Dynamic Acceleration (Only for HCE 2.0)
Preparations
Before dynamic acceleration, you need to perform two checks. Applications can be dynamically accelerated only when both conditions are met.
- Run the following command to check whether the binary file to be optimized can be located again:
application can be replaced with the binary file to be checked.
readelf -a application | grep .rela.text
Figure 1 Example of a readelf command
- If the binary file contains .rela.text, the file can be located again. In this case, the application can be optimized.
- If the binary file does not contain .rela.text, to allow BOLT to re-arrange functions in your program, you need to add --emit-relocs or -q to the command that was used to create the binary file.
- Run hce-wae --check /data/apps/mysql-8.0.28/bin/mysqld to check whether the application supports dynamic acceleration.
If 3 is displayed, dynamic acceleration is supported.
Figure 2 Example of the check result 3
Procedure
In the following operations, the mysqld application in the /data/apps/mysql-8.0.28/bin directory is used as an example.
- Generate an instrumentation application and run it.
- Run the /data/hce-wae/dbo/gen_instrumentation /data/apps/mysql-8.0.28/bin/mysqld command to generate an instrumentation application.
Command format: /data/hce-wae/dbo/gen_instrumentationApplication path
Figure 3 Example of /data/hce-wae/dbo/gen_instrumentation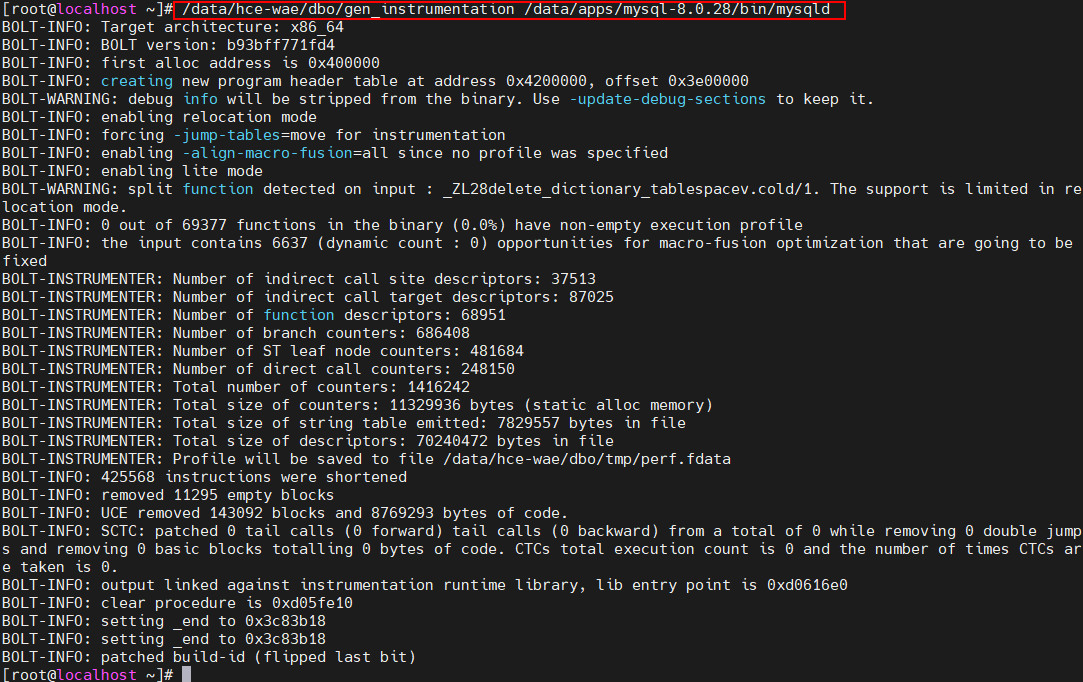
The mysqld.inst instrumentation file is generated in the current directory.
Figure 4 Example of querying an instrumentation file with the .inst suffix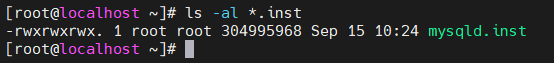
- Run the instrumentation file to obtain the PID of the application process. In this example, the PID is 87042.
