SFS Turbo Volumes
CCI 2.0 allows you to mount SFS Turbo volumes to container paths. SFS Turbo file systems are fast, on-demand, and scalable. They are suitable for DevOps, containerized microservices, and enterprise office applications.
Constraints
- SFS Turbo file systems are billed on a pay-per-use basis. For more information, see SFS Turbo Pricing.
- The SFS Turbo file system must be in the same VPC as the workload. If they are in different VPCs, the workload cannot use the SFS Turbo file system for persistent storage.
- If an SFS Turbo file system is in use, the VPC where the file system is deployed cannot be changed. Once the VPC is changed, the containers in CCI 2.0 will not be able to access the file system.
- If an SFS Turbo file system is deleted, containers in CCI 2.0 will become unavailable.
- SFS Turbo file systems do not involve AZs, so PVs of the SFS Turbo type do not support AZ affinity.
- CCI 2.0 supports SFS Turbo only in the TR-Istanbul and AF-Johannesburg regions.
Importing SFS Turbo File Systems
Currently, SFS Turbo file systems can only be used by CCI 2.0 containers through static PVC binding.
- Create an SFS Turbo file system. For details, see Creating an SFS Turbo File System.
- Create a PV.
- Obtain the IAM token.
curl -i -k -H 'Accept:application/json' -H 'Content-Type:application/json;charset=utf8' -X POST -d '{"auth": {"identity":{"methods": ["password"],"password":{"user": {"name": "$username","password": "$password","domain": {"name": "$domain"}}}},"scope": {"project":{"name": "$project"}}}}' https://iam.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/v3/auth/tokens | grep "X-Subject-Token"|awk -F ": " '{print $2}'|sed "s/\r//"
- Call the API for creating a PV.
curl -H "X-Auth-Token:$token" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -X POST -d @pv.json -k -v https://cci.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/apis/cci/v2/persistentvolumes
In this command, $token is the IAM token obtained in 2.a, and pv.json is the information about the PV to be created. The following is an example:
{ "apiVersion": "cci/v2", "kind": "PersistentVolume", "metadata": { "annotations": { }, "name": "pv-sfs-test" }, "spec": { "accessModes": [ "ReadWriteMany" ], "capacity": { "storage": "500Gi" }, "csi": { "driver": "sfsturbo.csi.everest.io", "fsType": "nfs", "volumeHandle": "**************", "volumeAttributes": { "everest.io/share-export-location": "*******" } }, "persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy": "Retain", "storageClassName": "csi-sfsturbo", "mountOptions": [ ] } }Table 1 Key parameters Parameter
Mandatory
Type
Description
accessModes
Yes
List
Description: Storage access mode.
Constraint: The value must be ReadWriteMany for SFS Turbo volumes.
driver
Yes
String
Description: Storage driver that the volume depends on.
Constraint: The value must be sfsturbo.csi.everest.io.
fsType
Yes
String
Description: Storage instance type.
Constraint: The value must be nfs, which indicates file system volumes.
volumeHandle
Yes
String
Description: ID of the SFS Turbo file system.
Constraint: The ID must be that of an existing SFS Turbo file system.
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy
Yes
String
Description: PV reclaim policy.
Constraint: Only the Retain policy is supported.
Retain: When a PVC is deleted, both the PV and underlying storage are retained. You need to manually delete these resources. After the PVC is deleted, the PV is in the Released state and cannot be bound to a PVC again.
storage
Yes
String
Description: Storage capacity, in Gi.
Constraint: Set it to the size of the SFS Turbo file system.
storageClassName
Yes
String
Description: Storage class name of the SFS Turbo volume.
Constraint: The storage class name of SFS Turbo volumes is csi-sfsturbo.
volumeHandle is the ID of the SFS Turbo file system created in 1, and everest.io/share-export-location is the shared path of the SFS Turbo file system.
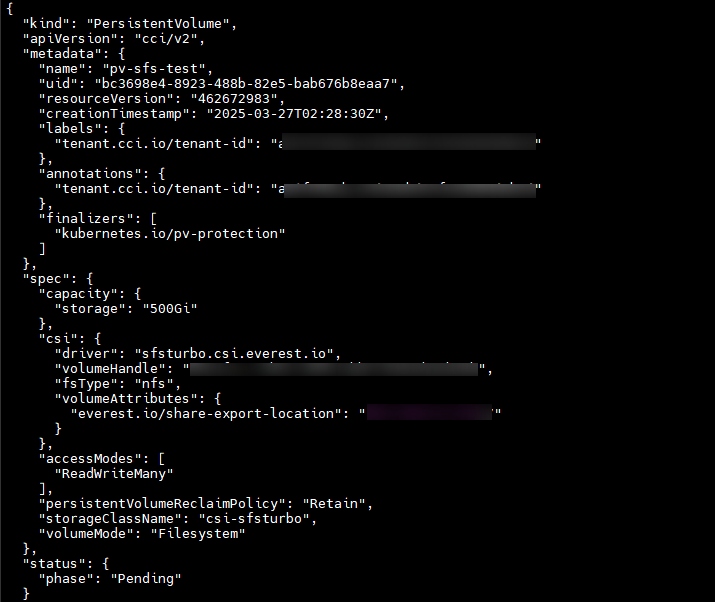
The following figure shows the response to the request for creating a PV.
- Obtain the IAM token.
- Create a PVC.
- Obtain the IAM token. For details, see 2.a.
- Call the API for creating a PVC and bind the created PV.
curl -H "X-Auth-Token:$token" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' X POST -d @pvc.json -k -v https://cci.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/apis/cci/v2/namespaces/${namespace}/persistentvolumeclaimspvc.json indicates the information about the PVC to be created. The following is an example:
{ "apiVersion": "cci/v2", "kind": "PersistentVolumeClaim", "metadata": { "name": "pvc-sfs", "annotations": { } }, "spec": { "accessModes": [ "ReadWriteMany" ], "resources": { "requests": { "storage": "500Gi" } }, "storageClassName": "csi-sfsturbo", "volumeName": "pv-sfs-test" } }Table 2 Key parameters Parameter
Mandatory
Type
Description
storage
Yes
String
Description: PVC capacity, in Gi.
Constraints
- Set it to the size of the SFS Turbo file system.
- The value is the same as the capacity set for the PV in Table 1.
storageClassName
Yes
String
Description: Storage class name.
Constraint: The value must be the same as the storage class name of the PV in Table 1. The storage class name of SFS Turbo volumes is csi-sfsturbo.
volumeName
Yes
String
Description: PV name.
Constraint: The value must be the same as the PV name in Table 1.
volumeName indicates the name of the PV created in 3.
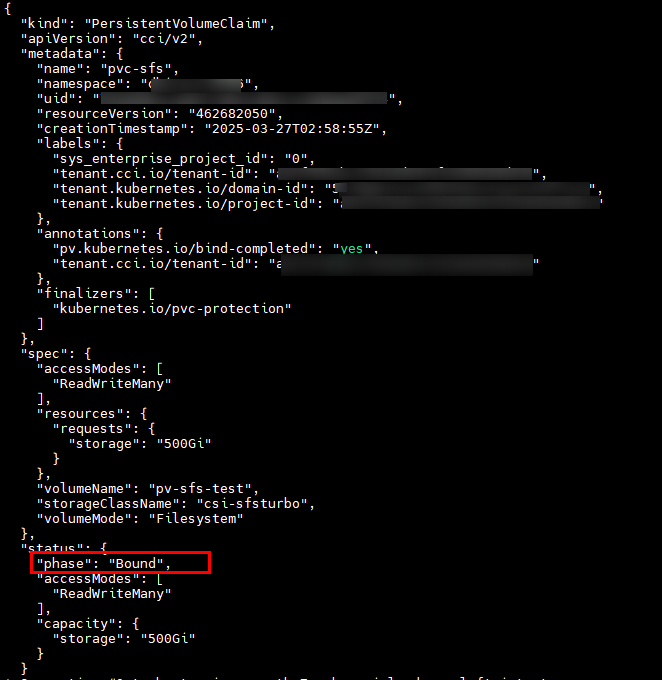
The following figure shows the response to the request for creating a PVC, and the PVC has been bound to the PV.
Using SFS Turbo Volumes
For details, see Deployments. Add the volume configuration to the workload YAML file.
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: cci/v2
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: test-ns
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
volumes:
- name: my-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: PVC name
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1Gi
volumeMounts:
- name: my-storage
mountPath: mount path of a container
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
restartPolicy: Always
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
dnsPolicy: Default
securityContext: {}
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 25%
maxSurge: 25%
- When an SFS Turbo file system is being created, an independent VM will also be created, and this will take a long time. Therefore, you are advised to select existing SFS Turbo volumes.
- subPath is a sub-directory in the root path of the SFS Turbo file system. If there is no sub-directory, a sub-directory is automatically created in the SFS Turbo file system. Note that subPath must be a relative path.
- If SFS Turbo volumes are used, workloads can be created only using YAML or ccictl.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





