Using pg_waldump to Parse WAL Logs of RDS for PostgreSQL
After buying an RDS for PostgreSQL instance, you can log in to a Linux ECS, install a PostgreSQL client on the ECS, and then use the open-source pg_waldump to parse WAL logs of the RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Step 1: Buy an ECS
- Log in to the management console and check whether there is an ECS available.
- If there is a Linux ECS, go to Step 2: Install a PostgreSQL Client.
- If there is no Linux ECS, go to 2.
- Buy an ECS and select Linux (for example, CentOS) as its OS.
To download a PostgreSQL client to the ECS, bind an EIP to the ECS.
For details about how to purchase a Linux ECS, see Purchasing an ECS in Custom Config Mode in the Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
Step 2: Install a PostgreSQL Client
The PostgreSQL client version must be the same as the RDS for PostgreSQL instance version. Otherwise, WAL logs may fail to be parsed.
- Log in to the ECS. For details, see Logging In to a Linux ECS Using VNC in the Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
- Install a PostgreSQL client.
The PostgreSQL community provides client installation methods for different OSs. You can download and install a client using the installation tool of the OS. This installation method is simple but can be used only for the OSs supported by the PostgreSQL community.
In this example, CentOS 7 is used. Use the default installation tool of the OS to install a client (PostgreSQL 15 or earlier).
Figure 1 Obtaining the installation tool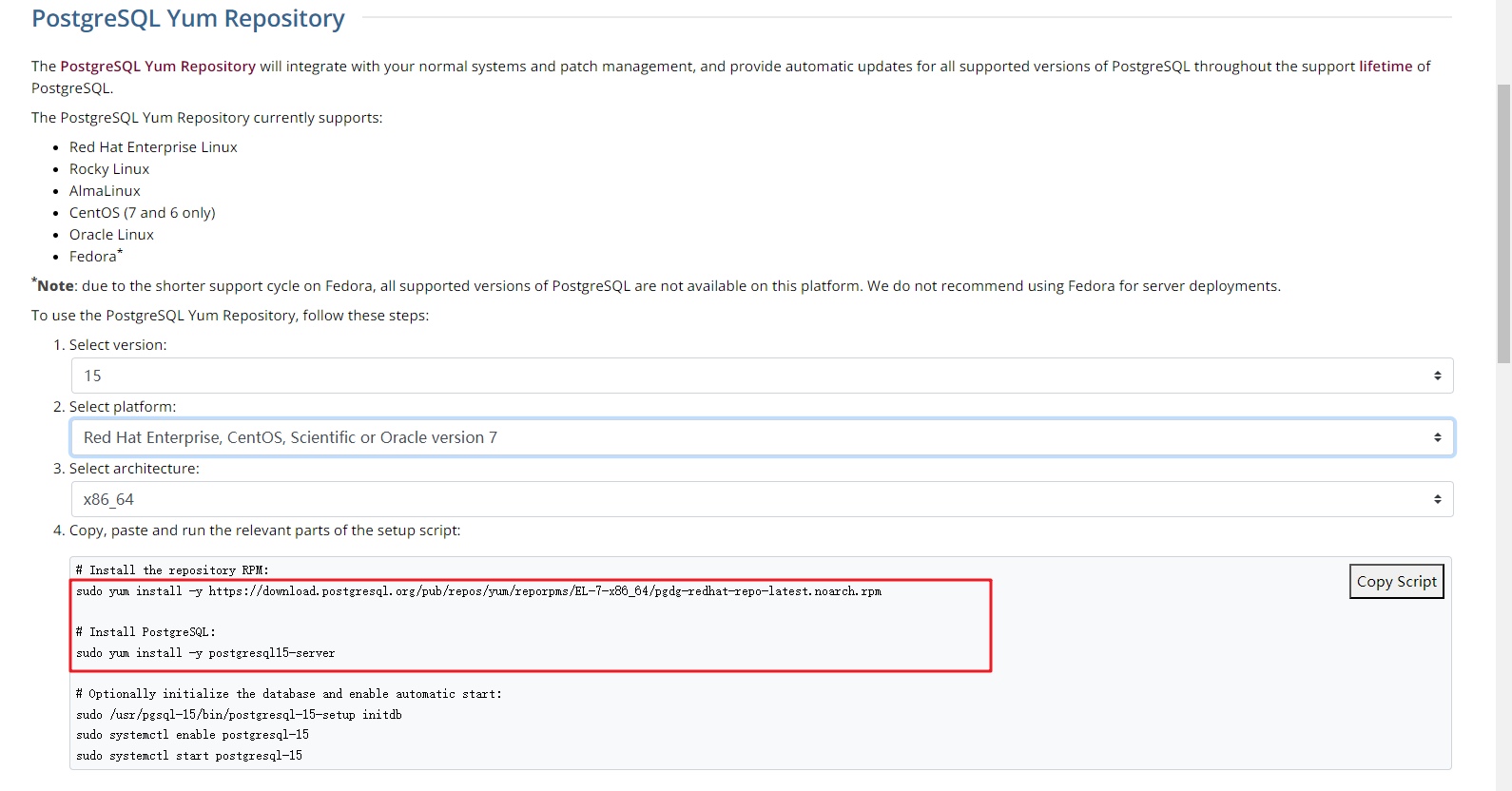
Run the installation commands:
sudo yum install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm sudo yum install -y postgresql15-server
Check whether the installation is successful.
psql -V
Figure 2 Successful installation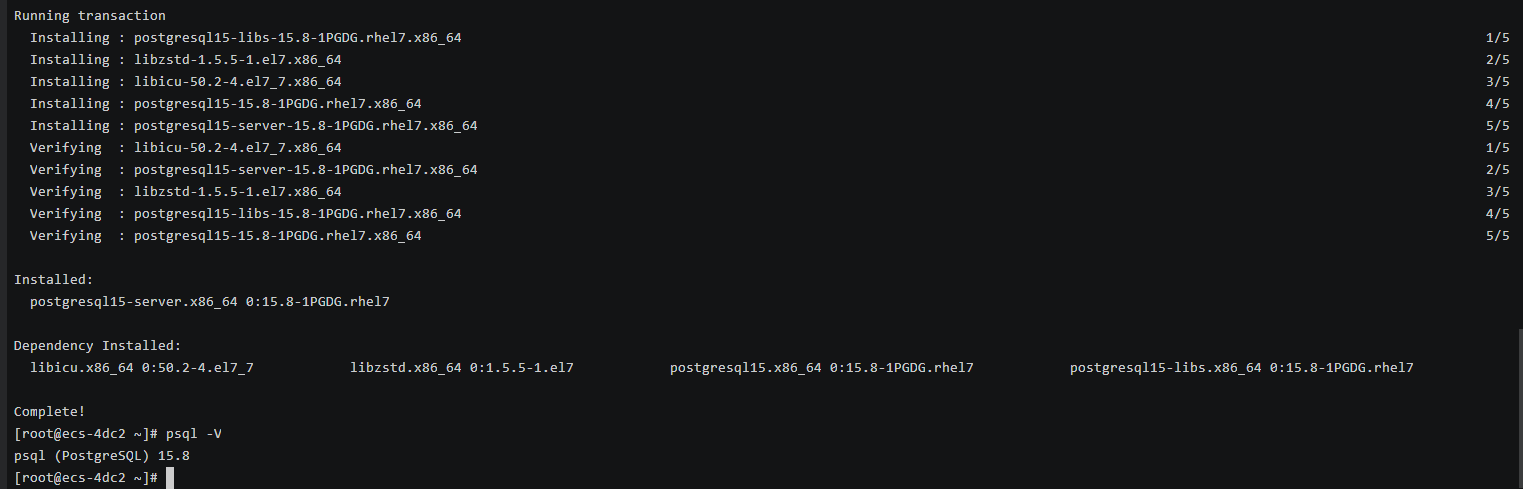
- Log in to the ECS. For details, see Logging In to a Linux ECS Using VNC in the Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
- Install a PostgreSQL client.
Installation from source code: This installation method has no restrictions on RDS PostgreSQL instance versions and ECS OS types.
The following uses an ECS using the Huawei Cloud EulerOS 2.0 image as an example to describe how to install a PostgreSQL 16.4 client.
Figure 3 Checking the ECS image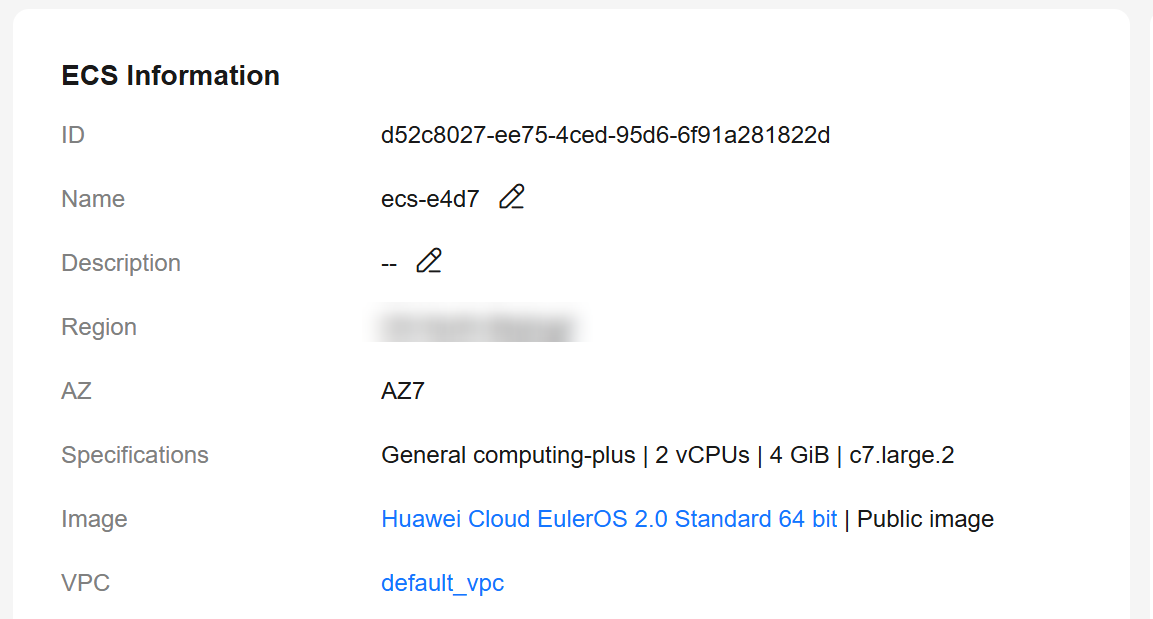
- To use SSL, download OpenSSL to the ECS in advance.
sudo yum install -y openssl-devel
- Obtain the code download link, run wget to download the installation package to the ECS, or download the installation package to the local PC and then upload it to the ECS.
wget https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/source/v16.4/postgresql-16.4.tar.gz
- Decompress the installation package.
tar xf postgresql-16.4.tar.gz
- Compile the source code and then install the client.
cd postgresql-16.4 ./configure --without-icu --without-readline --without-zlib --with-openssl make -j 8 && make install

If --prefix is not specified, the default path is /usr/local/pgsql. The client can be installed in the simplest way.
Figure 4 Compilation and installation
- Add the following code to the /etc/profile file to configure environment variables:
export PATH=/usr/local/pgsql/bin:$PATH export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/pgsql/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH source /etc/profile
- Test whether the psql is available.
psql -V
Figure 5 Testing psql
- To use SSL, download OpenSSL to the ECS in advance.
Step 3: Obtain Incremental WAL Logs from an RDS for PostgreSQL Instance
- Download incremental backups and store them in a directory (for example, /download/backup).
- Decompress the script and run the following command to decompress the incremental backups to a temporary directory (for example, /tmp/wal).
python restore_wal.py /download/backup /tmp/wal
- /download/backup: the directory where PostgreSQL incremental backups are stored
- /tmp/wal: the directory where PostgreSQL WAL logs are stored temporarily
Step 4: Use pg_waldump to Parse the Specified WAL Logs
Example: Run the following command to display the first five lines of the WAL log 000000010000000000000003.
pg_waldump -n 5 000000010000000000000003
The command output is as follows:
rmgr: Standby len (rec/tot): 50/ 50, tx: 0, lsn: 0/03000028, prev 0/02000100, desc: RUNNING_XACTS nextXid 765 latestCompletedXid 764 oldestRunningXid 765 rmgr: XLOG len (rec/tot): 114/ 114, tx: 0, lsn: 0/03000060, prev 0/03000028, desc: CHECKPOINT_SHUTDOWN redo 0/3000060; tli 1; prev tli 1; fpw true; xid 0:765; oid 16393; multi 1; offset 0; oldest xid 730 in DB 1; oldest multi 1 in DB 1; oldest/newest commit timestamp xid: 0/0; oldest running xid 0; shutdown rmgr: XLOG len (rec/tot): 54/ 54, tx: 0, lsn: 0/030000D8, prev 0/03000060, desc: PARAMETER_CHANGE max_connections=200 max_worker_processes=8 max_wal_senders=10 max_prepared_xacts=10 max_locks_per_xact=64 wal_level=logical wal_log_hints=off track_commit_timestamp=off rmgr: Standby len (rec/tot): 50/ 50, tx: 0, lsn: 0/03000110, prev 0/030000D8, desc: RUNNING_XACTS nextXid 765 latestCompletedXid 764 oldestRunningXid 765 rmgr: Standby len (rec/tot): 50/ 50, tx: 0, lsn: 0/03000148, prev 0/03000110, desc: RUNNING_XACTS nextXid 765 latestCompletedXid 764 oldestRunningXid 765
For more information about pg_waldump, see the community documentation.
FAQ
Q: What can I do if the following error is reported during command execution?
pg_waldump: error: could not find a valid record after xxx/xxxxxxxx
A: Run the pg_waldump -V command to check whether the major version of pg_waldump is the same as that of the RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
If they are inconsistent, perform Step 2: Install a PostgreSQL Client again to install a client of the correct version.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





