Managing Logstash Cluster Logs
CSS provides log query and log backup, enabling you to easily manage and analyze logs to efficiently locate faults, optimize performance, and enhance system security.
- Log query: On the log management page of the CSS management console, you can query the latest log records by node, so you can quickly locate or diagnose issues.
- Log backup: Cluster logs are periodically synchronized to OBS buckets. You can download them for in-depth analysis at any time. You can configure custom log backup policies by specifying backup schedules and storage locations. The system backs up all critical logs, including run logs and deprecation logs. They provide comprehensive data for auditing and troubleshooting purposes.
Impact on Billing
When log backup is enabled, the generated log backups are stored in OBS buckets, which will result in additional costs. For details, see Object Storage Service Billing.
Prerequisites
The OBS bucket used for storing log backups has been created. The OBS bucket must meet the following requirements:
- Storage Class: Standard.
- Region: the same as that of the cluster.
Querying Logs
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > Logstash.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The cluster information page is displayed.
- Choose Logs > Log Search. The Log Search page is displayed.
You can search log records by node or keyword. For a detailed description of each type of logs, see Log Types.
When a log file reaches 128 MB or when the time reaches 00:00 UTC, the system automatically compresses and archives it. Only unarchived logs appear on the log search page, while archived logs remain accessible through the log backup function.
Backing Up Logs
Cluster logs can be backed up to OBS buckets, where you can download them for in-depth analysis at any time.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > Logstash.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The cluster information page is displayed.
- Choose Logs > Log Backup. The Log Backup page is displayed.
- Enable log backup.
- Back up logs. Two options are available: automatic or manual.
- Check the backed-up log files.
Logs are backed up incrementally. After the backup is successful, you can access the target OBS bucket to obtain the full log files by clicking Log Path.
Figure 3 OBS bucket address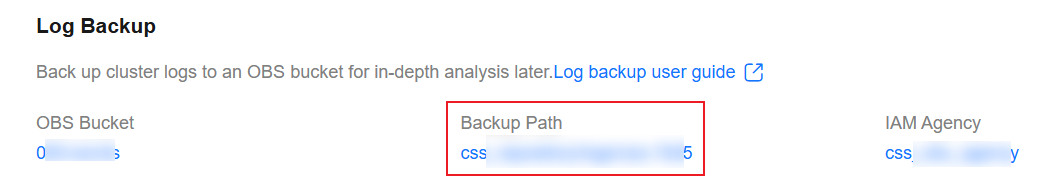
Table 3 lists the log types.
- If the log backup function is no longer needed, you can disable it.
On the Log Backup page, click Disable Backup. In the displayed dialog box, click OK. Disabling log backup does not automatically delete existing log backups. Instead, you need to manually delete them on the OBS console.
Log Types
|
Log Type |
Description |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
Run logs |
Run logs record a cluster's node and pipeline status, such as source-destination connectivity, pipeline creation or modification, and pipeline running errors. |
Check run logs to troubleshoot pipeline errors. |
|
Deprecation logs |
Deprecation logs record deprecation warnings. Deprecation warnings are written to this log when you use APIs, configurations, or functions that are marked for removal in future versions. You cannot check deprecation logs on the console. To check them, you need to back them up to an OBS bucket first. |
Check for APIs or features that are about to expire in future versions. |
- Run log description
Run logs record a cluster's node and pipeline status. For example, the log record below indicates that the destination cluster could not be reached. You need to check whether the cluster address is correct and whether the cluster status is normal.
Figure 4 A sample of run logs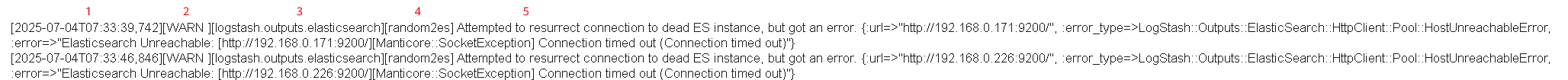 Log content:
Log content:- 1. Log generation time
- 2. Log level, which can be DEBUG, INFO, WARN, or ERROR
- 3. Log-generating module
- 4. Name of the log-generating node
- 5. Log content
- Deprecation log description
Deprecation logs record deprecation warnings.
Figure 5 A sample of deprecation logs Log content:
Log content:- 1. Log generation time
- 2. Log level, which can only be DEPRECATION.
- 3. Log-generating module
- 4. Log content. The log record shown in the figure above indicates that the ECS compatibility mode was not explicitly declared for a plugin when Logstash was started.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot