Migrating Data from Hive to MRS with CDM
Scenarios
Cloud Data Migration (CDM) is an efficient and easy-to-use service for batch data migration. Leveraging cloud-based big data migration and intelligent data lake solutions, CDM offers user-friendly functions for migrating data and integrating diverse data sources into a unified data lake. These capabilities simplify the complexities of data source migration and integration, significantly enhancing efficiency.
You can use CDM to migrate full and incremental data from Hive. CDM implements full migration by migrating files in batches, enabling efficient data extraction and writing. CDM data migration leverages the distributed computing framework to enable data transfer between the source and destination by migrating data in batches.
This section uses the Huawei Cloud CDM service as an example to describe how to migrate all data from Hive clusters in an on-premises IDC or on a public cloud to Huawei Cloud MRS clusters. The data volume can be tens of TBs or less.
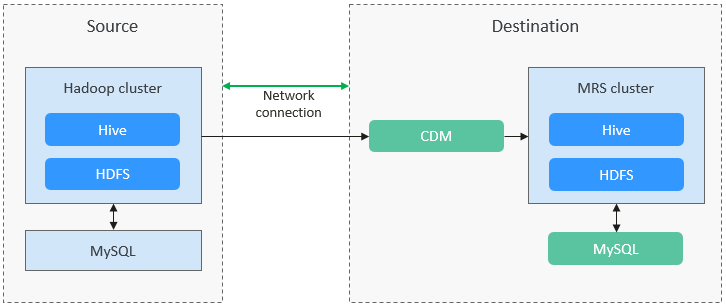
Solution Architecture
Hive data consists of two parts:
- Hive metadata, which is stored in the databases such as MySQL. By default, the metadata of an MRS Hive cluster is stored in MRS DBService. You can also use RDS for MySQL as the external metadata database.
- Hive service data, which is stored in HDFS or OBS.
Solution Advantages
Scenario-based migration migrates snapshots and then restores table data to speed up migration.
Migration Survey
Before migrating Hive data, you need to conduct a survey on the source Hive component to evaluate the risks that may occur during the migration and impact on the system. The survey covers the Hive component version, amount of data to be migrated, tables, and number of tasks. For details, see Table 1.
|
Survey Item |
Content |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Version compatibility |
Hive version |
3.1.1 |
|
Data volume |
Total amount of Hive data to be migrated |
Total data volume: 10 TB per node |
|
Tables |
How many Hive tables need to be migrated, the number of partitioned tables, and how many tables there are of different sizes (tables smaller than 1 GB, tables smaller than 1 TB, and the size of the largest table); and the largest number of partitions in any table (it cannot be more than several tens of thousands) |
There are three databases for Hive tables to be migrated, each database has 3000 tables, and 10% of the tables have partitions. The largest table is 100 TB, most tables are 20 GB, and the largest number of partitions is 1000. |
|
Number of tasks |
Number of tasks processed by Hive every day and the maximum number of concurrent tasks |
Hive processes 10,000 tasks every day. Each task contains two or three SQL statements, and each SQL statement is associated with two or three tables. The maximum number of concurrent tasks is 10. |
|
Permissions |
|
|
|
Job submission |
Method used to submit Hive jobs. For example, you can run the hive or beeline command to submit a job. |
Run the beeline command to submit a job. |
|
User-defined function (UDF) |
Whether UDFs are used. If UDFs are used, collect the number and types of UDFs. |
20 UDFs are used, including UDF, UDTF, and UDAF. |
Networking Types
The migration solution supports various networking types, such as the public network, VPN, and Direct Connect. Select a networking type based on your requirements. Ensure that the source Hive and destination MRS clusters can communicate with both the CDM cluster and MgC Agent. In this way, data can be migrated and verified.
|
Migration Network Type |
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
|
Direct Connect |
|
|
|
VPN |
|
|
|
Public IP address |
|
|
Notes and Constraints
- This section uses CDM 2.9.1.200 as an example to describe how to migrate data. The operations may vary depending on the CDM version. For details, see the operation guide of the required version.
- For details about the data sources supported by CDM, see Supported Data Sources. If the data source is Apache Hive, the recommended version is 1.2.X or 3.1.X. Version 2.x is not supported. Before performing the migration, ensure that the data source supports migration.
- Migrating a large volume of data has high requirements on network communication. When a migration task is executed, other services may be adversely affected. You are advised to migrate data during off-peak hours.
- During the migration, data inconsistency may occur if the changes on the Hive tables in the source cluster are not timely synchronized to the destination cluster. You can use the verification tool to identify inconsistent data, and migrate or add the data.
- Data attributes, such as the owner, ACL, and checksum, cannot be migrated using CDM. For details, see Constraints and Limitations on CDM Data Migration.
Migrating Hive Data
- Log in to the CDM console.
- Create a CDM cluster. The security group, VPC, and subnet of the CDM cluster must be the same as those of the destination cluster to ensure that the CDM cluster can communicate with the MRS cluster.
- On the Cluster Management page, locate the row containing the desired cluster and click Job Management in the Operation column.
- On the Links tab page, click Create Link.
- Create links to the source and destination clusters by referring to Creating a Link Between CDM and a Data Source.
Set the connector type based on the actual cluster. For an MRS cluster, select MRS Hive. For a self-built cluster, select Apache Hive.
Figure 2 Creating a Hive Link
- Create a storage database after data migration in the destination cluster.
- Choose Job Management and click the Table/File Migration tab. Then, click Create Job.
- On the displayed page, configure the job name, select the data links created in 5 as the source link and destination link, select the database and table to be migrated, and click Next. For more information about job parameters, see Table/File Migration Jobs.
Figure 3 Hive job parameters

- Configure the mapping between the source fields and destination fields and click Next.
- On the task configuration page that is displayed, click Save without any modification.
- Choose Job Management and click Table/File Migration. Locate the row containing the job to run and click Run in the Operation column to start migrating Hive data.
- After the migration is complete, you can run the same query statement in Hive Beeline in the source and destination clusters to compare the query results.
For example, query the number of records in the catalog_sales table in the destination and source clusters to check whether the number of data records is the same.
select count(*) from catalog_sales;Figure 4 Data records of the source cluster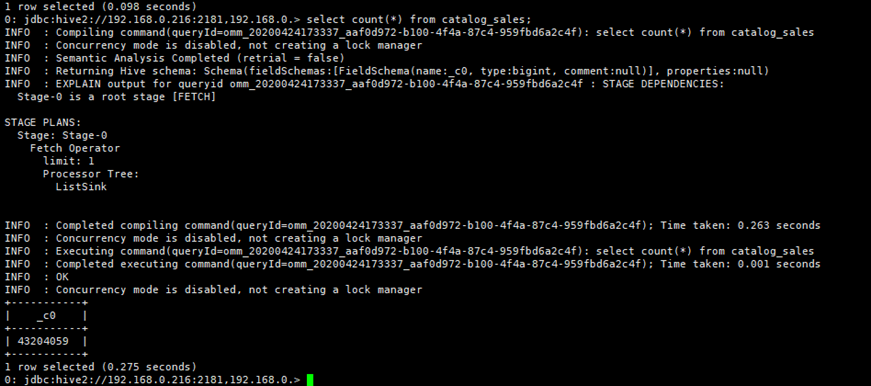 Figure 5 Data records of the destination cluster
Figure 5 Data records of the destination cluster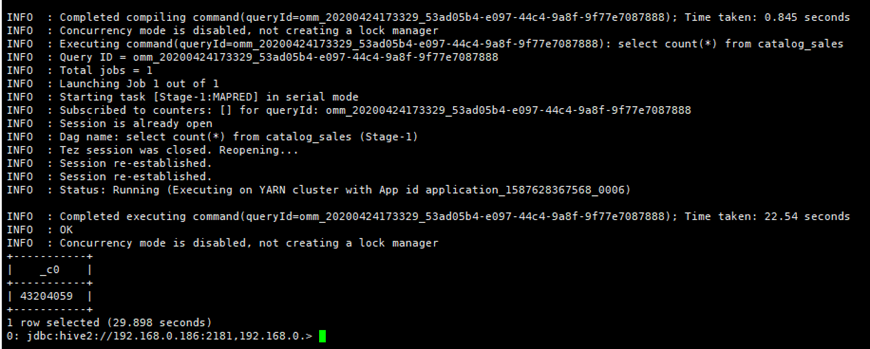
- (Optional) If new data in the source cluster needs to be periodically migrated to the destination cluster, perform the migration based on the data adding mode. Configure a scheduled task to migrate incremental data until all services are migrated to the destination cluster.
- If no table is added or deleted, the data structure of existing tables is not modified, and only the Hive table data is modified, you only need to migrate the Hive files stored on HDFS or OBS. For details about how to migrate data, see the description about the new data migration method in Migrating Data from Hadoop to MRS with CDM.
- If a Hive table is added, choose Job Management and click the Table/File Migration tab. Click Edit in the Operation column of the Hive migration job and select the new data table for data migration.
- If a Hive table is deleted or the data structure of an existing table is modified, manually delete the table from the destination cluster or manually update the table structure.
Verifying Hive Data Migration
The following operations use the MgC Agent for Linux as an example to describe how to verify Hive data consistency after the migration. The MgC Agent version is 25.3.3. The actual operations may vary depending on the Agent version. For details, see Big Data Verification.
- Create two Linux and one Windows ECSs. The security groups, VPCs, and subnets of the ECSs must be the same as those of the destination MRS cluster. For details, see Purchasing an ECS in Custom Config Mode.
In subsequent operations, the MRS cluster client and MgC Agent need to be installed on different ECSs.
- Install an MRS cluster client.
Install the MRS cluster client on the newly created Linux host. For details, see Installing a Client (MRS 3.x).
- Create an MgC project.
- Log in to the MgC console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Other > Settings.
- Choose Migration Projects and click Create Project.
- In the window displayed on the right, select Complex migration (for big data) for Project Type and set Project Name. For example, set the name to mrs-hive.

The project type cannot be changed after the project is created.
- Click Create. After the project is created, you can view it in the project list.
- Deploy the MgC Agent on the other newly created Linux host and create a connection. For details about MgC Agent deployment, see Deploying the MgC Agent (Formerly Edge).
- On the top of the navigation pane, select the created project and choose Overview > MgC Agent to download the Agent installation package.
In the Linux area, click Download Installation Package or Copy Download Command to download the MgC Agent installation program to the Linux host.
- Decompress the MgC Agent installation package.
tar zxvf MgC-Agent.tar.gz
- Go to the scripts directory in the MgC Agent installation directory.
cd MgC-Agent/scripts/
- Run the MgC Agent installation script.
./install.sh
- Enter the EIP bound to the NIC of the Linux host. The IP address will be used for accessing the MgC Agent console.
If the entered IP address is not used by the Linux host, the system will display a message, asking you whether to use a public IP address of the Linux host as the MgC Agent access address.
- Check if the message shown in the following figure is displayed. If it is, the MgC Agent for Linux has been installed. The port in the following figure is for reference only. Note the actual port returned.
Figure 6 MgC Agent successfully installed

Update environment variables.
source /opt/cloud/MgC-Agent/scripts/setenv.sh
You need to allow inbound TCP traffic on port 27080. You can do that by adding an inbound rule to the security group of the Linux host where the MgC Agent is installed. For the rule, set Source to the IP address of the Windows host you use to remotely access the MgC Agent console.
- After the installation is complete, open a browser on the Windows host created in 1 and enter https://<IP-address>:<Port-number> to access the MgC Agent login page. For example, if the IP address is 192.168.x.x and the port number is 27080, the MgC Agent access address is https://192.168.x.x:27080.
The IP address is the one you entered in 4.e, and the port number is the one displayed in 4.f after the MgC Agent is successfully installed.
- Log in to the MgC Agent console.
- On the login page, select Huawei Cloud Access Key.
- Enter an AK/SK pair of your Huawei Cloud account, and select the region where you create the migration project on MgC from the drop-down list.
- Click Log In. The Overview page of the MgC Agent console will open.
- (Required only for the first login) On the Overview page, click Connect Now in the upper right corner. The Connect to MgC page is displayed.
- Set the following parameters on the displayed page:
- Step 1: Select Connection Method
Enter an AK/SK pair of your Huawei Cloud account.
- Step 2: Select MgC Migration Project
MgC Migration Project: Click List Migration Projects, and select the migration project created in 3 from the drop-down list.
- Step 3: Preset MgC Agent Name
MgC Agent Name: Enter a custom MgC Agent name, for example, Agent.
- Step 1: Select Connection Method
- Click Connect, confirm the connection to MgC, and click OK.
If Connected shows up on the overview page, the connection to MgC is successful.
- Set the following parameters on the displayed page:
- On the top of the navigation pane, select the created project and choose Overview > MgC Agent to download the Agent installation package.
- Create a credential for the executor.
- In the navigation pane, choose Agent-based Discovery > Credentials.
- Click Add Credential above the list and set the following parameters to create source and destination credentials.
Table 3 Parameters for creating a Hive credential Parameter
Configuration
Resource Type
Select Bigdata.
Resource Subtype
Select Big Data Machine.
Credential Name
Enter a custom credential name. For example, the source credential name is source_executor, and the destination credential name is target_executor.
Authentication Method
Select Username/Password.
Username
Enter the username for connecting to the source Hive client or the destination MRS cluster client node, for example, hive_user.
Password
Enter the user password.
After the credential is created, wait until Sync Status of the credential in the credential list changes to Synced.
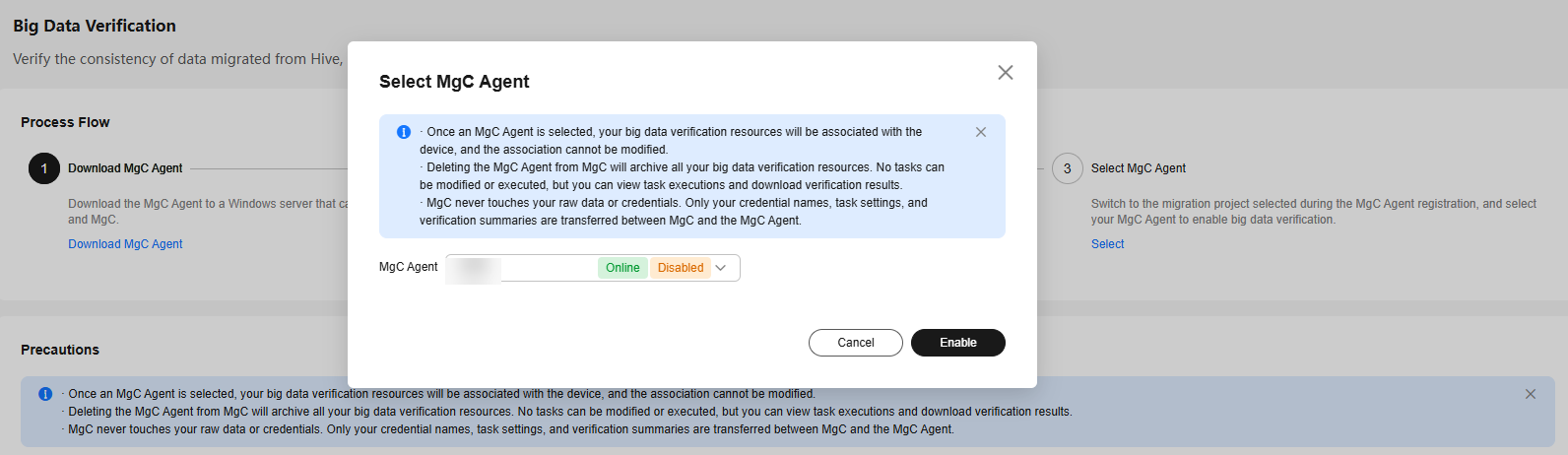
- Select and enable the MgC Agent (required only when you use it for the first time).
- Log in to the MgC console.
- In the upper left corner of the page, select the project created in 3.
- In the navigation pane, choose Migrate > Big Data Verification.
- Click Select MgC Agent. The Select MgC Agent dialog box is displayed.
- Select the MgC Agent that has been successfully connected to MgC from the drop-down list and click Enable.
Figure 7 Enabling the MgC Agent
- Create a Hive Metastore source connection.
- In the Features area of the Big Data Verification page, click Migration Preparations. The Migration Preparations page is displayed.
- Choose Connection Management and click Create Connection. On the displayed page, select Hive MetaStore for Big Data Component and click Next.
- On the Configure Connection page, set the following parameters. For details, see "Parameters for creating a connection to Hive Metastore" in Creating a Connection to a Source Component.
Table 4 Parameters for the source Hive connection Parameter
Configuration
Connection To
Select Source.
Connection Name
The default name is Hive-Metastore-4 random characters (including letters and digits). You can also enter a custom name.
MgC Agent
Select the enabled MgC Agent.
Secure Connection
Choose whether to enable Secure Connection as required. For example, do not select Secure Connection.
Hive Version
Select the version of the source Hive cluster.
Hive Metastore IP Address
Enter the IP address for connecting to the Hive Metastore.
Hive Metastore Thrift Port
Enter the port for connecting to the Hive Metastore Thrift service. The default port is 9083.
- Click Test. After the test is successful, click Confirm to create the source Hive MetaStore connection.
- Create and run a metadata collection task.
- On the Migration Preparations page, click Metadata Management. In the displayed area, click Create Metadata Collection Task on the Tasks tab page. In the displayed Create Task -Metadata Collection window, set the following parameters and click Confirm.
- Task Name: Enter a task name.
- Metadata Connection: Select the source Hive Metastore connection created in 7.
- Databases (Optional): Enter the name of the database whose data needs to be verified, for example, bigdata_test.
- Locate the row that contains the created task in the task list and click Execute Task in the Operation column.
- After the task is executed, locate the row that contains the task and click View Executions in the Operation column.
- Click the Tables tab to view the collected tables.
- On the Migration Preparations page, click Metadata Management. In the displayed area, click Create Metadata Collection Task on the Tasks tab page. In the displayed Create Task -Metadata Collection window, set the following parameters and click Confirm.
- Create a table group and add tables to the table group.
- In the navigation pane, choose Migrate > Big Data Verification. In the Features area, click Table Management.
- On the Table Groups tab page, click Create. In the displayed Create Table Group dialog box, set the following parameters and click Confirm.
- Table Group: Enter a table group name, for example, hive.
- Metadata Connection: Select the source Hive Metastore connection created in 7.
- Verification Rule: Select a verification rule based on your requirements.
- Click the Tables tab and add the tables to be verified to the table group created in 9.b.
In the table list, select the tables to be verified, choose Option > Add Tables to Group. On the displayed dialog box, select the table group created in 9.b and click Confirm.
- After the tables are added to the table group, you can view the table group name of the tables in the table list. The name is that of the table group to which the tables are added, for example, hive.
- Create an executor connection.
- In the navigation pane, choose Migrate > Migration Preparations.
- On the Connection Management tab page, click Create Connection. In the displayed window, select CDH executor for Executor, and click Next.
- Configure the following parameters on the displayed page:
Table 5 Parameters for the source Hive connection Parameter
Configuration
Connection To
Select Source.
Connection Name
Enter a custom connection name, for example, CDH executor-source.
MgC Agent
Select the enabled MgC Agent.
Executor Credential
Select the source executor credential created in 5.
Executor IP Address
Enter the IP address of the host where the source Hive client is located.
You can run the hive, beeline, or spark-sql commands on the host to connect to the source Hive cluster.
Executor Port
Enter the port number of the host where the source Hive client is located.
Installation Directory
Enter the directory where the source Hive client is located.
SQL File Location
Enter the manually created directory for storing SQL files.
- Click Test. After the test is successful, click Confirm to create the source connection.
- Click Create Connection again. In the displayed window, select MRS executor for Executor and click Next.
- Configure the following parameters on the displayed page:
Table 6 Parameters for the source Hive connection Parameter
Configuration
Connection To
Select Target.
Connection Name
Enter a custom connection name, for example, MRS executor-target.
MgC Agent
Select the enabled MgC Agent.
Executor Credential
Select the destination executor credential created in 5.
Executor IP Address
Enter the IP address for connecting to the MRS executor, that is, the IP address of the ECS node created in 1 where the MRS cluster client is installed.
Executor Port
Enter the port number of the node where the MRS cluster client is located.
Installation Directory
Enter the installation directory of the MRS cluster client.
SQL File Location
Enter the manually created directory for storing SQL files.
- Click Test. After the test is successful, click Confirm to create the destination connection.
- You can view the created source and destination connections in the connection list.
- Create and execute a verification task.
- In the navigation pane, choose Migrate > Big Data Verification. In the Features area, click Task Management.
- Click Create Task in the upper right corner of the page. In the displayed window, set Big Data Component to Hive, Verification Method to Full Verification, and click Next.
- Set the following parameters and click Save to create a source task.
Table 7 Parameters for creating a task Parameter
Configuration
Task Name
The default name is Component-Full-Verification-4 random characters (including letters and digits). You can also enter a custom name.
Table Groups
Select the table group created in 9, for example, hive.
Executor Connection
Select the source executor connection created in 10.
Non-partitioned Table Verification
Decide how to verify non-partitioned tables. For example, select Verify all.
OBS Bucket Check
Determine whether you need to select I confirm that I only need to view logs and data verification results on MgC Agent and do not need to upload them to OBS as required.
Execution Command
Decide how to execute Hive commands. The options are beeline, hive, and spark-sql. For example, select hive.
- Create a destination task by referring to 11.b to 11.c. Set Executor Connection to the destination executor connection created in 10, and Execution Command to beeline.
- In the task list, locate the rows that contain the tasks created for the source and destination and click Execute in the Operation column. Click OK in the displayed dialog box.
- View the verification results.
- View the verification task status on the Task Executions tab page.
- In task execution list, locate the row that contains the verification task, choose More > View Verification Results. On the displayed page, view the verification results.
- You can also click View Details in the Operation column to view the verification results of a table.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





