Managing Fleets
This section describes how to create a fleet, add clusters to the fleet, add a permission policy for the fleet, remove clusters from the fleet, unregister clusters from the fleet, and delete the fleet.
Creating a Fleet
- Log in to the UCS console. In the navigation pane, choose Fleets. On the Fleets tab, click Create Fleet.
- Enter the fleet information.
Figure 1 Creating a fleet

- Fleet Name: Enter a name, starting with a lowercase letter and not ending with a hyphen (-). Only lowercase letters, digits, and hyphens (-) are allowed.
- Add Cluster: Clusters not in the fleet are displayed in the list. You can add clusters when creating a fleet or after the fleet is created. If you do not select any cluster, an empty fleet will be created. After the fleet is created, see Adding a Cluster.
- Description: description of the fleet to which the cluster is added

A registered cluster will follow the fleet permissions policies, not its own ones.
- Click OK.
Adding a Cluster
- Log in to the UCS console. In the navigation pane, choose Fleets.
- In the card view of the target fleet, click Add Cluster, or click
 in the upper right corner.
in the upper right corner.
You can also click the fleet name to access the fleet console. In the navigation pane, choose Container Clusters. On the displayed page, click Add Cluster in the upper right corner.
Figure 2 Adding a cluster to a fleet
- Select one or more existing clusters. A cluster can be added to only one fleet. The clusters displayed in the list are not added to any fleet.
Figure 3 Adding a cluster


- Only clusters not added to a fleet can be added. To add a cluster from another fleet, remove the cluster from that fleet first.
- After a cluster is added to a fleet, the cluster will follow the fleet permission policies, not its own ones.
- If cluster federation is enabled for a fleet, clusters added to the fleet will automatically become federated. For details about cluster federation, see Enabling Cluster Federation.
- If a CCE cluster in the current region is added to a fleet with federation enabled, a VPC endpoint will be created in the VPC where the cluster is running for network connectivity. If the cluster is not in the current region, bind an EIP to the cluster.
- If a service mesh is enabled for a fleet, only CCE clusters can be added.
- Click OK.
Adding Permissions
- Log in to the UCS console. In the navigation pane, choose Permissions.
- Select a cluster or fleet for which you want to add permissions from the drop-down list on the right.
- Click Add Permission in the upper right corner.
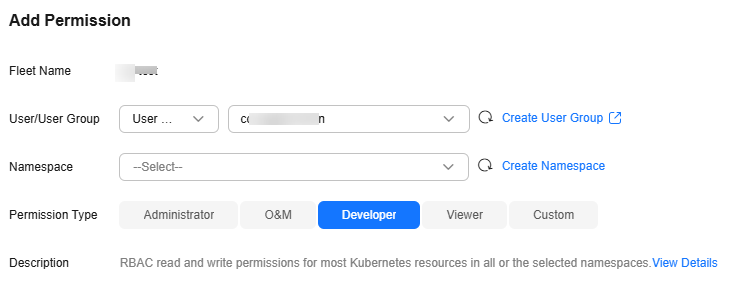
- In the window that slides from the right, confirm the cluster or fleet name, set Namespace (for example, select All namespaces), select the target user or user group, and set Permission Type.
- User/User Group: A user group can contain multiple users, and a user can be added to multiple user groups. A user has all the permissions of the user group that the user belongs to.
- Namespace: You can select All namespaces or other namespaces. All namespaces includes the existing namespace of the fleet and the namespace to be added to the fleet. If you select this option, you cannot select other namespaces. If you do not select this option, UCS provides several common namespaces, such as default, kube-system, and kube-public. You can also add a namespace, which should exist in the cluster.
- Click OK.
Figure 4 Adding permissions for a fleet
Removing a Cluster from a Fleet
- Log in to the UCS console. In the navigation pane, choose Fleets.
- On the Fleets tab, click the fleet name to access the fleet console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Container Clusters. In the card view of the target cluster, click
 in the upper right corner.
in the upper right corner. - Read the precautions carefully and confirm the risks. Then click OK.
After a cluster is removed from a fleet, it is displayed on the Clusters Not in Fleet tab. You can add the cluster to the fleet again. For details, see Managing Clusters Not in the Fleet.
Unregistering a Cluster from a Fleet
- Log in to the UCS console. In the navigation pane, choose Fleets.
- On the Fleets tab, click the fleet name to access the fleet console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Container Clusters. In the card view of the target cluster, click
 in the upper right corner.
in the upper right corner. - In the Unregister Cluster dialog box, read the precautions carefully, confirm the risks, and click OK.
- (Optional) After an attached cluster is unregistered, run the following command to uninstall the agent component from the destination cluster:
kubectl -n kube-system delete deployments/proxy-agent secret/proxy-agent-cert
- (Optional) After an on-premises cluster is unregistered, run the uninstallation command to delete the cluster from the local host and clear resources:
./ucs-ctl delete cluster [Cluster name]

If the cluster fails to be deleted, perform operations in How Do I Manually Clear Nodes of an On-Premises Cluster?
Deleting a Fleet
If a fleet is no longer used, you can delete it. Before deleting a fleet, ensure that the fleet does not contain any clusters and cluster federation has been disabled. If there are clusters in the fleet, you can remove the clusters from the fleet and then add them to another fleet. If cluster federation has been enabled for the fleet, disable it following Disabling Cluster Federation.
- Log in to the UCS console. In the navigation pane, choose Fleets.
- On the Fleets tab, locate the target fleet and click
 in the upper right corner.
in the upper right corner. - In the dialog box displayed, click OK.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





