Adding Record Sets for a Public Zone
Scenarios
After creating a public zone for your domain name, you need to add record sets for your zone. DNS supports multiple types of record sets that apply to different service scenarios.
|
Record Set Type |
Where to Use |
|---|---|
|
An A record set maps domain names to IPv4 addresses of website servers. If you want to make your website accessible via a domain name, you need to add an A record set to map the domain name to the IPv4 address of your web server. |
|
|
A CNAME record set is used for scenarios like website resolution, CDN, enterprise mailbox, enterprise portal, web application firewall, object storage, and live video streaming. It maps one domain name to another domain name or multiple domain names to one domain name. |
|
|
An MX record set maps domain names to email servers. It is used for routing traffic to a mailbox. It records the email server's priority and host name. |
|
|
An AAAA record set maps domain names to IPv6 addresses of website servers. |
|
|
A TXT record set is used as a digital authentication certificate and for SPF (anti-spam) and domain name retrieval. It creates text records for domain names. |
|
|
An SRV record set records the services provided by servers, guiding clients to the correct server. It is commonly used for directory management at Microsoft. |
|
|
An NS record set is created by default. It specifies authoritative DNS servers of domain names. If you need to delegate a subdomain to a third-party DNS provider, you need to manually create an NS record for the subdomain. |
|
|
SOA |
An SOA record set provides basic information about domain names and details about authoritative servers. This type of record set is created by default and cannot be added manually. |
|
Grants certificate issuing permissions to certificate authorities (CAs). CAA record sets can prevent the issuance of unauthorized HTTPS certificates. |
This section describes how to add a record set for a public zone and the service scenarios and configuration rules of different types of record sets.
Preparations
- Prepare a domain name.
You have purchased a domain name from the domain name registrar and added it to the DNS console. For details, see Creating a Public Zone.
- The domain name is normal.
You have queried the domain name status from the domain name registrar or a third-party platform and confirmed that the domain name is in a normal status.
- The DNS server address is correct.
After adding the domain name to the DNS console, check its DNS server address in the list and ensure that the Huawei Cloud DNS server address is used.
If the DNS server addresses of the domain name do not contain the Huawei Cloud DNS server address, add the Huawei Cloud DNS server address for it. For details, see Changing DNS Servers for a Public Domain Name.
- You have obtained the value of the record set.
- To configure a record set for a website, you need to obtain the public IP address of the website server.
- To configure a record set for cloud services such as CDN, WAF, and OBS, you need to obtain the CNAME values provided by the cloud services.
- To configure an email domain name, you need to obtain the MX record provided by the email service provider.
Adding a Record Set
An A record set maps a domain name to an IPv4 address. If you have a website with a public IP address and domain name, you can map the domain name to the public IP address by adding an A record set. After the record set is added, the website can be accessed using the domain name.
Constraints
An A record cannot coexist with a CNAME, explicit URL, or implicit URL record for the same name and line.
For details about the conflict rules and handling measures, see Rules for Handling Record Set Conflicts.
Procedure
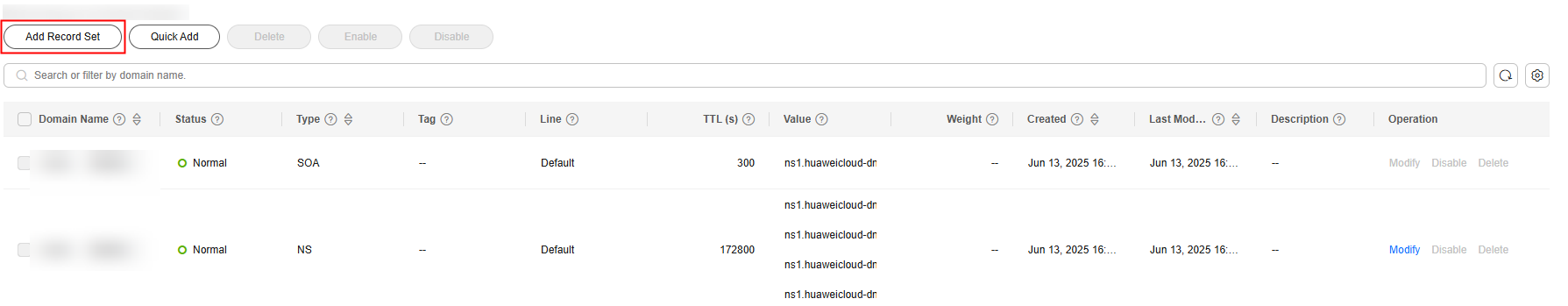
- Go to the Public Zones page.
- Locate the target zone and click Manage Record Sets in the Operation column.
- Click Add Record Set above the record set list.
- On the Add Record Set page, set record set parameters as instructed.
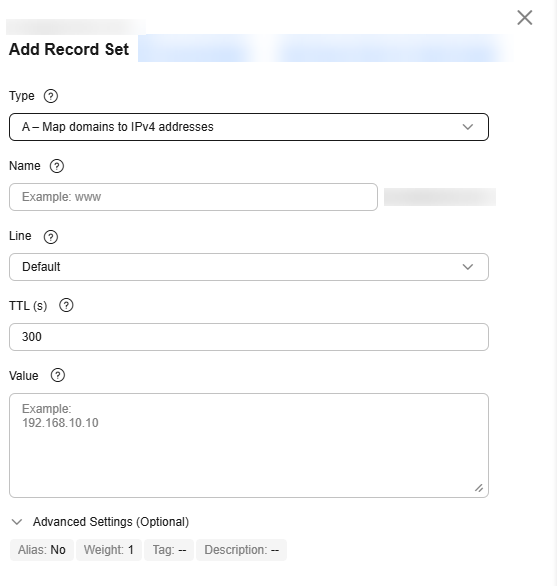
Table 1 Record set parameters Parameter
Description
Example
Type
Record set type.
Select a record set type based on service requirements.
For details, see Table 1.
A – Map domains to IPv4 addresses
Name
Prefix of the domain name to be resolved.
This value is left empty by default.
For example, if the domain name is example.com, the value of the Name can be as follows:
- www: The domain name is www.example.com and usually used for a website.
- Left blank: The domain name is example.com and usually used for a website.
To use an at sign (@) as the domain name prefix, just leave this parameter blank.
- abc: The domain name is abc.example.com, a subdomain of example.com.
- mail: The domain name is mail.example.com and usually used for email servers.
- *: The domain name is *.example.com. It covers all subdomains of example.com.
Leave it blank.
Line
A specific route or path that the DNS server uses to determine which IP address to return based on the user's location, ISP, or other attributes.
The default value is Default.
- Default: returns the default resolution result irrespective of where the visitors come from.
- ISP: returns the resolution result based on end users' carrier networks. For details, see Configuring ISP Lines.
- Region: returns the resolution result based on end users' geographical locations. For details, see Configuring Region Lines.
- Custom Lines: returns the resolution result based on specified IP address ranges. For details, see Configuring Custom Lines.
Default
TTL (s)
How long a local DNS server caches a DNS record. It is measured in seconds.
Default value: 300
Value range: 1 to 2147483647
If your service address changes frequently, set TTL to a smaller value. Otherwise, set TTL to a larger value.
300
Value
Record set value, which is usually the public IP address of a website server.
You can enter a maximum of 50 unique IP addresses, each on a separate line.
198.xx.xx.100
198.xx.xx.101
198.xx.xx.102
Alias
Whether to associate the record set with a cloud resource.
Unlike a CNAME record set, an alias supports second-level domain names.
This option is disabled by default.
Types of record sets that support alias include A, MX, AAAA, TXT, SRV and CAA.
Disabled
Alias Target
Cloud resource to be associated with the alias record set, which includes the cloud resource name and alias target.
-
Weight
Weight for the record set.
Default value: 1
Value range: 0 to 1000
If a resolution line in a zone contains multiple record sets of the same type, you can set different weights to each record set. For details, see Configuring Weighted Routing.
1
Tag
Identifier of the record set. Each tag contains a key and a value.
You can add up to 20 tags for a record set.
The tag key:
- Cannot be left blank.
- Must be unique for each resource.
- Can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
- Cannot start or end with a space, or cannot start with _sys_. Only letters, digits, spaces, and the following special characters are allowed: _.:=+-@
The tag value:
- Can be left blank.
- Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
- Can contain letters, digits, spaces, and special characters _ . : / = + - @.
NOTE:If your organization has configured tag policies for the DNS service, you need to add tags to your record sets based on the tag policies. If you add a tag that does not comply with the tag policies, record sets may fail to be created. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies.
example_key1
example_value1
Description
Supplementary information about the record set.
The description can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
Routing Internet traffic to a website
- Click OK.
A CNAME record maps a domain name to another. It is commonly used for domain name resolution of CDN, WAF, OBS buckets, and EWP. You can also use CNAME records to map a subdomain name (for example, starting with www.) to the primary domain name.
Constraints
A CNAME record cannot coexist with other types of records for the same name and line.
For details about the conflict rules and handling measures, see Rules for Handling Record Set Conflicts.
Procedure
- Go to the Public Zones page.
- Locate the target zone and click Manage Record Sets in the Operation column.
- Click Add Record Set above the record set list.

- On the Add Record Set page, set record set parameters as instructed.
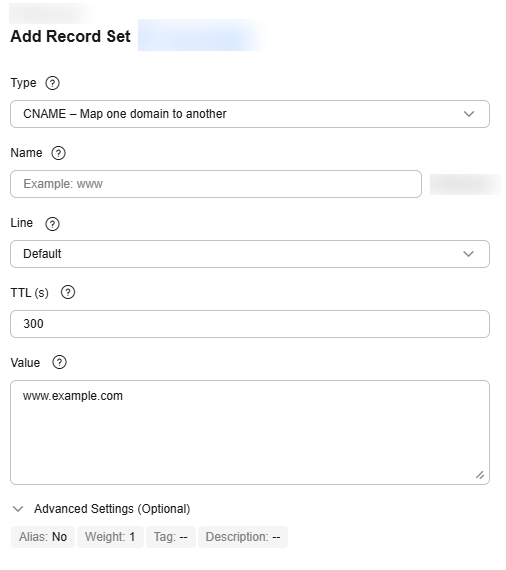
Table 2 Record set parameters Parameter
Description
Example
Type
Record set type.
Select a record set type based on service requirements.
For details, see Table 1.
CNAME – Map one domain to another
Name
Prefix of the domain name to be resolved.
This value is left empty by default.
For example, if the domain name is example.com, the value of the Name can be as follows:
- www: The domain name is www.example.com and usually used for a website.
- Left blank: The domain name is example.com and usually used for a website.
To use an at sign (@) as the domain name prefix, just leave this parameter blank.
- abc: The domain name is abc.example.com, a subdomain of example.com.
- mail: The domain name is mail.example.com and usually used for email servers.
- *: The domain name is *.example.com. It covers all subdomains of example.com.
Leave it blank.
Line
A specific route or path that the DNS server uses to determine which IP address to return based on the user's location, ISP, or other attributes.
The default value is Default.
- Default: returns the default resolution result irrespective of where the visitors come from.
- ISP: returns the resolution result based on end users' carrier networks. For details, see Configuring ISP Lines.
- Region: returns the resolution result based on end users' geographical locations. For details, see Configuring Region Lines.
- Custom Lines: returns the resolution result based on specified IP address ranges. For details, see Configuring Custom Lines.
Default
TTL (s)
How long a local DNS server caches a DNS record. It is measured in seconds.
Default value: 300
Value range: 1 to 2147483647
If your service address changes frequently, set TTL to a smaller value. Otherwise, set TTL to a larger value.
300
Value
The domain name returned for DNS resolution, which is usually another domain name that maps the target IP address.
You can enter a maximum of 50 unique IP addresses, each on a separate line.
www.example.com
Weight
Weight for the record set.
Default value: 1
Value range: 0 to 1000
If a resolution line in a zone contains multiple record sets of the same type, you can set different weights to each record set. For details, see Configuring Weighted Routing.
1
Tag
Identifier of the record set. Each tag contains a key and a value.
You can add up to 20 tags for a record set.
The tag key:
- Cannot be left blank.
- Must be unique for each resource.
- Can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
- Cannot start or end with a space, or cannot start with _sys_. Only letters, digits, spaces, and the following special characters are allowed: _.:=+-@
The tag value:
- Can be left blank.
- Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
- Can contain letters, digits, spaces, and special characters _ . : / = + - @.
NOTE:If your organization has configured tag policies for the DNS service, you need to add tags to your record sets based on the tag policies. If you add a tag that does not comply with the tag policies, record sets may fail to be created. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies.
example_key1
example_value1
Description
Supplementary information about the record set.
The description can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
Routing Internet traffic to a website
- Click OK.
A Mail Exchange (MX) record set is used to specify the mail server that handles emails from a specific domain name. When an email system sends an email, it searches for the desired MX record based on the domain name in the recipient address to determine the location of the target mail server, ensuring that the email can be correctly sent to the target server. An MX record set contains the addresses and priorities of multiple mail servers to ensure the reliability and efficiency of email transmission.
Constraints
An MX record cannot coexist with a CNAME, explicit URL, or implicit URL record for the same name and line.
For details about the conflict rules and handling measures, see Rules for Handling Record Set Conflicts.
Procedure
- Go to the Public Zones page.
- Locate the target zone and click Manage Record Sets in the Operation column.
- Click Add Record Set above the record set list.

- On the Add Record Set page, set record set parameters as instructed.
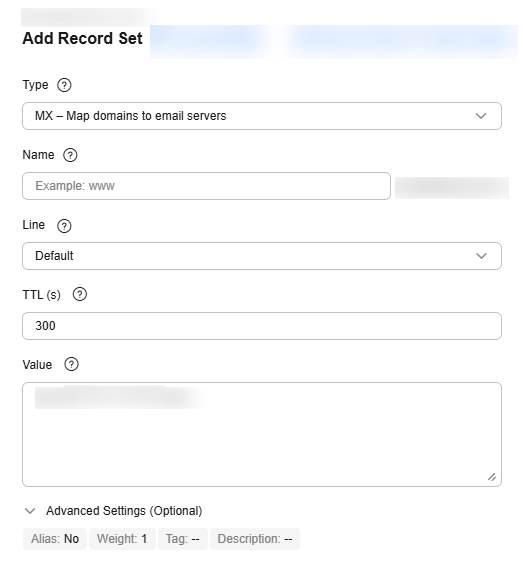
Table 3 Record set parameters Parameter
Description
Example
Type
Record set type.
Select a record set type based on service requirements.
For details, see Table 1.
MX – Map domains to email servers
Name
Prefix of the domain name to be resolved.
This value is left empty by default.
For example, if the domain name is example.com, the value of the Name can be as follows:
- www: The domain name is www.example.com and usually used for a website.
- Left blank: The domain name is example.com and usually used for a website.
To use an at sign (@) as the domain name prefix, just leave this parameter blank.
- abc: The domain name is abc.example.com, a subdomain of example.com.
- mail: The domain name is mail.example.com and usually used for email servers.
- *: The domain name is *.example.com. It covers all subdomains of example.com.
Leave it blank.
Line
A specific route or path that the DNS server uses to determine which IP address to return based on the user's location, ISP, or other attributes.
The default value is Default.
- Default: returns the default resolution result irrespective of where the visitors come from.
- ISP: returns the resolution result based on end users' carrier networks. For details, see Configuring ISP Lines.
- Region: returns the resolution result based on end users' geographical locations. For details, see Configuring Region Lines.
- Custom Lines: returns the resolution result based on specified IP address ranges. For details, see Configuring Custom Lines.
Default
TTL (s)
How long a local DNS server caches a DNS record. It is measured in seconds.
Default value: 300
Value range: 1 to 2147483647
If your service address changes frequently, set TTL to a smaller value. Otherwise, set TTL to a larger value.
300
Value
Enter email server addresses.
You can enter a maximum of 50 unique addresses, each on a separate line.
The format is [priority][mail-server-host-name].
Configuration rules:- priority: priority for an email server to receive emails. A smaller value indicates a higher priority.
- mail server host name: domain name provided by the email service provider
10 mailserver.example.com.
Alias
Whether to associate the record set with a cloud resource.
Unlike a CNAME record set, an alias supports second-level domain names.
This option is disabled by default.
Types of record sets that support alias include A, MX, AAAA, TXT, SRV and CAA.
Disabled
Alias Target
Cloud resource to be associated with the alias record set, which includes the cloud resource name and alias target.
-
Weight
Weight for the record set.
Default value: 1
Value range: 0 to 1000
If a resolution line in a zone contains multiple record sets of the same type, you can set different weights to each record set. For details, see Configuring Weighted Routing.
1
Tag
Identifier of the record set. Each tag contains a key and a value.
You can add up to 20 tags for a record set.
The tag key:
- Cannot be left blank.
- Must be unique for each resource.
- Can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
- Cannot start or end with a space, or cannot start with _sys_. Only letters, digits, spaces, and the following special characters are allowed: _.:=+-@
The tag value:
- Can be left blank.
- Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
- Can contain letters, digits, spaces, and special characters _ . : / = + - @.
NOTE:If your organization has configured tag policies for the DNS service, you need to add tags to your record sets based on the tag policies. If you add a tag that does not comply with the tag policies, record sets may fail to be created. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies.
example_key1
example_value1
Description
Supplementary information about the record set.
The description can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
Email domain name resolution
- Click OK.
An AAAA record is used to map a domain name to an IPv6 address. It is used for domain name resolution when websites support IPv6 addresses. If you have a website with a public IPv6 address and domain name, you can map the domain name to the IPv6 address by adding an AAAA record set. After the record set is added, the website can be accessed using the domain name.
Constraints
An AAAA record cannot coexist with a CNAME, explicit URL, or implicit URL record for the same name and line.
For details about the conflict rules and handling measures, see Rules for Handling Record Set Conflicts.
Procedure
- Go to the Public Zones page.
- Locate the target zone and click Manage Record Sets in the Operation column.
- Click Add Record Set above the record set list.

- On the Add Record Set page, set record set parameters as instructed.
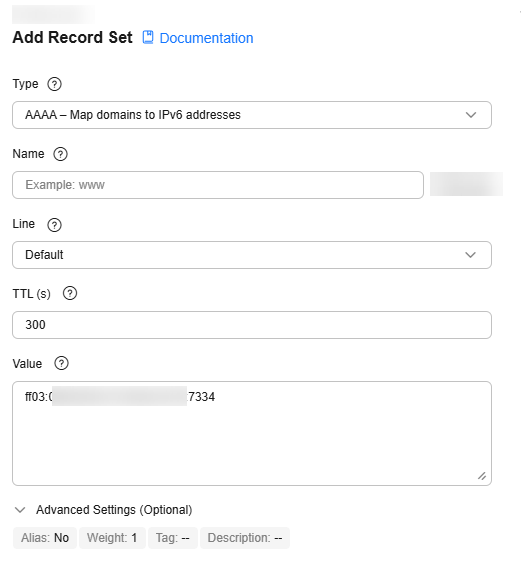
Table 4 Record set parameters Parameter
Description
Example
Type
Record set type.
Select a record set type based on service requirements.
For details, see Table 1.
AAAA – Map domain names to IPv6 addresses
Name
Prefix of the domain name to be resolved.
This value is left empty by default.
For example, if the domain name is example.com, the value of the Name can be as follows:
- www: The domain name is www.example.com and usually used for a website.
- Left blank: The domain name is example.com and usually used for a website.
To use an at sign (@) as the domain name prefix, just leave this parameter blank.
- abc: The domain name is abc.example.com, a subdomain of example.com.
- mail: The domain name is mail.example.com and usually used for email servers.
- *: The domain name is *.example.com. It covers all subdomains of example.com.
Leave it blank.
Line
A specific route or path that the DNS server uses to determine which IP address to return based on the user's location, ISP, or other attributes.
The default value is Default.
- Default: returns the default resolution result irrespective of where the visitors come from.
- ISP: returns the resolution result based on end users' carrier networks. For details, see Configuring ISP Lines.
- Region: returns the resolution result based on end users' geographical locations. For details, see Configuring Region Lines.
- Custom Lines: returns the resolution result based on specified IP address ranges. For details, see Configuring Custom Lines.
Default
TTL (s)
How long a local DNS server caches a DNS record. It is measured in seconds.
Default value: 300
Value range: 1 to 2147483647
If your service address changes frequently, set TTL to a smaller value. Otherwise, set TTL to a larger value.
300
Value
IPv6 addresses mapped to the domain name.
You can enter a maximum of 50 unique IP addresses, each on a separate line.
ff03:0db8:85a3:0:0:8a2e:0370:7334
Alias
Whether to associate the record set with a cloud resource.
Unlike a CNAME record set, an alias supports second-level domain names.
This option is disabled by default.
Types of record sets that support alias include A, MX, AAAA, TXT, SRV and CAA.
Disabled
Alias Target
Cloud resource to be associated with the alias record set, which includes the cloud resource name and alias target.
-
Weight
Weight for the record set.
Default value: 1
Value range: 0 to 1000
If a resolution line in a zone contains multiple record sets of the same type, you can set different weights to each record set. For details, see Configuring Weighted Routing.
1
Tag
Identifier of the record set. Each tag contains a key and a value.
You can add up to 20 tags for a record set.
The tag key:
- Cannot be left blank.
- Must be unique for each resource.
- Can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
- Cannot start or end with a space, or cannot start with _sys_. Only letters, digits, spaces, and the following special characters are allowed: _.:=+-@
The tag value:
- Can be left blank.
- Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
- Can contain letters, digits, spaces, and special characters _ . : / = + - @.
NOTE:If your organization has configured tag policies for the DNS service, you need to add tags to your record sets based on the tag policies. If you add a tag that does not comply with the tag policies, record sets may fail to be created. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies.
example_key1
example_value1
Description
Supplementary information about the record set.
Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
IPv6 address type
- Click OK.
A TXT record is used to identify and describe a domain name. It is usually used for configuring SPF (anti-spam), DKIM (email signature), and verifying the domain name ownership.
Constraints
A TXT record cannot coexist with a CNAME, explicit URL, or implicit URL record for the same name and line.
For details about the conflict rules and handling measures, see Rules for Handling Record Set Conflicts.
Procedure
- Go to the Public Zones page.
- Locate the target zone and click Manage Record Sets in the Operation column.
- Click Add Record Set above the record set list.

- On the Add Record Set page, set record set parameters as instructed.
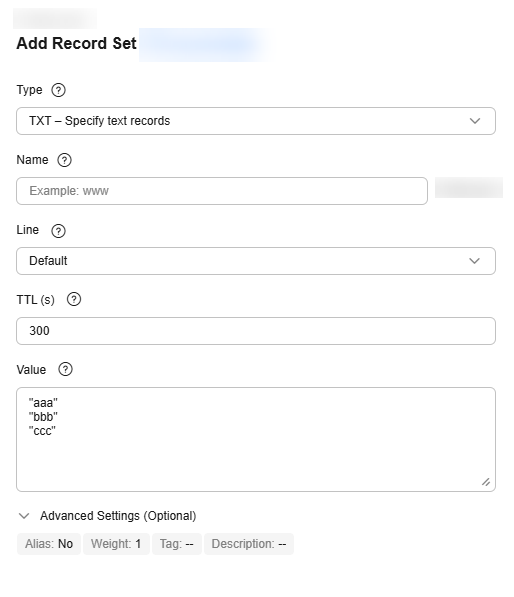
Table 5 Record set parameters Parameter
Description
Example
Type
Record set type.
Select a record set type based on service requirements.
For details, see Table 1.
TXT – Specify text records
Name
Prefix of the domain name to be resolved.
This value is left empty by default.
For example, if the domain name is example.com, the value of the Name can be as follows:
- www: The domain name is www.example.com and usually used for a website.
- Left blank: The domain name is example.com and usually used for a website.
To use an at sign (@) as the domain name prefix, just leave this parameter blank.
- abc: The domain name is abc.example.com, a subdomain of example.com.
- mail: The domain name is mail.example.com and usually used for email servers.
- *: The domain name is *.example.com. It covers all subdomains of example.com.
Leave it blank.
Line
A specific route or path that the DNS server uses to determine which IP address to return based on the user's location, ISP, or other attributes.
The default value is Default.
- Default: returns the default resolution result irrespective of where the visitors come from.
- ISP: returns the resolution result based on end users' carrier networks. For details, see Configuring ISP Lines.
- Region: returns the resolution result based on end users' geographical locations. For details, see Configuring Region Lines.
- Custom Lines: returns the resolution result based on specified IP address ranges. For details, see Configuring Custom Lines.
Default
TTL (s)
How long a local DNS server caches a DNS record. It is measured in seconds.
Default value: 300
Value range: 1 to 2147483647
If your service address changes frequently, set TTL to a smaller value. Otherwise, set TTL to a larger value.
300
Value
Enter text content as required.
Configuration rules:
- Text record values must be enclosed in double quotation marks.
- One or more text record values are supported, each on a separate line.
- A single text record value can contain multiple character strings, each of which is double quoted and separated from others using a space.
One character string cannot exceed 255 characters.
A value must not exceed 4,096 characters.
- The value cannot be left blank.
- The text cannot contain a backslash (\).
Alias
Whether to associate the record set with a cloud resource.
Unlike a CNAME record set, an alias supports second-level domain names.
This option is disabled by default.
Types of record sets that support alias include A, MX, AAAA, TXT, SRV and CAA.
Disabled
Alias Target
Cloud resource to be associated with the alias record set, which includes the cloud resource name and alias target.
-
Weight
Weight for the record set.
Default value: 1
Value range: 0 to 1000
If a resolution line in a zone contains multiple record sets of the same type, you can set different weights to each record set. For details, see Configuring Weighted Routing.
1
Tag
Identifier of the record set. Each tag contains a key and a value.
You can add up to 20 tags for a record set.
The tag key:
- Cannot be left blank.
- Must be unique for each resource.
- Can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
- Cannot start or end with a space, or cannot start with _sys_. Only letters, digits, spaces, and the following special characters are allowed: _.:=+-@
The tag value:
- Can be left blank.
- Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
- Can contain letters, digits, spaces, and special characters _ . : / = + - @.
NOTE:If your organization has configured tag policies for the DNS service, you need to add tags to your record sets based on the tag policies. If you add a tag that does not comply with the tag policies, record sets may fail to be created. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies.
example_key1
example_value1
Description
Supplementary information about the record set.
Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
TXT record set
- Click OK.
An SRV record is used to identify the services provided by a cloud server. It usually applies to VoIP, instant messaging, and email to provide load balancing, failover, and automatic service discovery.
Constraints
An SRV record cannot coexist with a CNAME, explicit URL, or implicit URL record for the same name and line.
For details about the conflict rules and handling measures, see Rules for Handling Record Set Conflicts.
Procedure
- Go to the Public Zones page.
- Locate the target zone and click Manage Record Sets in the Operation column.
- Click Add Record Set above the record set list.

- On the Add Record Set page, set record set parameters as instructed.
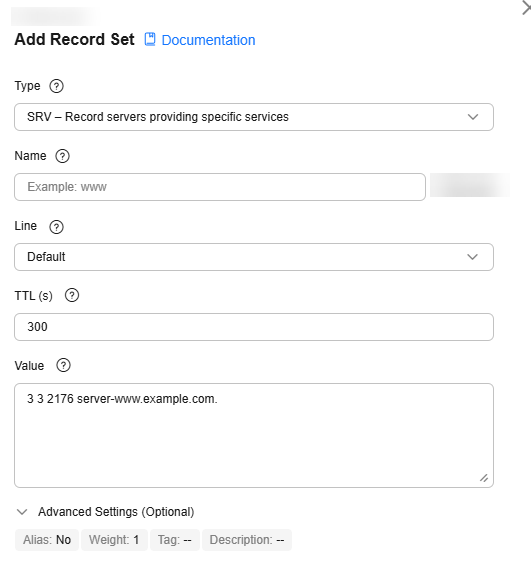
Table 6 Record set parameters Parameter
Description
Example
Type
Record set type.
Select a record set type based on service requirements.
For details, see Table 1.
SRV – Record servers providing specific services
Name
Prefix of the domain name to be resolved.
This value is left empty by default.
For example, if the domain name is example.com, the value of the Name can be as follows:
- www: The domain name is www.example.com and usually used for a website.
- Left blank: The domain name is example.com and usually used for a website.
To use an at sign (@) as the domain name prefix, just leave this parameter blank.
- abc: The domain name is abc.example.com, a subdomain of example.com.
- mail: The domain name is mail.example.com and usually used for email servers.
- *: The domain name is *.example.com. It covers all subdomains of example.com.
Leave it blank.
Line
A specific route or path that the DNS server uses to determine which IP address to return based on the user's location, ISP, or other attributes.
The default value is Default.
- Default: returns the default resolution result irrespective of where the visitors come from.
- ISP: returns the resolution result based on end users' carrier networks. For details, see Configuring ISP Lines.
- Region: returns the resolution result based on end users' geographical locations. For details, see Configuring Region Lines.
- Custom Lines: returns the resolution result based on specified IP address ranges. For details, see Configuring Custom Lines.
Default
TTL (s)
How long a local DNS server caches a DNS record. It is measured in seconds.
Default value: 300
Value range: 1 to 2147483647
If your service address changes frequently, set TTL to a smaller value. Otherwise, set TTL to a larger value.
300
Value
Enter the specific server address.
You can enter a maximum of 50 unique addresses, each on a separate line.
The value format is [priority] [weight] [port] [server host name].
Configuration rules:
- The priority, weight, and port number range from 0 to 65535.
- A smaller value indicates a higher priority.
- A larger value indicates a larger weight.
- The host name is the domain name of the target server.
NOTE:If the record set values have the same priority, requests to the domain name will be routed based on weights.
3 3 2176 server-www.example.com
Alias
Whether to associate the record set with a cloud resource.
Unlike a CNAME record set, an alias supports second-level domain names.
This option is disabled by default.
Types of record sets that support alias include A, MX, AAAA, TXT, SRV and CAA.
Disabled
Alias Target
Cloud resource to be associated with the alias record set, which includes the cloud resource name and alias target.
-
Weight
Weight for the record set.
Default value: 1
Value range: 0 to 1000
If a resolution line in a zone contains multiple record sets of the same type, you can set different weights to each record set. For details, see Configuring Weighted Routing.
1
Tag
Identifier of the record set. Each tag contains a key and a value.
You can add up to 20 tags for a record set.
The tag key:
- Cannot be left blank.
- Must be unique for each resource.
- Can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
- Cannot start or end with a space, or cannot start with _sys_. Only letters, digits, spaces, and the following special characters are allowed: _.:=+-@
The tag value:
- Can be left blank.
- Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
- Can contain letters, digits, spaces, and special characters _ . : / = + - @.
NOTE:If your organization has configured tag policies for the DNS service, you need to add tags to your record sets based on the tag policies. If you add a tag that does not comply with the tag policies, record sets may fail to be created. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies.
example_key1
example_value1
Description
Supplementary information about the record set.
Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
SRV record set
- Click OK.
An NS record specifies authoritative DNS servers for a domain name. If you want to delegate a subdomain to other DNS service providers, you can add an NS record for the subdomain.
Constraints
- The Name parameter is not left blank. This means that you can add NS record sets for subdomains of a domain name.
- The value of the Line parameter is not set to Default. This means that you can add NS record sets for the domain name with other resolution lines.
If a conflict occurs when you add an NS record, handle it by referring to Rules for Handling Record Set Conflicts.
Procedure
- Go to the Public Zones page.
- Locate the target zone and click Manage Record Sets in the Operation column.
- Click Add Record Set above the record set list.

- On the Add Record Set page, set record set parameters as instructed.
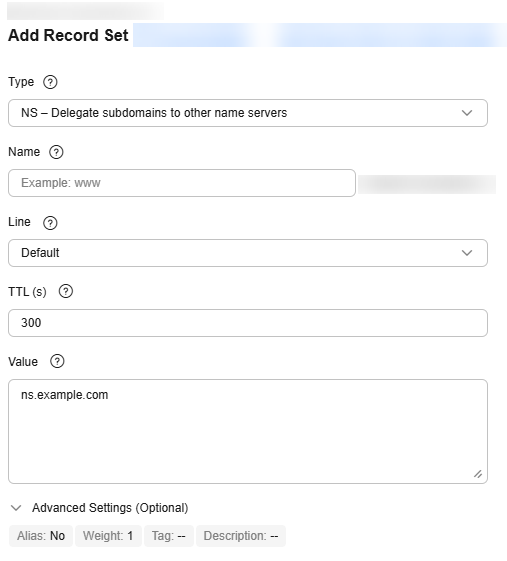
Table 7 Record set parameters Parameter
Description
Example
Type
Record set type.
Select a record set type based on service requirements.
For details, see Table 1.
NS – Delegate subdomains to other name servers
Name
Prefix of the domain name to be resolved.
This value is left empty by default.
For example, if the domain name is example.com, the value of the Name can be as follows:
- www: The domain name is www.example.com and usually used for a website.
- Left blank: The domain name is example.com and usually used for a website.
To use an at sign (@) as the domain name prefix, just leave this parameter blank.
- abc: The domain name is abc.example.com, a subdomain of example.com.
- mail: The domain name is mail.example.com and usually used for email servers.
- *: The domain name is *.example.com. It covers all subdomains of example.com.
www
Line
A specific route or path that the DNS server uses to determine which IP address to return based on the user's location, ISP, or other attributes.
The default value is Default.
- Default: returns the default resolution result irrespective of where the visitors come from.
- ISP: returns the resolution result based on end users' carrier networks. For details, see Configuring ISP Lines.
- Region: returns the resolution result based on end users' geographical locations. For details, see Configuring Region Lines.
- Custom Lines: returns the resolution result based on specified IP address ranges. For details, see Configuring Custom Lines.
Default
TTL (s)
How long a local DNS server caches a DNS record. It is measured in seconds.
Default value: 300
Value range: 1 to 2147483647
If your service address changes frequently, set TTL to a smaller value. Otherwise, set TTL to a larger value.
300
Value
Enter the addresses of the domain name servers to be authorized.
You can enter a maximum of 50 unique addresses, each on a separate line.
ns.example.com
Weight
Weight for the record set.
Default value: 1
Value range: 0 to 1000
If a resolution line in a zone contains multiple record sets of the same type, you can set different weights to each record set. For details, see Configuring Weighted Routing.
1
Tag
Identifier of the record set. Each tag contains a key and a value.
You can add up to 20 tags for a record set.
The tag key:
- Cannot be left blank.
- Must be unique for each resource.
- Can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
- Cannot start or end with a space, or cannot start with _sys_. Only letters, digits, spaces, and the following special characters are allowed: _.:=+-@
The tag value:
- Can be left blank.
- Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
- Can contain letters, digits, spaces, and special characters _ . : / = + - @.
NOTE:If your organization has configured tag policies for the DNS service, you need to add tags to your record sets based on the tag policies. If you add a tag that does not comply with the tag policies, record sets may fail to be created. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies.
example_key1
example_value1
Description
Supplementary information about the record set.
Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
NS record added for a subdomain
- Click OK.
A CAA record specifies the CA that issues HTTPS certificates for a domain name to prevent incorrect certificate issuing.
Constraints
A CAA record cannot coexist with a CNAME, explicit URL, or implicit URL record for the same name and line.
For details about the conflict rules and handling measures, see Rules for Handling Record Set Conflicts.
Procedure
- Go to the Public Zones page.
- Locate the target zone and click Manage Record Sets in the Operation column.
- Click Add Record Set above the record set list.

- On the Add Record Set page, set record set parameters as instructed.
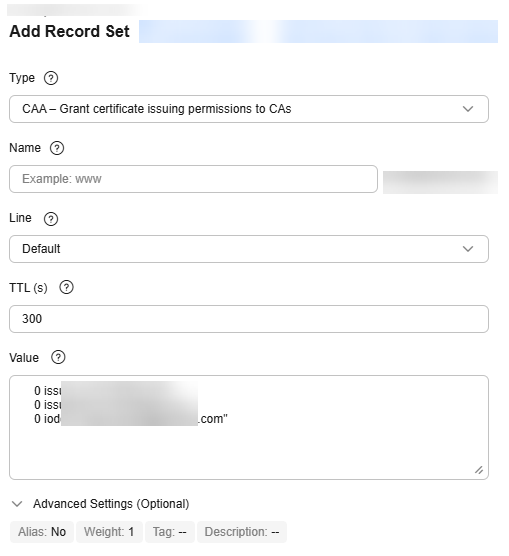
Table 8 Record set parameters Parameter
Description
Example
Type
Record set type.
Select a record set type based on service requirements.
For details, see Table 1.
CAA – Grant certificate issuing permissions to CAs
Name
Prefix of the domain name to be resolved.
This value is left empty by default.
For example, if the domain name is example.com, the value of the Name can be as follows:
- www: The domain name is www.example.com and usually used for a website.
- Left blank: The domain name is example.com and usually used for a website.
To use an at sign (@) as the domain name prefix, just leave this parameter blank.
- abc: The domain name is abc.example.com, a subdomain of example.com.
- mail: The domain name is mail.example.com and usually used for email servers.
- *: The domain name is *.example.com. It covers all subdomains of example.com.
Leave it blank.
Line
A specific route or path that the DNS server uses to determine which IP address to return based on the user's location, ISP, or other attributes.
The default value is Default.
- Default: returns the default resolution result irrespective of where the visitors come from.
- ISP: returns the resolution result based on end users' carrier networks. For details, see Configuring ISP Lines.
- Region: returns the resolution result based on end users' geographical locations. For details, see Configuring Region Lines.
- Custom Lines: returns the resolution result based on specified IP address ranges. For details, see Configuring Custom Lines.
Default
TTL (s)
How long a local DNS server caches a DNS record. It is measured in seconds.
Default value: 300
Value range: 1 to 2147483647
If your service address changes frequently, set TTL to a smaller value. Otherwise, set TTL to a larger value.
300
Value
CA to be authorized to issue certificates for a domain name or its subdomains.
You can enter a maximum of 50 different CAs, each on a separate line.
The format is [flag] [tag] [value].
Configuration rules:
- flag: CA identifier, an unsigned character ranging from 0 to 255. Usually, the value is set to 0.
- tag: You can enter 1 to 15 characters. Only letters and digits from 0 to 9 are allowed. The tag can be one of the following:
- issue: authorizes a CA to issue all types of certificates.
- issuewild: authorizes a CA to issue wildcard certificates.
- iodef: requests notifications once a CA receives invalid certificate requests.
- value: authorized CA or email address/URL required for notification once the CA receives invalid certificate requests. The value depends on the value of tag and must be enclosed in quotation marks (""). The value can contain a maximum of 255 characters. Only letters, digits, spaces, and the following special characters are allowed: -#*?&_~=:;.@+^/!%
0 issue "ca.abc.com"
0 issuewild "ca.def.com"
0 iodef "mailto:admin@domain.com"
0 iodef "http://domain.com/log/"
Alias
Whether to associate the record set with a cloud resource.
Unlike a CNAME record set, an alias supports second-level domain names.
This option is disabled by default.
Types of record sets that support alias include A, MX, AAAA, TXT, SRV and CAA.
Disabled
Alias Target
Cloud resource to be associated with the alias record set, which includes the cloud resource name and alias target.
-
Weight
Weight for the record set.
Default value: 1
Value range: 0 to 1000
If a resolution line in a zone contains multiple record sets of the same type, you can set different weights to each record set. For details, see Configuring Weighted Routing.
1
Tag
Identifier of the record set. Each tag contains a key and a value.
You can add up to 20 tags for a record set.
The tag key:
- Cannot be left blank.
- Must be unique for each resource.
- Can contain a maximum of 128 characters.
- Cannot start or end with a space, or cannot start with _sys_. Only letters, digits, spaces, and the following special characters are allowed: _.:=+-@
The tag value:
- Can be left blank.
- Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
- Can contain letters, digits, spaces, and special characters _ . : / = + - @.
NOTE:If your organization has configured tag policies for the DNS service, you need to add tags to your record sets based on the tag policies. If you add a tag that does not comply with the tag policies, record sets may fail to be created. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies.
example_key1
example_value1
Description
Supplementary information about the record set.
Can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
CAA record set
- Click OK.
- Go to the Public Zones page.
- Locate the target zone and click Manage Record Sets in the Operation column.
- Click Add Record Set above the record set list.

Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





