|
Mode preference |
- |
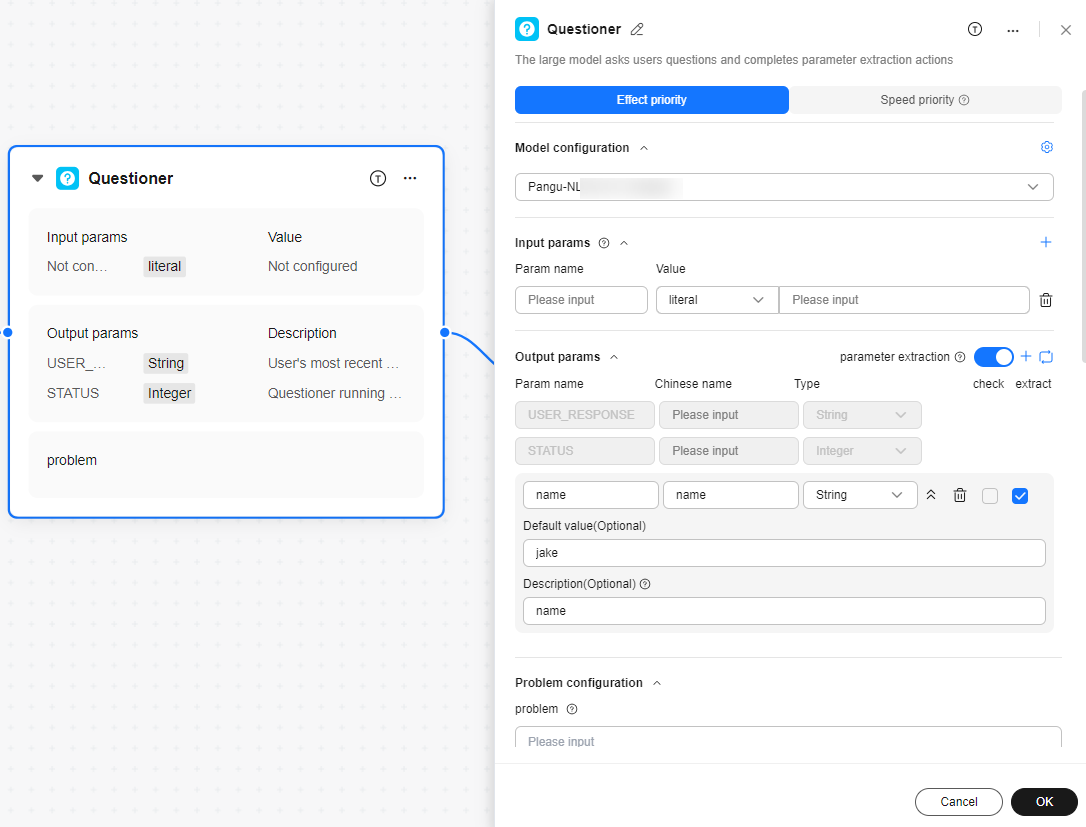
Effect priority: In this mode, the time augmentation and reflection functions are enabled, which improves the parameter improvement success rate but increases the latency.
- Time augmentation: The time and date in the natural language can be extracted as the time and date in the YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS format. For example, if the time is 12:30 tomorrow, the time is extracted as 2024-04-13 13:30:00.
- Reflection: After data is extracted, the model determines whether the data is correctly extracted and whether the format meets the requirements. If the format does not meet the requirements, the model makes some corrections. For example, if the expected extracted data is a phone number, the user enters "I don't remember the phone number", and the extracted data is 189******, then the model determines that the extracted data is incorrect and continues to ask the user more questions.
Speed priority: The latency is the lowest in this mode. The parameter improvement success rate may not be ensured. In this mode, the time augmentation and reflection functions are disabled. |
|
Model configuration
|
Model selection |
Select the model to be executed on this node. You can set parameters such as the generation diversity of the model on this node to make the model effectiveness meet your expectation.
The Questioner model is used to receive the natural language of the user and extract the output parameters configured by the user. When Effect priority is selected, the Questioner node is also used to extract the result for reflection and correction. |
|
Top P |
During output, the model selects words with the highest probability until the total probability of these words reaches the Top P value. The Top P value can restrict the model to select these high-probability words, thereby controlling the diversity of output content. You are advised not to adjust this parameter together with the Temperature parameter. |
|
Temperature |
Controls the randomness of the generation result. A higher temperature makes the model output more diverse and innovative. A lower temperature makes the output more compliant with the instruction requirements, but reduces the diversity of the model output. |
|
Parameter configuration
|
Input params |
Set the parameters to be added to the question. The parameter values can reference the output parameters of the previous node or be set to fixed text content. Multiple parameters can be referenced.
-
Param name: The value can contain only letters, digits, and underscores (_), and cannot start with a digit.
Example: The input parameter is pre_assigned_meeting_rooms. You want the user to select one from the specified options. The follow-up question is set to "The following meeting rooms are available: {{pre_assigned_meeting_rooms}}. Please select the meeting room you want to reserve."
- Type and Value: Type can be set to ref and literal.
- ref: You can select the output variable of the previous node of the node in the workflow as the value.
- literal: You can enter the variable value.
|
|
Output params |
This parameter is used to parse the output of the LLM node and provide the input for the subsequent node. Multiple parameters can be extracted.
- Default output
- USER_RESPONSE: original user output
- STATUS: extraction status
0: The extraction is successful, and the user has not confirmed the result.
10: The extraction is successful, and the user has confirmed the result.
100: Some parameters are obtained. The user proactively interrupts the operation. An error is reported for the parameters that have been submitted, and the parameters that have not been submitted are left empty based on the format.
101: Some parameters are obtained. The number of cycles exceeds the preconfigured number of rounds. The parameters that have not been submitted are left empty based on the format.
201: The LLM failed to be called.
202: An error occurred in the reflection module.
- parameter extraction: After this function is enabled, you can add parameters to be extracted. The configurable attributes of the parameters are as follows:
- Param name: The value can contain only letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-).
- Chinese name: It cannot be empty.
- Type: type of an output parameter. The options are String, Integer, Number, and Boolean.
- Default value: default value of the output parameter. If the LLM cannot extract the parameter and the maximum number of reply rounds is reached, the default value is used.
- Description: description of the output parameter.
- check: After this function is enabled, you can customize parameter verification rules to verify the standardization of output parameters. The rule includes the parameter name, verification type, and verification rule.
- extract: If this function is enabled, the parameter must be extracted or the default value is used if it is configured. If this function is disabled, the parameter can be left empty.
- Reference plug-in: Extracted parameters may be used by plug-ins. By referencing a plug-in, you can import the parameter information and verification information of the plug-in to improve the configuration efficiency.
|
|
Problem configuration |
Question |
This parameter is displayed in its original format in the dialog box. If this parameter is not set, the model automatically generates a question containing all keywords based on the output parameter description.
Example: What is your name?
Input parameters can be used in questions using the Jinjia syntax.
Example: Which class are you in? Available classes are {{classes}}. (The classes variable is preconfigured in the input parameters first.) |
|
Maximum number of reply rounds |
This parameter specifies the maximum number of interaction rounds with the model. If no parameter is extracted when the maximum number of interaction rounds is reached, the questioner exits. |
|
Advanced settings
|
Allow user to exit interaction |
After this function is enabled, if a user expresses the intention of ending the dialog with the questioner, the system automatically ends the current question and switches to the End node. |
|
user_confirmation_extraction_param |
After this function is enabled, users can confirm the questioner parameter extraction result. |
|
Extract constraints |
Provides additional constraints of the LLM for more accurate parameter extraction, for example, specifying the format requirements of the extracted parameters.
Example: The user wants to extract the phone number tel_number. The constraint configuration shows that the value of tel_number must contain 11 digits. |
|
Follow up mode |
The follow-up mode is used to configure the generation mode of the parameter follow-up questions returned by the system during multiple interactions.
- Default: The default built-in follow-up question template is used to generate follow-up questions. The content of each follow-up question is the same.
- Intelligent questioning: The large model is used to generate follow-up questions with good semantics and rich expressions. The content of each follow-up question is rich and diversified.
- Custom questioning: Follow-up questions are generated based on the user-defined template configuration. {unextracted_cn_field_names} cannot be modified or deleted. The content of each follow-up question is the same.
Example: Extract the name and age parameters.
- Default: Please provide your name and age.
- Intelligent questioning: Hello, we need to obtain your name and age. (The content is generated by the model and is not fixed.)
- Custom questioning: The customized question asking template is configured as follows: Please provide the following information: {unextracted_cn_field_names}.
Please provide the following information: name and age. |
|
Example configuration |
Provide an expected parameter extraction example of the LLM to enhance the LLM's understanding of the parameter extraction scenario.
Template:
Input query: I want to fly to Hohhot for training.
Parameters extracted: {"location": "Hohhot", "traveltool": "Aircraft"} |
|
Enumerated value of query display |
After this function is enabled, the enumerated values of the output parameters are displayed during the dialog. By default, this function is disabled. |