Managing Storage Capacity
Function Description
Data and log storage space and its changes significantly impact database performance. RDS for MySQL shows you the distribution and changes of used storage on the Storage Analysis page. It also provides storage autoscaling, intelligent tablespace diagnosis, and analysis of top 50 largest databases and tables.
|
Function |
Description |
Related Operations |
|---|---|---|
|
Overview |
You can view storage usage, available storage, total storage, daily increase in the last week, and estimated available days of storage. |
|
|
Tablespaces |
It shows you tables with abnormal tablespace growth, tables without primary keys, and tables without indexes. |
|
|
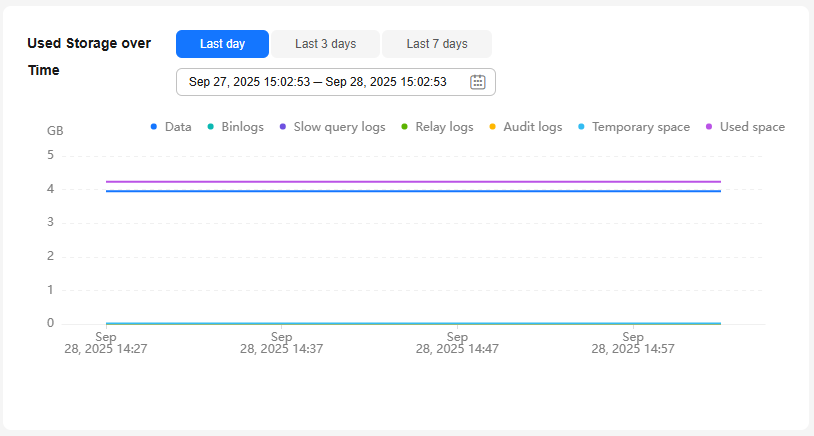
Used Storage and Used Storage over Time |
You can view the distribution of storage space and its changes over time. |
|
|
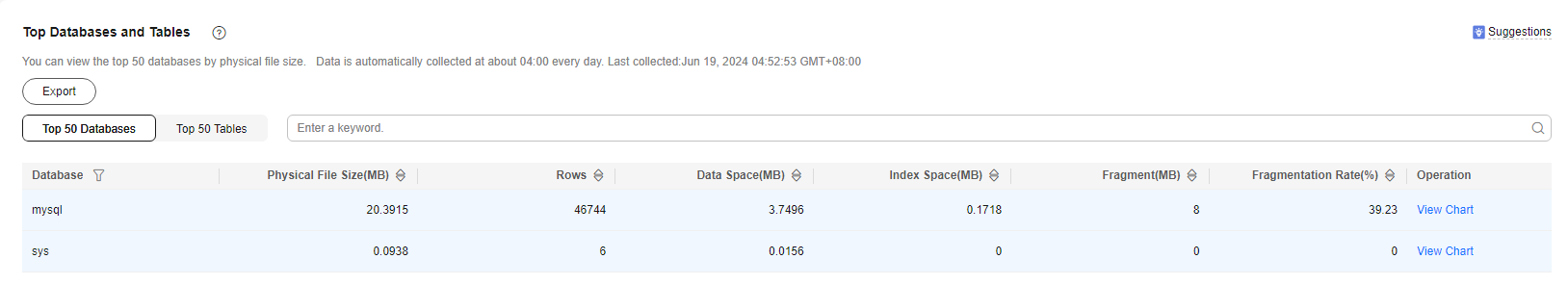
Top Databases and Tables |
You can view the top 50 databases and tables by physical file size and identify the databases and tables with high usage based on storage space distribution. |
Procedure
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region.
in the upper left corner and select a region. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service. - On the Instances page, click the target DB instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose Storage Analysis under DBA Assistant.
- Check your storage usage. If the storage is insufficient, scale it up. Or you can enable storage autoscaling.
Figure 1 Overview
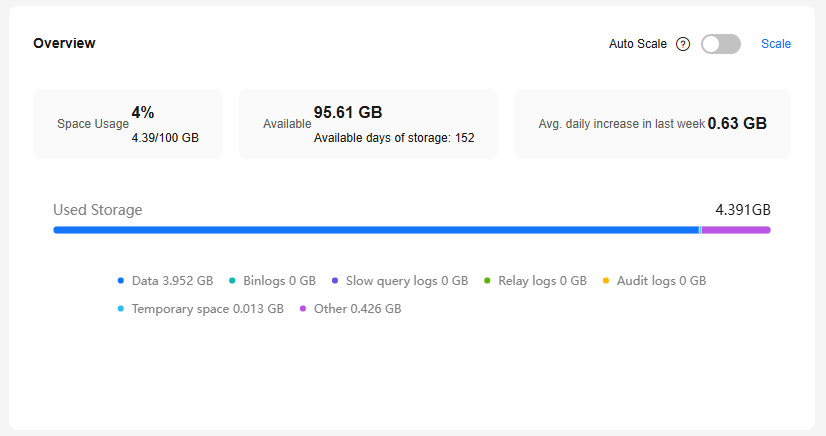
If the average daily increase in last week is 0 GB, the estimated available days of storage are unlimited and are not displayed.
