Basic Concepts
Permission
New IAM users do not have any permissions assigned by default. You need to first add them to one or more groups and then attach policies or roles to these groups. The users then inherit permissions from the user group and can perform specified operations on cloud services.
Permission Type
- Roles: A coarse-grained authorization strategy that defines permissions by job responsibility. Only a limited number of service-level roles are available for authorization. When using roles to grant permissions, you also need to assign dependency roles. Roles are not ideal for fine-grained authorization and least privilege access.
- Policies: A fine-grained authorization strategy that defines permissions required to perform operations on specific cloud resources under certain conditions. This type of authorization is more flexible and is ideal for least privilege access. For example, you can grant users only the permissions required to manage ECSs of a certain type.
IAM supports both system-defined policies and custom policies.
System-Defined Policy
A system-defined policy defines the common actions of a cloud service. System-defined policies can be used to assign permissions to user groups, and they cannot be modified. For details about the system-defined policies of all cloud services, see System-defined Permissions.
If there are no system-defined policies for a specific service, it indicates that IAM does not support this service. You can submit a service ticket and apply for permissions management on IAM.
Custom Policy
You can create custom policies using the actions supported by cloud services to supplement system-defined policies for more refined access control. You can create custom policies in visual editor or JSON view.
Authentication Process
When a user initiates an access request, the system authenticates the request based on the actions in the policies that have been attached to the group that the user belongs to. The following diagram shows the authentication process.
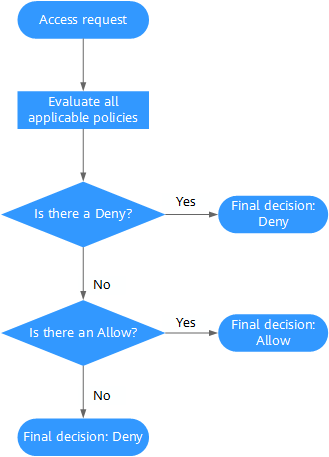
- A user initiates an access request.
- The system looks for a Deny among the applicable actions of the policies from which the user gets permissions. If the system finds an applicable Deny, it returns a decision of Deny, and the authentication ends.
- If no Deny is found applicable, the system looks for an Allow that would apply to the request. If the system finds an applicable Allow, it returns a decision of Allow, and the authentication ends.
- If no Allow is found applicable, the system returns a decision of Deny, and the authentication ends.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





