Running a Hive SQL Job
A Hive SQL job is a data analytics task that is written and run based on the Hive data warehouse tool. It is mainly used to process large-scale structured or semi-structured data in a Hadoop distributed cluster. Hive SQL is a SQL dialect defined by Hive. Its syntax is similar to standard SQL, but it is optimized for big data scenarios. Hive SQL jobs can convert SQL statements into MapReduce or Spark jobs for execution, making Hive SQL suitable for non-programmers to quickly perform data query, statistics, and analysis.
MRS allows you to submit and run your own programs, and get the results. This section will show you how to submit a Hive SQL job in an MRS cluster.
A Hive SQL job supports both SQL statements and scripts. If SQL statements contain sensitive information, you can submit the job using a script.
You can create a job online and submit it for running on the MRS console, or submit a job in CLI mode on the MRS cluster client.
Prerequisites
- You have uploaded the program packages and data files required by jobs to OBS or HDFS.
- If the job program needs to read and analyze data in the OBS file system, you need to configure storage-compute decoupling for the MRS cluster. For details, see Configuring Storage-Compute Decoupling for an MRS Cluster.
Notes and Constraints
- When the policy of the user group to which an IAM user belongs changes from MRS ReadOnlyAccess to MRS CommonOperations, MRS FullAccess, or MRS Administrator, or vice versa, wait for five minutes after user synchronization for the System Security Services Daemon (SSSD) cache of the cluster node to refresh. Submit a job on the MRS console after the new policy takes effect. Otherwise, the job submission may fail.
- If the IAM username contains spaces (for example, admin 01), you cannot create jobs on the MRS console.
Submitting a Job
You can create and run jobs online using the management console or submit jobs by running commands on the cluster client.
- Develop an SQL script.
A Hive SQL job can execute SQL statements directly or execute an SQL script file.
In this section, the script for creating a database and data table, and inserting data in Hive is used as an example. Upload the developed hive_basic.sql script file to a specified directory on HDFS, OBS, or an MRS cluster node. For details, see Uploading Application Data to an MRS Cluster.
-- Create a database. CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS test_db; -- Use the database. USE test_db; -- Create a data table. CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS test_table ( id INT, name STRING, age INT, gender STRING ) ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','; -- Insert a single row of data. INSERT INTO test_table VALUES (1, 'Zhangsan', 30, 'Male'); - Log in to the MRS console.
- On the Active Clusters page, select a running cluster and click its name to switch to the cluster details page.
- On the Dashboard page, click Synchronize on the right side of IAM User Sync to synchronize IAM users.
Perform this step only when Kerberos authentication is enabled for the cluster.
After IAM user synchronization, wait for five minutes before submitting a job. For details about IAM user synchronization, see Synchronizing IAM Users to MRS.
- Click Job Management. On the displayed job list page, click Create.
- Set Type to HiveSql and configure Hive SQL job information by referring to Table 1.
Figure 1 Creating a Hive SQL job
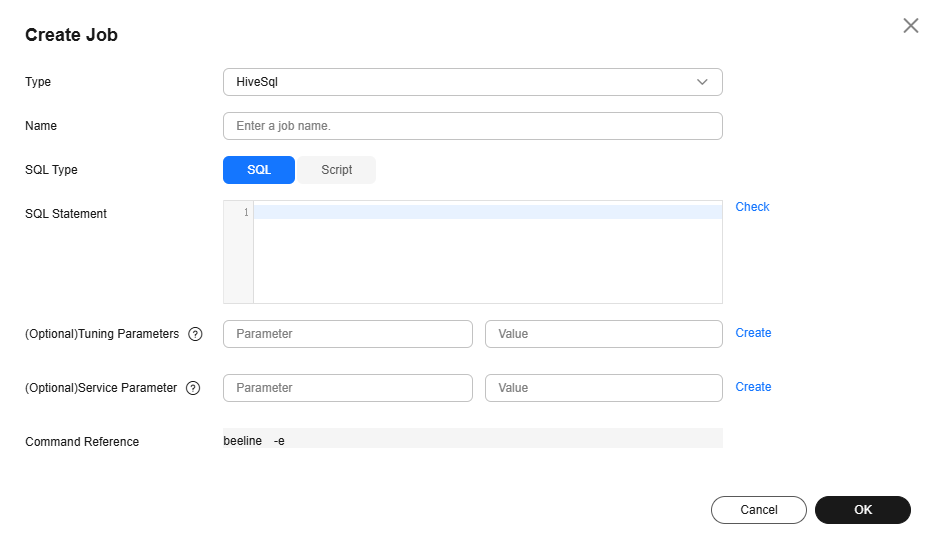
Table 1 Job parameters Parameter
Description
Example
Name
Job name. It can contain 1 to 64 characters. Only letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_) are allowed.
hive_job
SQL Type
Submission type of the SQL statement.
- SQL: Run the entered SQL statement.
- Script: Load SQL scripts from HDFS or OBS to run SQL statements.
Script
SQL Statement
This parameter is valid only when SQL Type is set to SQL. Enter the SQL statement to be executed, and then click Check to check whether the SQL statement is correct.
If you want to submit and execute multiple statements at the same time, use semicolons (;) to separate them.
-
SQL File
This parameter is available only when SQL Type is set to Script. It specifies the path of the SQL script file to be executed. You can enter the path or click HDFS or OBS to select a file.
- The path can contain a maximum of 1,023 characters. It cannot contain special characters (;|&>,<'$) and cannot be left blank or all spaces.
- The OBS program path starts with obs://. The HDFS program path starts with hdfs://hacluster, for example, hdfs://hacluster/user/XXX.jar.
- The HiveScript file must end with .sql.
obs://mrs-demotest/program/hive_basic.sql
Tunning Parameters
(Optional) Used to configure optimization parameters such as threads, memory, and vCPUs for the job to optimize resource usage and improve job execution performance.
Table 2 lists the common program parameters of Hive SQL jobs. You can configure the parameters based on the execution program and cluster resources. If you do not configure the parameters, the default values of the cluster are used.
-
Service Parameter
(Optional) Service parameters for the job.
To modify the current job, change this parameter. For permanent changes to the entire cluster, refer to Modifying the Configuration Parameters of an MRS Cluster Component and modify the cluster component parameters accordingly.
For example, if decoupled storage and compute is not configured for the MRS cluster and jobs need to access OBS using AK/SK, you can add the following service parameters:
- fs.obs.access.key: key ID for accessing OBS.
- fs.obs.secret.key: key corresponding to the key ID for accessing OBS.
-
Command Reference
Commands submitted to the background for execution when a job is submitted.
N/A
Table 2 HiveSQL job running program parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
--hiveconf
Configure the Hive service.
For example, you can set hive.execution.engine to mr or tez to specify the execution engine.
- Parameter: --hiveconf
- Value: hive.execution.engine=mr
--hivevar
Set user-defined variables.
Set the variable ID as follows:
- Parameter: --hivevar id
- Value: "123" select * from test where id = ${hivevar:id};
- Confirm job configuration information and click OK.
- After the job is submitted, you can view the job running status and execution result in the job list. After the job status changes to Completed, you can view the analysis result of related programs.
In this sample program, you can click View Log to view the detailed execution process of the Hive job.
Figure 2 Viewing job execution details
After the job is successfully executed, connect to Hive Beeline through the client to view the Hive table data.
- If Kerberos authentication has been enabled for the current cluster, create a service user with job submission permissions on FusionInsight Manager in advance. For details, see Creating an MRS Cluster User.
In this example, create human-machine user testuser, and associate the user with user group supergroup and role System_administrator.
- Install an MRS cluster client.
For details, see Installing an MRS Cluster Client.
The MRS cluster comes with a client installed for job submission by default, which can also be used directly. In MRS 3.x or later, the default client installation path is /opt/Bigdata/client on the Master node. In versions earlier than MRS 3.x, the default client installation path is /opt/client on the Master node.
- Run the following command to go to the client installation directory:
cd /opt/Bigdata/client
Run the following command to load the environment variables:
source bigdata_env
If Kerberos authentication is enabled for the current cluster, run the following command to authenticate the user. If Kerberos authentication is disabled for the current cluster, you do not need to run the kinit command.
kinit testuser
- Run the following command to access Hive Beeline and view the generated data:
beeline
Run the following command to view the generated Hive table data:
select * from test_db.test_table;
Figure 3 Viewing Hive table data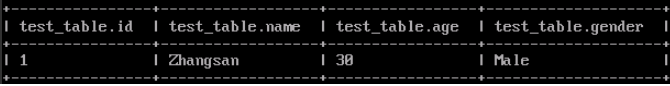
- If Kerberos authentication has been enabled for the current cluster, create a service user with job submission permissions on FusionInsight Manager in advance. For details, see Creating an MRS Cluster User.
- Develop an SQL script.
A Hive SQL job can execute SQL statements directly or execute an SQL script file.
In this section, the script for creating a database and data table, and inserting data in Hive is used as an example. Upload the developed hive_basic.sql script file to a specified directory on HDFS, OBS, or an MRS cluster node. For details, see Uploading Application Data to an MRS Cluster.
-- Create a database. CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS test_db; -- Use the database. USE test_db; -- Create a data table. CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS test_table ( id INT, name STRING, age INT, gender STRING ) ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','; -- Insert a single row of data. INSERT INTO test_table VALUES (1, 'Zhangsan', 30, 'Male'); - If Kerberos authentication has been enabled for the current cluster, create a service user with job submission permissions on FusionInsight Manager in advance. For details, see Creating an MRS Cluster User.
In this example, create human-machine user testuser, and associate the user with user group supergroup and role System_administrator.
- Install an MRS cluster client.
For details, see Installing an MRS Cluster Client.