Figure 5 Example of running an instrumentation file to obtain a PID
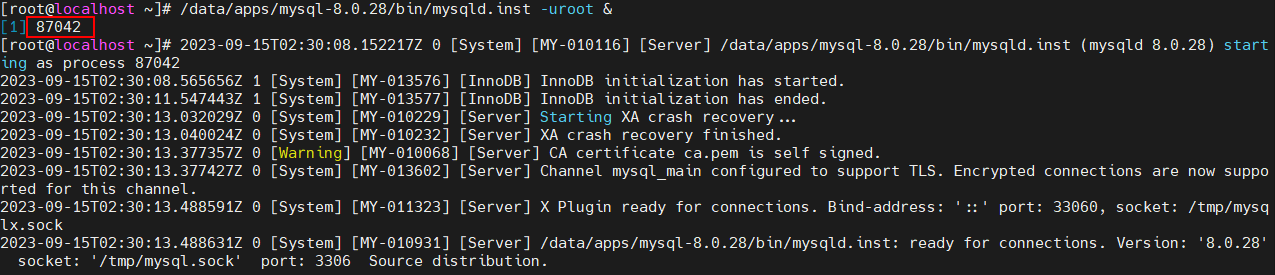
- Run the /data/hce-wae/dbo/gen_instrumentation /data/apps/mysql-8.0.28/bin/mysqld command to generate an instrumentation application.
- Create a dynamic acceleration configuration file for mysqld.
Each application to be optimized must have a configuration file. Workload Accelerator dynamically accelerates the application based on the configuration file.
- Run the following command to copy the default configuration file /data/hce-wae/config/mysqld.conf:
[root@localhost]# cp /data/hce-wae/config/hce-wae-tmp.conf /data/hce-wae/config/mysqld.conf
- Set the origin-exe field in the /data/hce-wae/config/mysqld.conf configuration file.
origin-exe indicates the location of the application to be optimized. In this example, the location is /data/apps/mysql-8.0.28/bin/mysqld.
[root@localhost]# vim /data/hce-wae/config/mysqld.conf
Figure 6 Example of the origin-exe field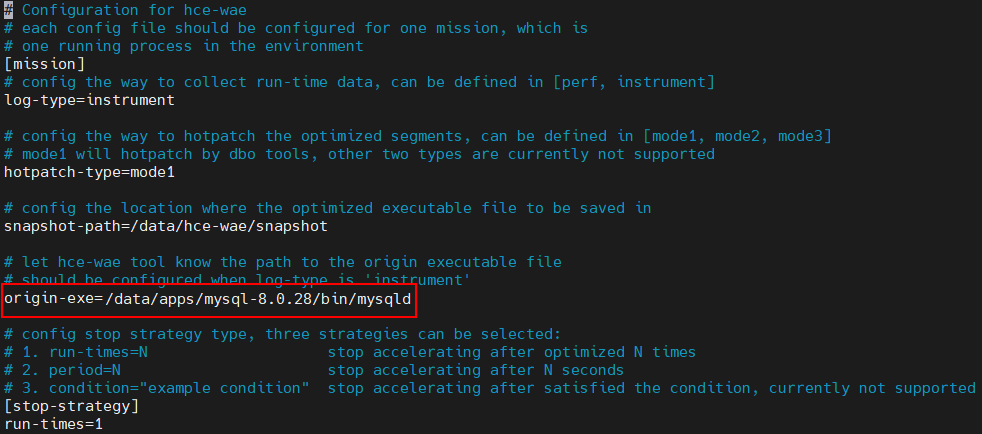
- Run the following command to copy the default configuration file /data/hce-wae/config/mysqld.conf:
- Use the configuration file and the PID to configure dynamic acceleration.
Command format: hce-wae --conf [PID] [/path/to/config]
Figure 7 Example of configuring dynamic acceleration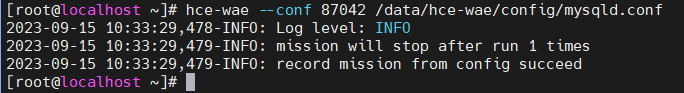
- Enable dynamic acceleration to optimize the instrumentation application.
Command format: hce-wae --start [PID]
Figure 8 Enabling dynamic acceleration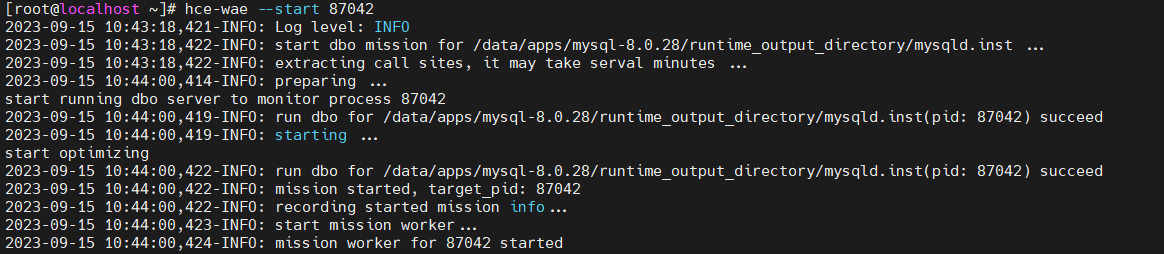
You can view the optimization status from the --status parameter. If the status is Running, the process is being optimized. If the status is Finished, the process has been optimized.
Command format: hce-wae --status [PID]
Figure 9 Viewing the optimization status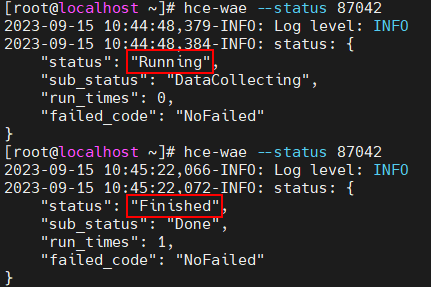
- Use the --snapshot parameter to generate an optimized .dbo binary snapshot file. In this example, the file is mysqld.dbo.
Figure 10 Example of generating an optimized .dbo binary snapshot file
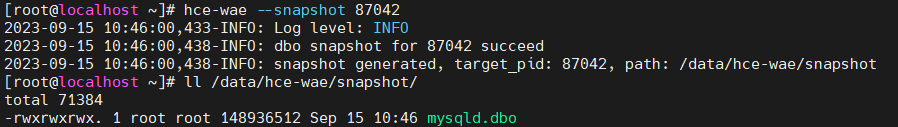
The default snapshot path is /data/hce-wae/snapshot/. You can change the path in the configuration file as needed. You can use this snapshot file to run the application without repeated optimization.
- Terminate dynamic acceleration to stop application optimization.
Command format: hce-wae --stop [PID]
Figure 11 Example of stopping dynamic acceleration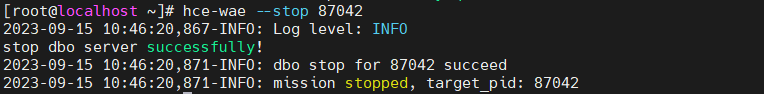
CLI for Dynamic Acceleration
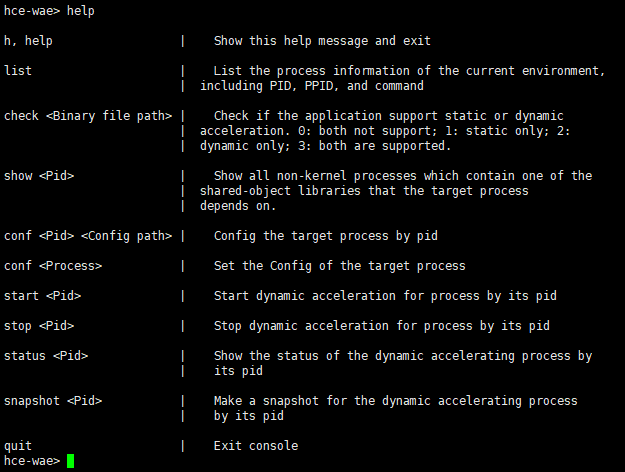
A CLI is provided for dynamic acceleration. Table 1 lists the supported commands.
|
Command |
How to Use |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
list |
list |
Obtains the process information in the current environment, including the PID, PPID, and command information. |
|
status |
status <PID> |
Queries ongoing dynamic acceleration tasks and their status. The following information is returned:
|
|
check |
check <PID> |
Checks whether the current process supports static or dynamic acceleration and displays the text result. |
|
show |
show <PID> |
Queries the process dependencies. |
|
conf |
conf <PID> |
Configures the dynamic acceleration capability for the target process. After you run the command, configuration options are displayed in sequence. Configure the options as prompted. |
|
start |
start <PID> |
Enables dynamic acceleration. |
|
stop |
stop <PID> |
Stops dynamic acceleration. |
|
snapshot |
snapshot <PID> |
Generates a dynamic acceleration snapshot. |
|
quit |
quit |
Exits the CLI. |
|
h/help |
h/help |
Shows help information. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





