Arrears
If there is not a sufficient account balance to pay for your bill and there is no other payment method configured, your account will go into arrears. To continue using your cloud services, top up your account in a timely manner.
Arrears Reason
In pay-per-use mode, your account balance is insufficient.
Impact of Arrears
- Yearly/Monthly
This is a pre-paid billing mode, so you can continue using yearly/monthly resources even if your account is in arrears.
- Pay-per-use
If your account is insufficient to pay your amount, your account goes into arrears.
- However, your resources will not be stopped immediately; instead, they enter the grace period. You are still responsible for fees incurred during the grace period. You can view the charges on the Billing Center > Overview page and pay any past due balances as needed. Huawei Cloud will automatically deduct this amount when you top up.
- If you do not pay the arrears within the grace period, your resources will enter the retention period and become frozen. You cannot perform any operations on the pay-per-use resources during this period.
- If you do not bring your account balance current before the retention period ends, your resource will be released and the data cannot be restored.
Figure 1 IoTDA instance lifecycle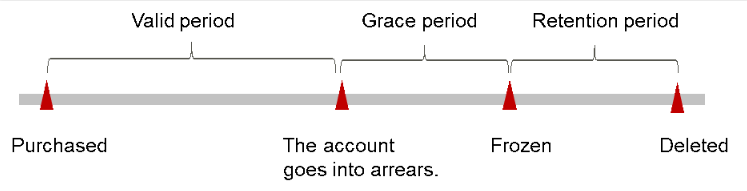
Both the grace period and retention period for Huawei Cloud International are 15 days.
Avoiding and Handling Arrears
If you are in arrears, top up your account in time. For details, see Top-up and Repayment..
Configure the Balance Alert function on the Billing Center > Overview page. When the total amount of the available quota, general cash coupons, and cash coupons is lower than the threshold, the system automatically notifies you by SMS or email.
If your account is in arrears, top up your account in a timely manner.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