The MRS cluster comes with a client installed for job submission by default, which can also be used directly. In MRS 3.x or later, the default client installation path is /opt/Bigdata/client on the Master node. In versions earlier than MRS 3.x, the default client installation path is /opt/client on the Master node.
- Log in to the node where the client is located as the MRS cluster client installation user.
For details, see Logging In to an MRS Cluster Node.
- Run the following command to go to the client installation directory:
cd /opt/Bigdata/client
Run the following command to load the environment variables:
source bigdata_env
If Kerberos authentication is enabled for the current cluster, run the following command to authenticate the user. If Kerberos authentication is disabled for the current cluster, you do not need to run the kinit command.
kinit testuser
- Run a beeline command to connect to Hive and execute the related job.
beeline -f /opt/hive_basic.sql
After running the beeline command, you can directly execute SQL statements in the Beeline.
beeline
After the script is executed, view the generated Hive table data in Beeline.
select * from test_db.test_table;
Figure 4 Viewing Hive table data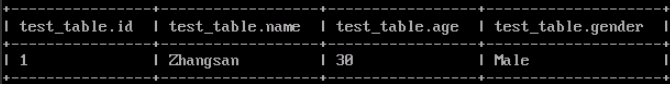
Use the command below to specify a component service user for clusters with Kerberos authentication disabled. If no service user is specified, HiveServer will be connected using the current OS user.
beeline -nMRS cluster service user
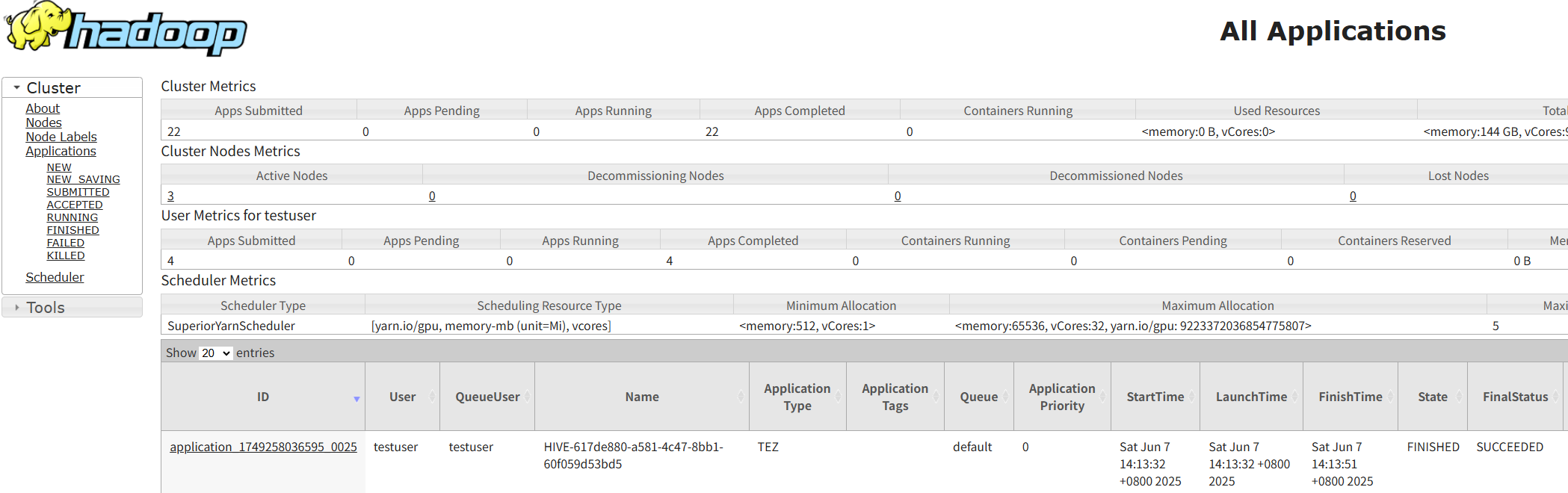
- For jobs submitted to YARN for execution, log in to FusionInsight Manager as user testuser, choose Cluster > Services > Yarn, click the hyperlink on the right of ResourceManager Web UI to access the YARN Web UI, and click the application ID of a job to view the job running information and related logs.
Figure 5 Viewing Hive SQL job details
Helpful Links
- You can view logs of each job created on the MRS console. For details, see Viewing MRS Job Details and Logs.
- Kerberos authentication has been enabled for a cluster and IAM user synchronization has not been performed. When you submit a job, an error is reported. For details about how to handle the error, see What Can I Do If the System Displays a Message Indicating that the Current User Does Not Exist on Manager When I Submit a Job?
- After a Hive job is submitted, you can view the SQL statements of the job on the YARN Web UI. For details, see How Do I View SQL Statements of Hive Jobs on the YARN Web UI?
- For more Hive job troubleshooting cases, see Job Management FAQs and Hive Troubleshooting.
- For more MRS application development sample programs, see MRS Developer Guide.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





