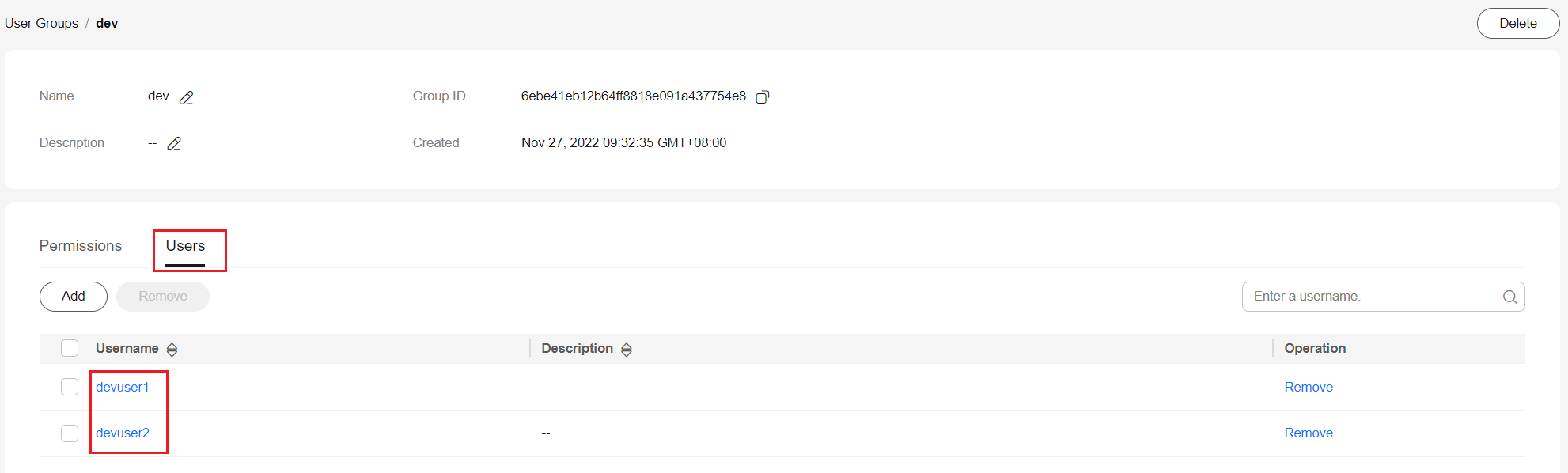
For details, see UCS Resource Permissions (IAM-based). To use some UCS functions that depend on other cloud services, grant permissions to related cloud services. For example, the management team needs to obtain the list of IAM users when creating permissions, so grant both the UCS FullAccess and VDC ReadOnlyAccess permissions to the management team.
Management Team: Building Infrastructure and Configuring Permission Policies
- Select a cluster or fleet.
A fleet contains multiple clusters and can be used for the unified permissions management of these clusters. The management team adds the development permissions for the fleet, so that clusters subsequently added to the fleet will have the permissions. In this way, developers are allowed to perform operations on cluster resources (such as creating workloads) in the fleet. For details, see Managing Fleets.
- Add permissions.
Add the development permissions to the user group.
A user group can contain multiple users, and a user can be added to multiple user groups. A user has all the permissions of the user group that the user belongs to.
Figure 6 Adding the development permissions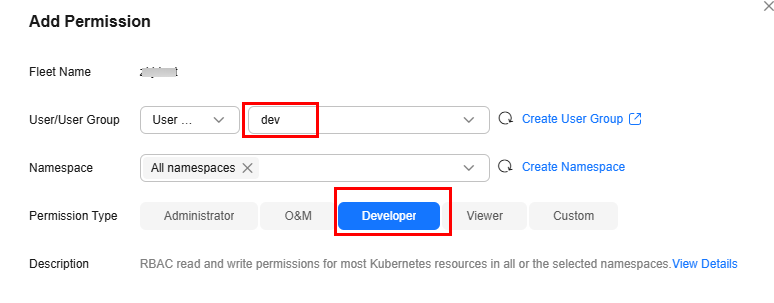
- Register clusters and add them to the fleet.
UCS supports the registration of Huawei Cloud clusters, on-premises clusters, and attached clusters. The management team can select a cluster type as needed. For details, see Huawei Cloud Clusters, Overview, or Overview.
- Enable cluster federation.
Enable it to enjoy unified orchestration of multiple clusters, cross-cluster auto scaling & service discovery, and other capabilities. Enabling cluster federation for the fleet will federate the registered clusters in the fleet.
Development Team: Creating Workloads and Distributing Traffic
After the management team builds the multi-cluster federation infrastructure, developers can use the infrastructure resources. For details, see Workload Management and Traffic Distribution.
O&M Team: Viewing and Monitoring Resource Usages
The O&M team can use the functions provided by CIA, such as intelligent analysis, dashboard, notification configuration, and 24/7 daemon, to monitor workload resources in real time, analyze application health, and complete other routine O&M tasks. For details, see Container Intelligent Analysis.
Guests: Viewing Resources
Guests (persons who have only the permission for viewing resources) can view resources such as clusters, fleets, and workloads.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot