Unified Metric Monitoring
This section describes how to centrally monitor metric data of different accounts.
Scenario
O&M personnel of an e-commerce platform need to monitor metric data of different accounts in real time.
Solution
Create a Prometheus instance for multi-account aggregation and connect accounts, cloud services, and cloud service metrics. On the Metric Browsing page, you can monitor metrics of multiple member accounts and set alarm rules for them. If a metric is abnormal, an alarm will be triggered immediately and a notification will be sent.
Prerequisites
- The monitoring account and the monitored account have been added to an organization. The monitoring account must be an organization administrator. If not, perform step 2 to set a delegated administrator.
- The metrics that can be aggregated include the metrics ingested to Prometheus instances for cloud services, as well as CCE and ECS metrics collected by ICAgent.
Step 1: Connecting Cloud Services for a Monitored Account
The following uses FunctionGraph and ECS as examples. The procedure for connecting CCE is similar to that for connecting ECS. However, ICAgents are automatically installed by default when you purchase CCE clusters. The procedure for connecting FunctionGraph is similar to that for connecting other cloud services.
- Connecting FunctionGraph
- Log in to the AOM 2.0 console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Access Center > Access Center.
To switch from the new access center to the old one, click Back to Old Version in the upper right corner.
- Under Cloud Services, click FunctionGraph. In the displayed dialog box, set parameters to connect the cloud service.
Table 1 Connecting the cloud service Parameter
Description
Example Value
Select Prometheus Instance for Cloud Services
Ingest cloud service metrics to the Prometheus instance for cloud services.
- Enterprise Project: the belonged enterprise project.
- If Enterprise Project is set to All on the global settings page, select an enterprise project from the drop-down list here.
- If you have already selected an enterprise project on the global settings page, this option will be grayed and cannot be changed.
- Prometheus Instance for Cloud Services
By default, the Prometheus instance for cloud services under your specified enterprise project is selected. If there is no such a Prometheus instance, create one.
- Enterprise Project: Select default.
- Prometheus Instance for Cloud Services: prometheus_cloudservice_default
Connect Cloud Service Tags
You can determine whether to add cloud service tags to metric dimensions. After this function is enabled, tags of cloud service resources will be added to metric dimensions. Tag changes will be synchronized every hour. If the existing tags cannot meet your requirements, click Go to Tag Management Service (TMS) to add tags.
-
- Enterprise Project: the belonged enterprise project.
- Click Connect Now to connect the cloud service to the Prometheus instance.
- Connecting ECS
- Obtain an access code. For details, see Managing Access Codes.
- In the navigation pane, choose Global Settings.
- In the navigation pane, choose Collection Settings > UniAgents. Select a host where the UniAgent has been installed and click Plug-in Batch Operation.
To switch from the new UniAgent management function to the old one, click Back to Old Version in the upper right corner of the page.
- In the displayed dialog box, set Operation to Install and Plug-in to ICAgent, and then select a desired version.
- Click OK to install ICAgents.
Step 2: Enable Access for AOM and Set a Delegated Administrator (Skip this Step You Are an Organization Administrator)
- Log in to the Organizations console as an administrator.
- In the navigation pane, choose Services.
- In the service list, locate Application Operations Management (AOM) and click Enable Access in the Operation column.
- Click Specify Delegated Administrator in the Operation column of AOM, select the desired account, and click OK. As shown in Figure 1, paas_aom is specified as the delegated administrator.
Step 3: Create an Instance for Multi-Account Aggregation
- Log in to the AOM 2.0 console as an administrator or delegated administrator.
- In the navigation pane, choose Prometheus Monitoring > Instances. On the displayed page, click Add Prometheus Instance.
- Enter an instance name and select the Prometheus for Multi-Account Aggregation instance type.
- Click OK. As shown in Figure 2, a multi-account aggregation instance named test-aom is created.
- In the Prometheus instance list, click the name of the created instance. On the displayed page, select the accounts, cloud services, and cloud service metrics to connect.
For example, connect member accounts paas_apm and paas_aom. Connect cloud services such as FunctionGraph, DCS, and ECS. Click Add Metric. In the displayed dialog box, select desired metrics.
Figure 3 Connecting accounts
Wait for 2 to 3 minutes and view the ingested metric data on the Metric Browsing page.
Step 4: Configuring Unified Monitoring
- Check whether the metrics of the created instance are ingested.
- In the navigation pane, choose Metric Browsing. In the Prometheus Instance drop-down list, select instance test-aom created in step 3.
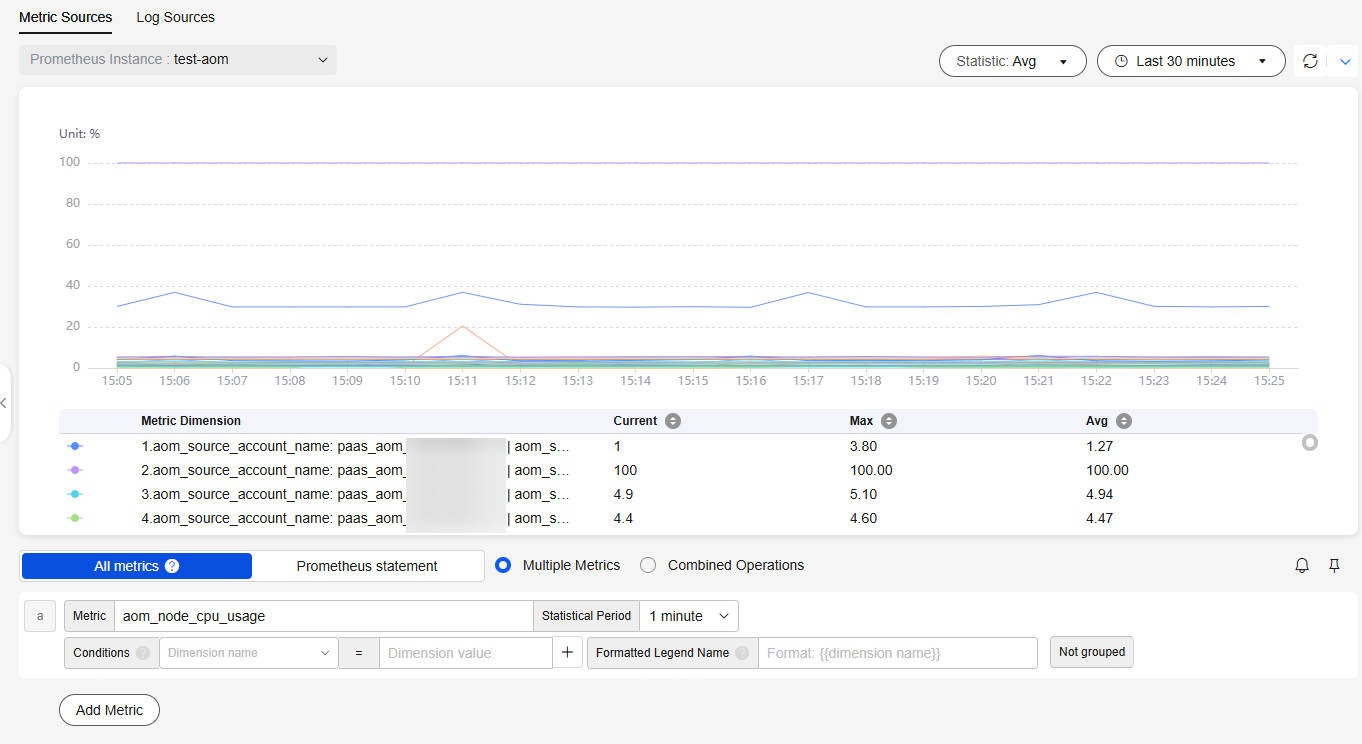
- Click All metrics, select a metric, and copy the metric name. In this example, select aom_node_cpu_usage.
- Click Prometheus statement and enter sum(metric name) by (aom_source_account_name) to check whether the metric is ingested. For example, enter sum(aom_node_cpu_usage) by (aom_source_account_name).
Figure 4 Checking metrics
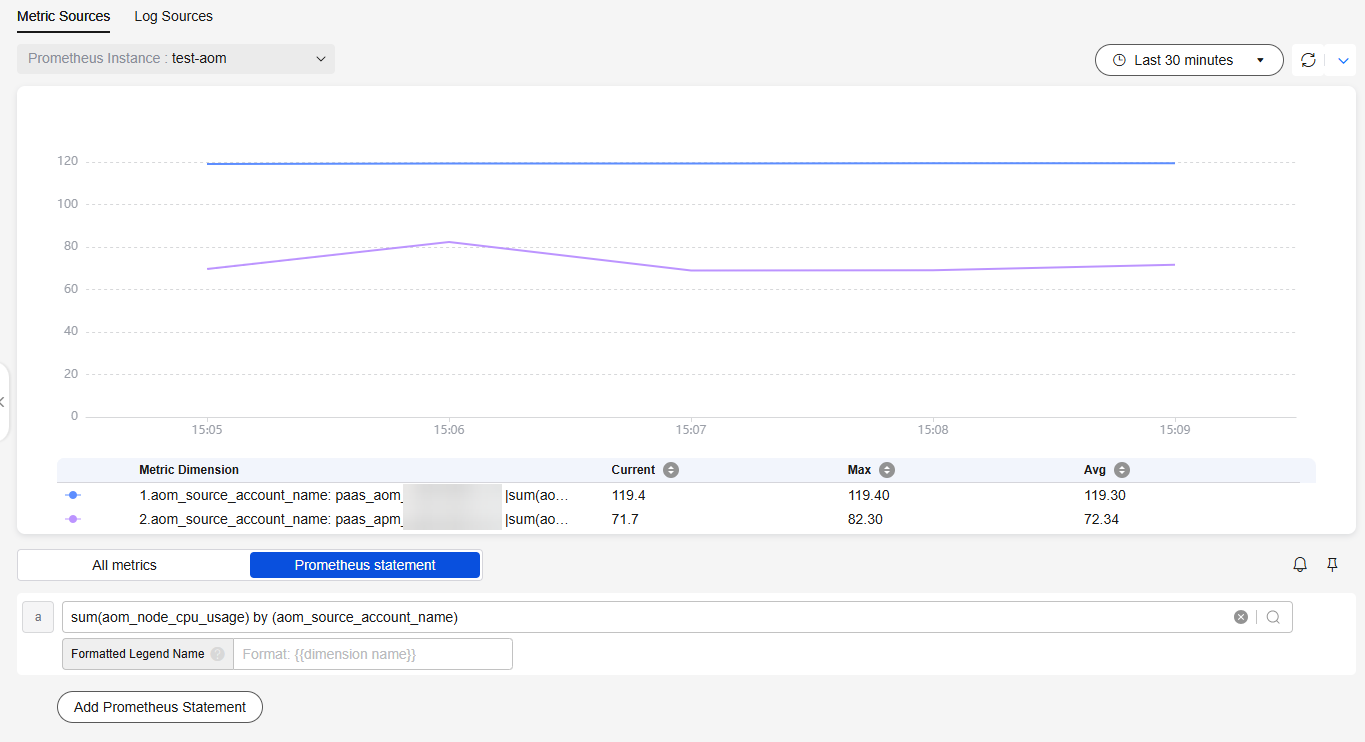
- Click All metrics and select the metric to be monitored. As shown in Figure 5, select the aom_node_cpu_usage metric so that its values and trends under the paas_apm and paas_aom accounts can be monitored in real time.
- Click
 in the upper right corner of the metric list to add an alarm rule for the selected metric.
in the upper right corner of the metric list to add an alarm rule for the selected metric.
- Set basic information about the alarm rule by referring to Table 2.
Table 2 Basic information Parameter
Description
Example Value
Original Rule Name
Original name of the alarm rule. Enter a maximum of 256 characters and do not start or end with any special character. Only letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-) are allowed.
monitor
Rule Name
Name of the alarm rule. Max.: 256 characters. Only letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_) are allowed. Do not start or end with a hyphen or underscore. In this example, leave this parameter blank.
-
Enterprise Project
Select the required enterprise project. The default value is default.
default
Description
Description of the rule. Enter up to 1,024 characters. In this example, leave this parameter blank.
-
- Set the detailed information about the alarm rule.
- By default, the rule type, configuration mode, and Prometheus instance in the alarm rule settings are the same as those on the Metric Browsing page.
- Set alarm rule details. By default, the metric selected on the Metric Browsing page is automatically displayed.
You need to set information such as the statistical period, condition, detection rule, trigger condition, and alarm severity. The detection rule consists of the statistical mode (Avg, Min, Max, Sum, and Samples), determination criterion (≥, ≤, >, and <), and threshold value. For example, if Statistical Period is 1 minute, Rule is Avg >1, Consecutive Periods is 3, and Alarm Severity is Critical, a critical alarm will be generated when the average metric value is greater than 1 for three consecutive periods.
Figure 6 Setting an alarm rule
- Click Advanced Settings and set information such as Check Interval and Alarm Clearance. For details about the parameters, see Table 3.