If the total number of files in your storage (including data space, binlog space, slow query log space, relay log space, audit log space, temporary space, and other space) exceeds 10,000, RDS will not collect information about the files or display space distribution and usages over time on the console. This prevents performance slowdowns caused by collecting statistics on too many files. If this happens, submit a service ticket.
- Data space: Disk space occupied by user data (including temporary table files and ib_logfile files generated by the database)
- Binlogs: Disk space occupied by binlogs
- Slow query logs: Disk space occupied by slow logs
- Relay logs: Disk space occupied by relay logs
- Audit logs: Disk space occupied by audit logs
- Temporary space: Disk space occupied by temporary files
- Other: Disk space occupied by files such as ibdata1, ib_buffer_pool, ib_doublewrite, and error.log, plus the reserved space (about 5% of the disk space) for OS
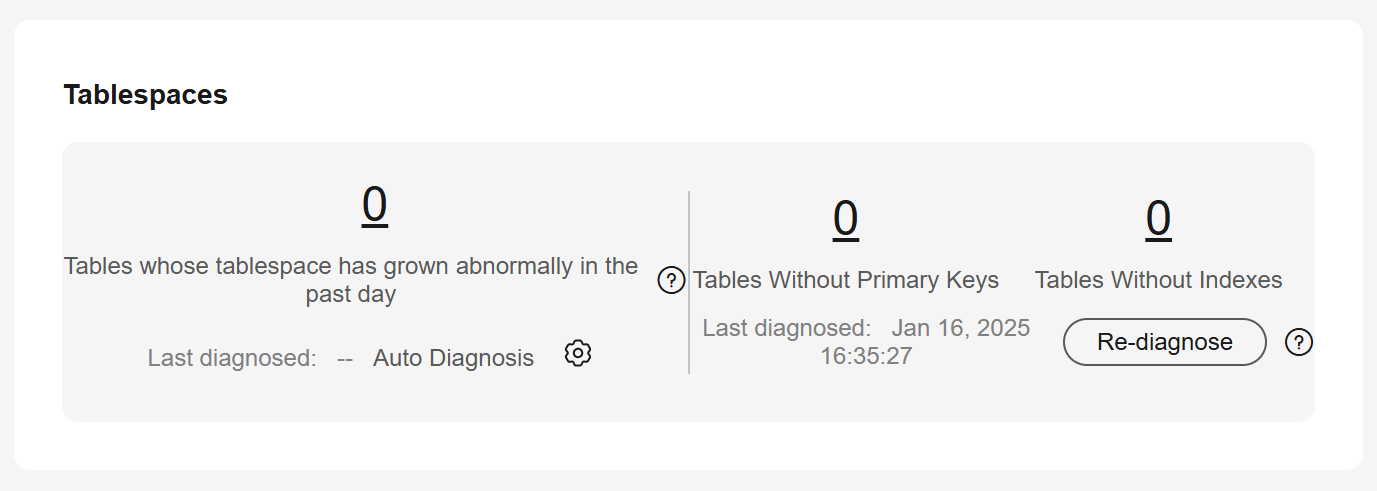
This function counts tables with abnormal tablespace growth, tables without primary keys, and tables without indexes. To use this function, upgrade DBA Assistant first.
- Click the Storage Analysis tab to view abnormal tables.
Figure 2 Tablespaces

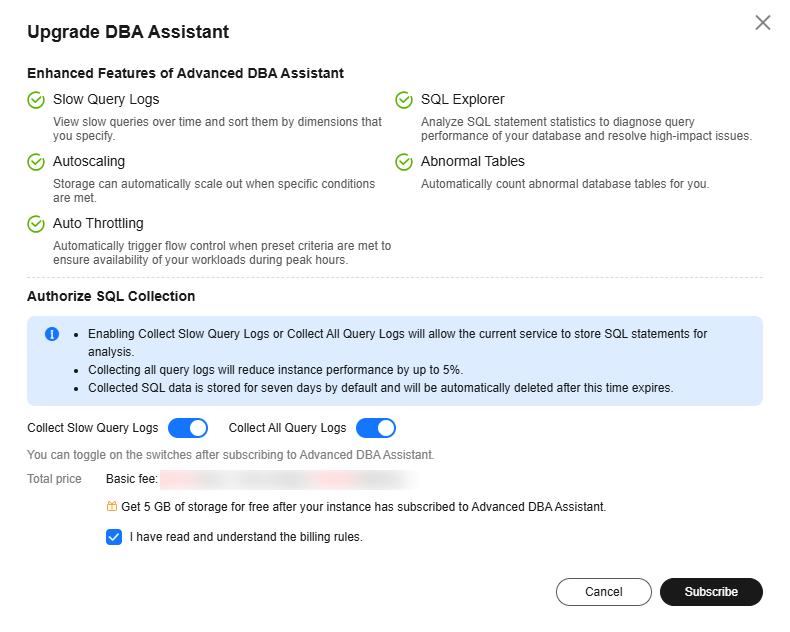
- Click Upgrade DBA Assistant. In the displayed dialog box, you can learn about the enhanced features and billing rules.
Figure 3 Upgrading DBA Assistant
- After the upgrade is complete, view the table diagnosis results of your instance.
Figure 4 Table diagnosis results
- Click
 next to Auto Diagnosis. In the displayed dialog box, configure the daily tablespace increase limit and click OK.
Figure 5 Configuring a daily tablespace increase limit
next to Auto Diagnosis. In the displayed dialog box, configure the daily tablespace increase limit and click OK.
Figure 5 Configuring a daily tablespace increase limit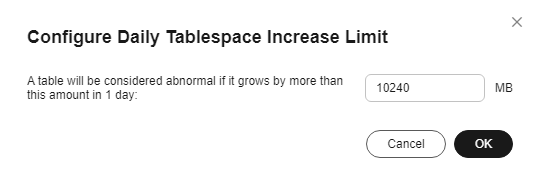
You can view the top 50 databases and tables by physical file size and identify the databases and tables with high usage based on storage space distribution.
- Physical file sizes are precisely recorded, but other fields' values are estimated. If there is a large gap between a file size and another field, run ANALYZE TABLE on the table.
- A database or table whose name contains special characters, including slashes (/) and #p#p, is not counted.
- Top databases and tables are available only in RDS for MySQL 5.7 and 8.0.
- If your instance's memory usage is greater than 85% or it has more than 50,000 tables, RDS will not collect related information. This prevents performance slowdowns caused by collecting statistics on too many databases and tables.
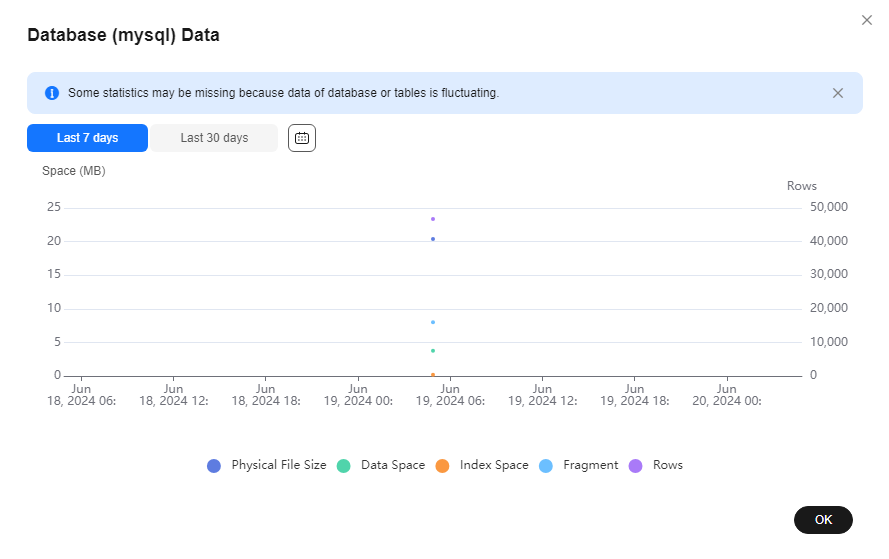
Click View Chart to view data volume changes in the last 7 days, last 30 days, or a custom time period (spanning no more than 30 days).
FAQ
Q: What can I do if the storage space of my DB instance is full?
- Scale up the storage space: Services are not interrupted during storage scale-up. You can also enable autoscaling. When the available storage of a DB instance drops to the threshold, autoscaling is triggered.
- Reducing disk data: Delete useless historical data.
- If your instance becomes read-only, unlock it from this state first. If your instance is not in the read-only state, you can delete data directly.
- Check the top 50 databases and tables with large physical files and identify the historical table data that can be deleted. For details, see Top Databases and Tables by Physical File Size.
- To clear up space, you can optimize tables with a high fragmentation rate during off-peak hours.
To delete data of an entire table, run DROP or TRUNCATE. To delete part of table data, run DELETE and OPTIMIZE TABLE.
- If temporary files generated by sorting queries occupy too much storage space, optimize your SQL query statements.
You can query slow query logs, and analyze and optimize the problematic SQL statements.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot