Record Set Types and Configuration Rules
Record Set Types and Configuration Rules
Record set types for public zones include A, CNAME, MX, AAAA, TXT, SRV, NS, SOA, and CAA. For details, see Table 1.
Wildcard Resolution Rules
DNS allows you to add a record set with the record set name set to an asterisk (*), for example, *.example.com. This can map all subdomains to the same value.
If you have added a wildcard record set for a domain name and added multiple record sets of the same type but different line for a specific subdomain, the DNS resolution complies with the following rules:
- Priority: Line match has a higher priority than domain name match.
- Priority of queries in the same line: If the line type is the same, exact match has a higher priority than fuzzy match.
- Priority for interaction between intelligent resolution and default lines: Wildcard domain name query matches the intelligent line, and exact domain name query matches the default line. If both of them are matched, the exact domain name query result is used.
Take example.com as an example.
- Configure wildcard records and a record for the subdomain starting with www.
The following table lists the parameter settings.
Subdomain
Line
Record Set Type
Value
www.example.com
Default
A
4.4.xx.xx
*.example.com
Default line for China Telecom
A
1.1.xx.xx
*.example.com
Default line for China Unicom
A
2.2.xx.xx
*.example.com
Default line for China Mobile
A
3.3.xx.xx
When a visitor is a China Telecom, China Unicom, or China Mobile user, 4.4.xx.xx is returned.
Rule: If both wildcard and exact domain name queries are matched, the exact domain name query result is used.
- Configure intelligent resolution for the subdomain www.example.com.
Subdomain
Line
Record Set Type
Value
www.example.com
Default
A
4.4.xx.xx
*.example.com
Default line for China Telecom
A
1.1.xx.xx
www.example.com
Default line for China Telecom
A
1.1.xx.xx
*.example.com
Default line for China Unicom
A
2.2.xx.xx
www.example.com
Default line for China Unicom
A
2.2.xx.xx
*.example.com
Default line for China Mobile
A
3.3.xx.xx
www.example.com
Default line for China Mobile
A
3.3.xx.xx
When visitors are China Telecom, China Unicom, or China Mobile users and they are accessing www.example.com, 1.1.xx.xx is returned for the China Telecom user, 2.2.xx.xx is returned for the China Unicom user, and 3.3.xx.xx is returned for the China Mobile user.
Rule: Line match has a higher priority than domain name match. If the line type is the same, exact match has a higher priority than fuzzy match.
TTL Setting Rules
TTL (time to live) specifies how long records are cached on a local DNS server. It is measured in seconds. Common TTL values for DNS records include 300 seconds (5 minutes), 3,600 seconds (1 hour), and 86,400 seconds (24 hours). The default TTL value for Huawei Cloud DNS is 300 seconds.
When receiving requests for a domain name, the local DNS server asks the authoritative DNS server for the required DNS record, and then caches the record for a period of time, as defined by the TTL value specified in the record.
- During this TTL period, if the local DNS server receives requests for this domain name again, it will not request the record from the authoritative DNS server, but directly returns the cached record.
- When the TTL expires, the local DNS server clears the cached record. If the local DNS server receives new DNS queries for the domain name, it forwards the new DNS queries to the authoritative DNS server to obtain the latest resolution result and caches the result.
|
TTL Setting |
Scenarios |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Increase the TTL value. |
Reducing network traffic |
A larger TTL value allows DNS records to be cached on the client or server for a longer period, leading to fewer queries to the authoritative DNS servers and reduced network load. |
|
Faster response |
In IP packets, a larger TTL value allows packets to survive longer on the network. This helps reduce the number of retransmission requests and prevent network congestion. |
|
|
Stable network |
In a stable network with low packet loss, a large TTL value can improve data transmission efficiency by avoiding the need for retransmissions. |
|
|
Decrease the TTL value. |
Quick update |
|
|
Testing and diagnosis |
In network testing, a small TTL value is beneficial for quickly identifying and troubleshooting network issues. By setting a low TTL, packets are designed to expire quickly, which makes them easy to trace and analyze. |
|
|
Dynamic network environment |
A small TTL value can minimize the impact of outdated routing data on a network where routes are frequently changing. This improves network adaptability and response speed. |
|
|
Reducing network congestion |
A small TTL value can help prevent network congestion, particularly in bandwidth-constrained environments. |
To set the TTL value, you need to consider both the stability and update requirements of records. For stable records, set a large TTL value, while for frequently changed records, set a small TTL value. Pay attention to the following points:
- A balance between load and response: When adjusting the TTL value, you need to balance the network load and response speed. This aims to prevent delays in updates out of a high TTL value or load increase out of a low TTL value.
- Network environment evaluation: You need to set an appropriate TTL value after considering both the network stability and packet loss rate.
- Monitoring and testing: After adjusting the TTL value, you need to monitor and test its impact to ensure the desired outcome and make further adjustments if needed.
- Change management: Before changing a DNS record, such as changing the server IP address, set a lower TTL value to allow you to get fresh IPs more often. Once the change is applied, change the TTL value to the original one.
Record Set Application Example
Record sets are used in following scenarios:
- Routing Internet traffic to a website
A and AAAA record sets are usually used to map domain names used by websites to IPv4 or IPv6 addresses of web servers where the websites are deployed.
Figure 1 Accessing a website over the Internet using domain name
- Private domain name resolution
On a private network, A and AAAA record sets translate private domain names into private IP addresses.
Figure 2 Private domain name resolution
- Email domain name resolution
MX, CNAME, and TXT record sets are usually used for email services.
Figure 3 Email domain name resolution
- Reverse resolution on a private network
PTR records translate private IP addresses into private domain names.
Figure 4 Reverse resolution on a private network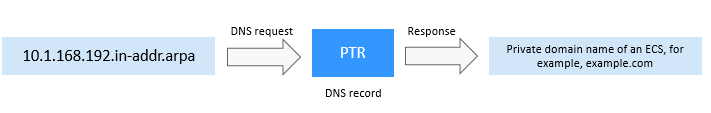
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





