Loop Node
The Loop node provides the capability of executing nodes cyclically. You can configure the nodes to be executed cyclically in the loop body. You can orchestrate nodes in the loop body to execute processing tasks for multiple times.
A loop is a common control mechanism used to repeatedly execute a series of tasks until a certain condition is met. You can add a Loop node for a workflow if you need to repeatedly perform some operations or process a group of data in a loop.
The Loop node is an optional node. If it does not need to be configured, skip this section.
To configure the Loop node, perform the following steps:
- Click Add Node in the lower part of the canvas and drag the Loop node in the node drawer to the canvas, drag other nodes that need to be executed cyclically to the loop body canvas and orchestrate them. (Execution in a loop starts from the loop input node, and the output is connected to the loop output node. Currently, the Input node, Planning node, and Loop node are not supported.)
- Configure the Loop node by referring to Table 1.
Table 1 Loop node configuration Configuration Type
Parameter Name
Description
Loop type
Using array loop
The array loop is similar to the for syntax structure in the programming language. The traversal loop is used to traverse a known sequence and perform a series of same steps on each element in the sequence.
When using the array loop, you need to specify the value of arr_loop_var. This parameter can only reference the output of the upstream node and must be in array format. When a Loop node is executed in array loop mode, the number of loops depends on the length of the array referenced by the loop array.
When an array loop is used, the Loop node traverses each element in the array. In each loop, the element in the current loop is assigned to the built-in variable. Built-in variables can be used only in Loop nodes. Currently, the following built-in variables are supported:
- item: array element, that is, the array element that is looped to.
- index: array index. index+1 indicates the round of the current loop.
Specify the number of cycles
This loop type is usually used in scenarios where data is processed in batches or in sequence. You also need to set Number of cycles.
The default number of cycles is 5. You can set a value ranging from 1 to 1000.
Reference:
For a turn-based game, set the number of cycles to 3 if the winner is the one who wins two out of three rounds.
For a web crawler, set the number of cycles to 1000 if the crawler needs to crawl information about the first 1000 offerings.
Variable configuration
loop_array
This parameter can be configured only when the array loop is used. The name is fixed to arr_loop_var. Only the output of the upstream node can be referenced.
Intermediate variable
An intermediate variable can be set for a Loop node. This variable can be used for each loop. An intermediate variable is usually used together with the Variable Assignment node in the loop body. After each loop ends, a new value is set for the intermediate variable and the new value is used in the next loop.
Output params
The output parameters of the Loop node can be set to the execution result set of the loop body, meaning that after all elements in the array are executed, the execution results of all loops are packaged and output to the downstream. It can also be set to the value of an intermediate variable.
Termination conditions
Expression
The branch consists of [Judgment parameter comparison Condition comparison Parameter], which forms a condition expression.
- Judgment parameter: left part of the condition expression. You need to select the output parameter from the previous node.
- Comparison condition: middle part of a condition expression. Currently, the following comparison conditions are supported: length greater than, length greater than or equal to, length less than, length less than or equal to, equal to, not equal to, including, not including, empty, and not empty. Comparison conditions displayed vary depending on judgment parameter types.
- Comparison parameter: right part of a condition expression. It supports the reference and input types.
- ref: You can select the output variable values of the previous nodes contained in the workflow and the memory variables in the global configuration.
- literal: The value can be customized.
- Add conditions: Click + to add multiple condition expressions to the current condition branch. The multiple condition expressions are connected by AND or OR.
- Click and or or to switch the operation logic of the branch expression.
Figure 1 Loop node configuration example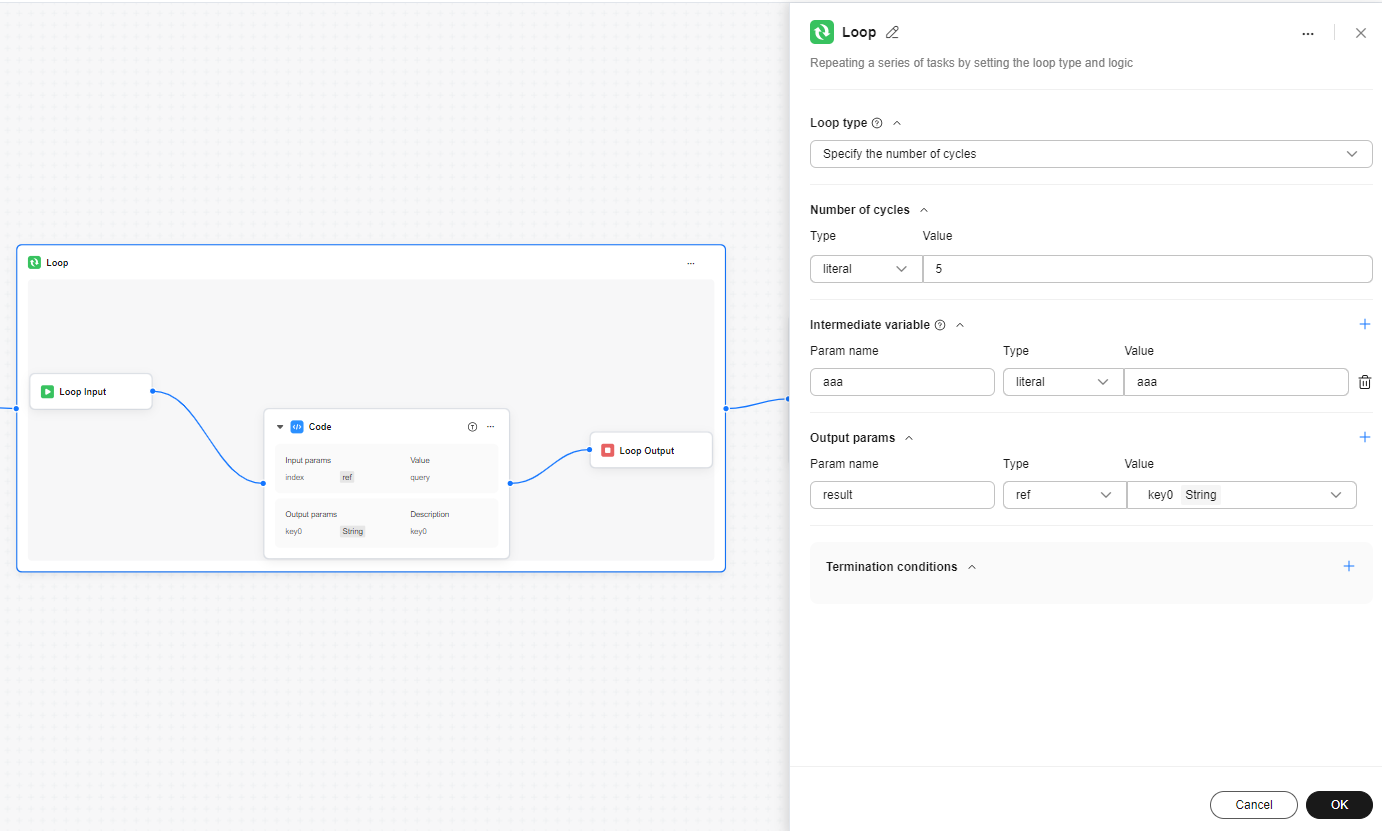
- After completing the configuration, click OK.
- Connect the Loop node to other nodes.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