Table 3 Advanced settings Parameter
Description
Example Value
Check Interval
Interval at which metric query and analysis results are checked.
Custom interval: 1 minute
Alarm Clearance
The alarm will be cleared when the alarm condition is not met for a specified number of consecutive periods.
1
Action Taken for Insufficient Data
Action to be taken if there is no or insufficient metric data within the monitoring period. Enable this option if needed.
Enabled: If the data is insufficient for 1 period, the status will change to Insufficient data and an alarm will be sent.
Tags
Click
 to add tags for alarm rules. They will be synchronized to TMS. They can be used to filter alarm rules and group alarms to reduce noise. They can also be referenced as "${event.metadata.tag key}" in message templates.
to add tags for alarm rules. They will be synchronized to TMS. They can be used to filter alarm rules and group alarms to reduce noise. They can also be referenced as "${event.metadata.tag key}" in message templates.Alarm tags are attributes that can be used to identify alarms. They are in the format of "key:value". In this example, leave this parameter blank.
-
Annotations
Click
 to add attributes (key-value pairs) for alarm rules. Annotations will not be synchronized to TMS, but can be used to group alarms to reduce noise and referenced as "${event.metadata.annotation key}" in message templates.
to add attributes (key-value pairs) for alarm rules. Annotations will not be synchronized to TMS, but can be used to group alarms to reduce noise and referenced as "${event.metadata.annotation key}" in message templates.Alarm annotations are attributes that cannot be used to identify alarms. They are in the format of "key:value". In this example, leave this parameter blank.
-
- Set an alarm notification policy. For details, see Table 4.
Figure 7 Alarm notification
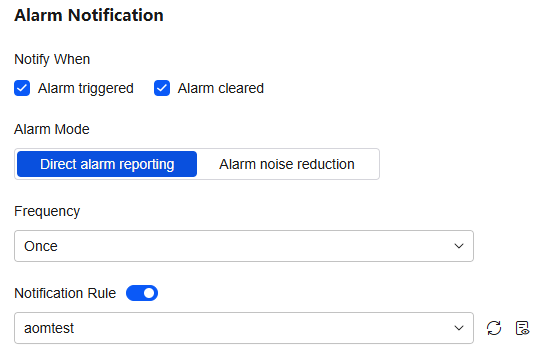
Table 4 Alarm notification policy parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Notify When
Set the scenario for sending alarm notifications. By default, Alarm triggered and Alarm cleared are selected.
- Alarm triggered: If the alarm trigger condition is met, the system sends an alarm notification to the specified personnel by email or SMS.
- Alarm cleared: If the alarm clearance condition is met, the system sends an alarm notification to the specified personnel by email or SMS.
Retain the default value.
Alarm Mode
- Direct alarm reporting: An alarm is directly sent when the alarm condition is met. If you select this mode, set an interval for notification and specify whether to enable a notification rule.
- Frequency: interval for sending alarm notifications. Select a desired value from the drop-down list.
- Notification Rule: After the rule is enabled, the system sends notifications based on the associated SMN topic and message template. If there is no notification rule you want to select, click Add Rule in the drop-down list to create one. For details, see Creating an Alarm Notification Rule.
Alarm Mode: Select Direct alarm reporting.
Frequency: Select Once.
Notification Rule: aomtest
- Click Confirm. Then click View Rule to view the created rule.
Click a rule name to view details. If a monitored object meets the configured alarm condition, a metric alarm is generated on the alarm list page. To view the alarm, choose Alarm Center > Alarm List in the navigation pane. If a host meets the preset notification policy, the system sends an alarm notification to the specified personnel by email, SMS, or WeCom.
- Set basic information about the alarm rule by referring to Table 2.
- Click
 in the upper right corner of the metric list to add the graph to the dashboard.
in the upper right corner of the metric list to add the graph to the dashboard.
- Select a dashboard from the drop-down list and enter the graph name. If the dashboards in the list cannot meet your requirements, click Add Dashboard to add one. For details, see Creating a Dashboard.
Figure 8 Adding the graph to a dashboard

- Click Confirm. The dashboard page is displayed. As shown in Figure 9, the CPU Usage graph is added to the aom dashboard so that its values and trends under the paas_apm and paas_aom accounts can be monitored in real time.
- Select a dashboard from the drop-down list and enter the graph name. If the dashboards in the list cannot meet your requirements, click Add Dashboard to add one. For details, see Creating a Dashboard.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot