Fast Access
Creating a Product
A smoke detector product model is provided to help you understand the product model. This smoke detector can report the smoke density, temperature, humidity, and smoke alarms, and execute the ring alarm command. The following uses the smoke detector as an example to introduce the procedures of message reporting and property reporting.
- Access the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
- Choose Products in the navigation pane and click .
Figure 1 Creating a product
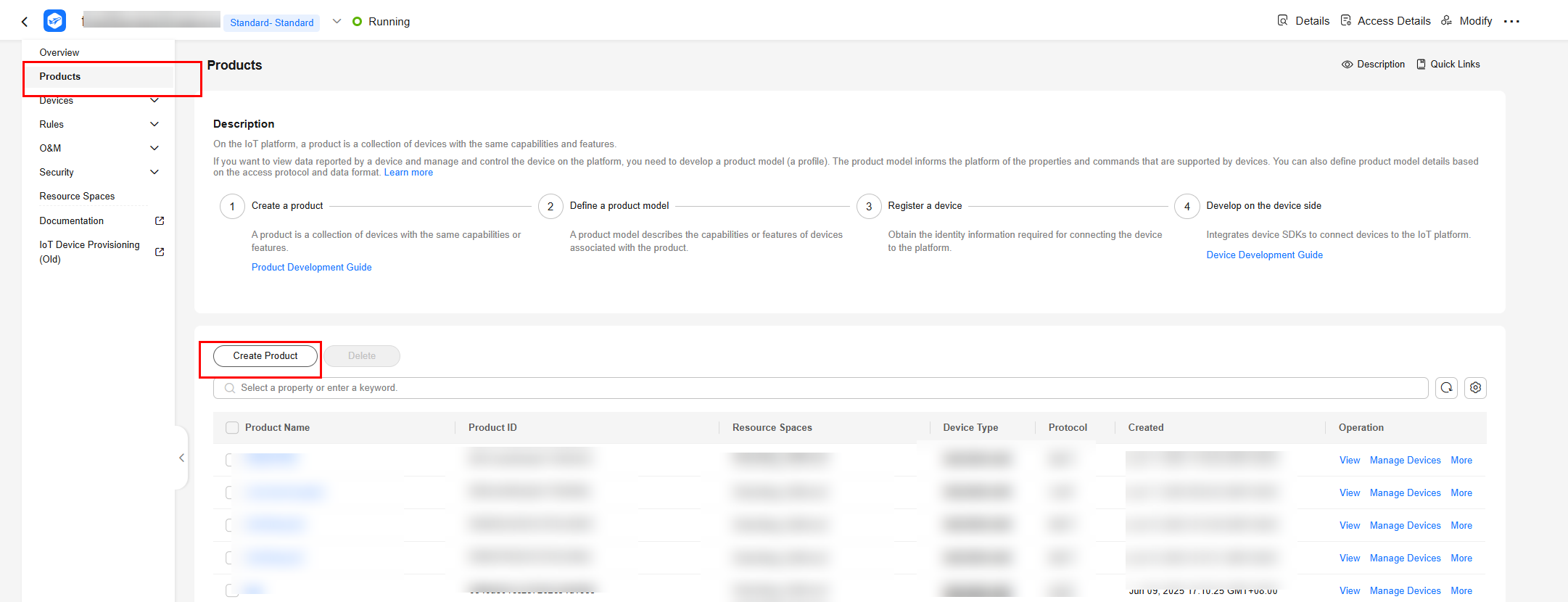
- Set the parameters as prompted and click OK.
Basic Info
Resource Space
The platform automatically allocates the created product to the default resource space. You can also select an existing resource space from the drop-down list or create one.
Product Name
Customize the product name. The name can contain letters, numbers, underscores (_), and hyphens (-).
Protocol
Select MQTT.
Data Type
Select JSON.
Device Type Selection
Select Custom.
Device Type
Select smokeDetector.
Advanced Settings
Product ID
Leave this parameter blank.
Description
Set this parameter based on service requirements.
Figure 2 Creating a product - MQTT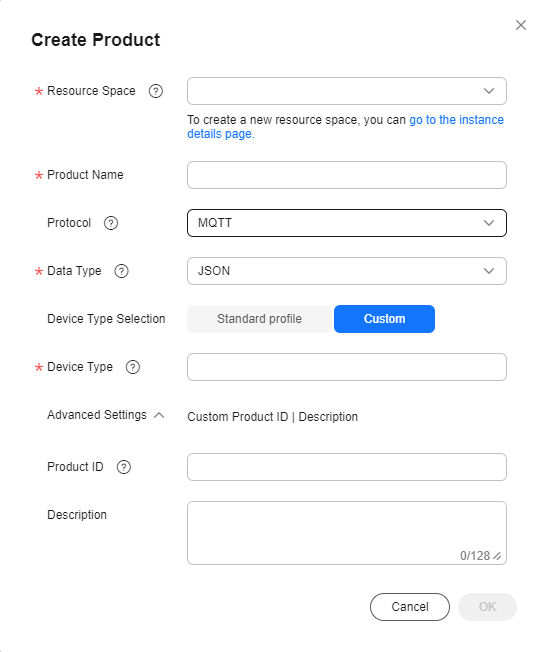
Uploading a Product Model
- Download the smokeDetector product model file.
- Click the name of the created product to access its details page.
- On the Basic Information tab page, click Import from Local to upload the product model file obtained in 1.
Figure 3 Product - Uploading a product model

Registering a Device
- In the navigation pane, choose Devices > All Devices, and click Register Device.
- Set the parameters as prompted and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Resource Space
Ensure that the device and the created product belong to the same resource space.
Product
Select the created product.
Node ID
Customize a unique physical identifier for the device. The value consists of letters and digits.
Device Name
Customize the device name.
Authentication Type
Select Secret.
Secret
Customize the device secret. If this parameter is not set, the platform automatically generates a secret.
After the device is registered, save the node ID, device ID, and secret.
Initializing a Device
- Obtain the access address by choosing Overview > Access Details on the console.
Figure 4 Access information - MQTT access address on the device side
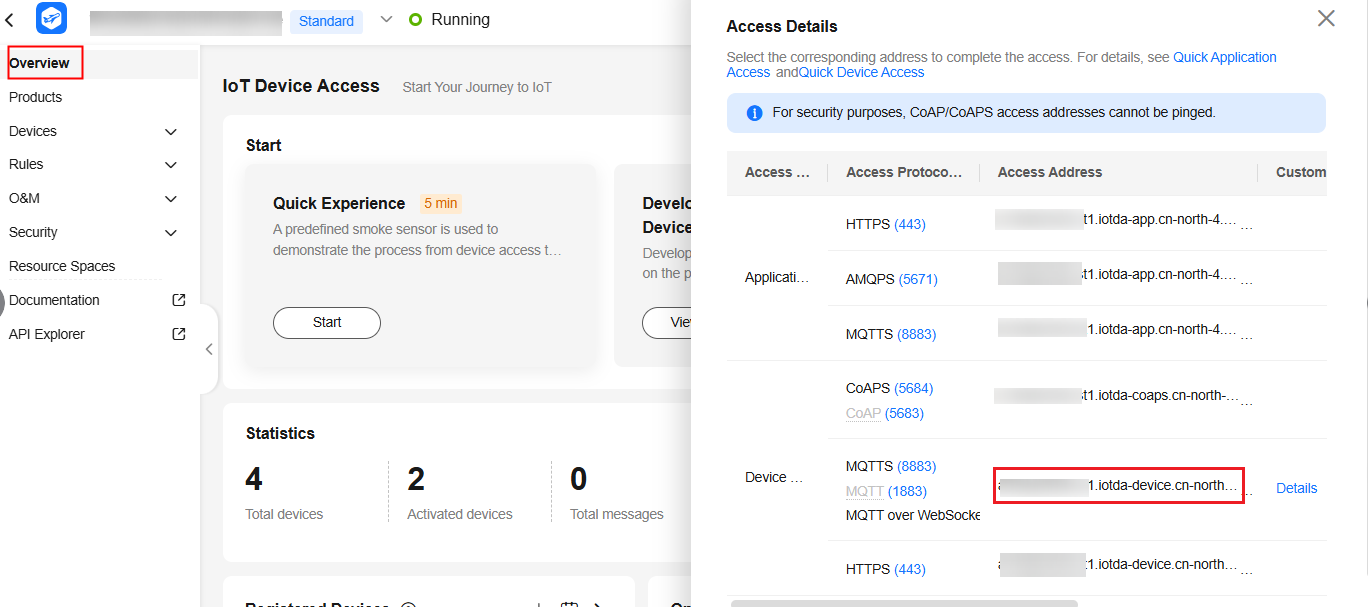
- Enter the device connection information. Enter the device ID and secret obtained during device registration and the device connection information obtained in 1. The format is ssl://Domain name:Port or ssl://IP address:Port.
1 2 3 4 5 6
// Obtaining the certificate path: Load the CA certificate of the platform and use the default ca.jks of the SDK for server verification. URL resource = MessageSample.class.getClassLoader().getResource("ca.jks"); File file = new File(resource.getPath()); // For example, modify the following parameters in MessageSample.java in the iot-device-demo file: IoTDevice device = new IoTDevice("ssl://Domain name:8883", "5e06bfee334dd4f33759f5b3_demo", "mysecret", file);
All files that involve device IDs and passwords must be modified accordingly.
- Establish a connection. Call init of the IoT Device SDK. The thread is blocked until a result is returned. If the connection is established, 0 is returned.
1 2 3
if (device.init() != 0) { return; }
If the connection is successful, information similar to the following is displayed:12023-07-17 17:22:59 INFO MqttConnection:105 - Mqtt client connected. address :ssl://Domain name: 8883
- After the device is created and connected, it can be used for communication. Call getClient of the IoT Device SDK to obtain the device client. The client provides communication APIs for processing messages, properties, and commands.

The SDK automatically enables reconnection. Upon calling device.init(), if the connection fails due to an unstable or unreachable network, or proactive disconnection by the platform, the SDK initiates reconnection in the backend.
Reporting a Message
Message reporting is the process in which a device reports messages to the platform.
- Call getClient of the IoT Device SDK to obtain the client.
- Call reportDeviceMessage to enable the client to report a device message. In the sample (MessageSample) below, messages are reported periodically.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
while (true) { device.getClient().reportDeviceMessage(new DeviceMessage("hello"), new ActionListener() { @Override public void onSuccess(Object context) { log.info("reportDeviceMessage ok"); } @Override public void onFailure(Object context, Throwable var2) { log.error("reportDeviceMessage fail: " + var2); } }); // Report messages through custom topics, which must be configured on the platform first. String topic = "$oc/devices/" + device.getDeviceId() + "/user/wpy"; device.getClient().publishRawMessage(new RawMessage(topic, "hello raw message "), new ActionListener() { @Override public void onSuccess(Object context) { log.info("publishRawMessage ok: "); } @Override public void onFailure(Object context, Throwable var2) { log.error("publishRawMessage fail: " + var2); } }); Thread.sleep(5000); }
- Modify the main function of the MessageSample class, replace the device parameters with your own device parameters, and run the MessageSample class. If the log contains the following information, the message is reported successfully:
12024-04-16 16:43:11 INFO MessageSample:98 - reportDeviceMessage ok
- On the IoTDA console, choose Devices > All Devices and check whether the device is online.
Figure 5 Device list - Device online status
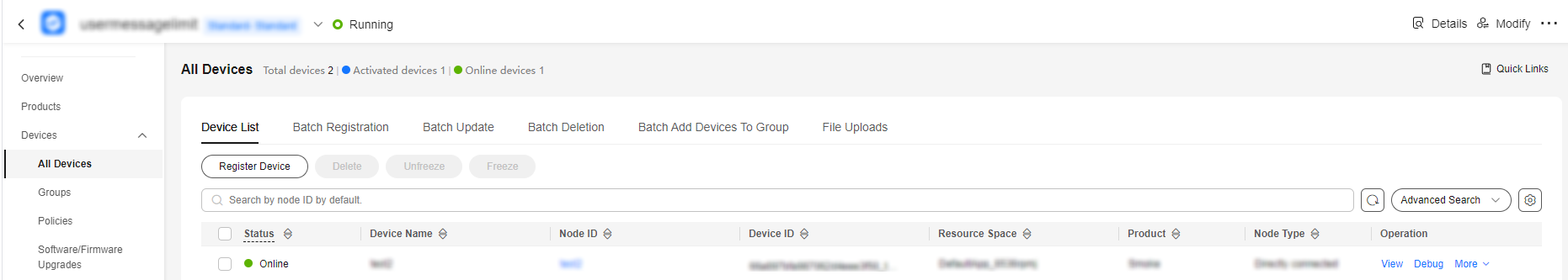
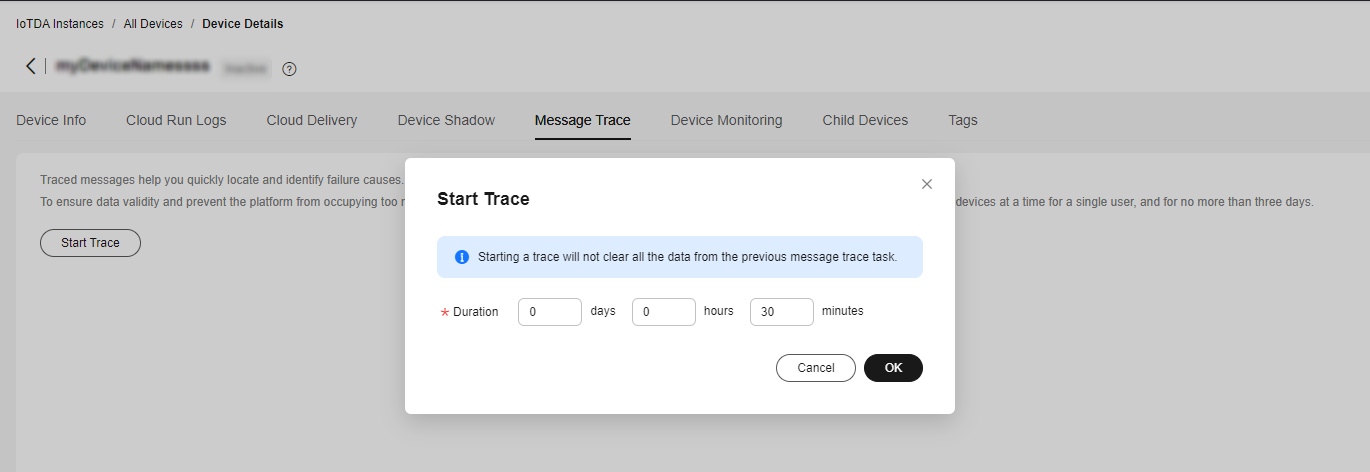
- Select the device, click View, and enable message trace on the device details page.
Figure 6 Message tracing - Starting message tracing
- Check the message tracing result to see whether the platform has received messages from the device.

Message tracing may be delayed. If no data is displayed, wait for a while and refresh the page.
Figure 7 Message tracing - Viewing device_sdk_java tracing result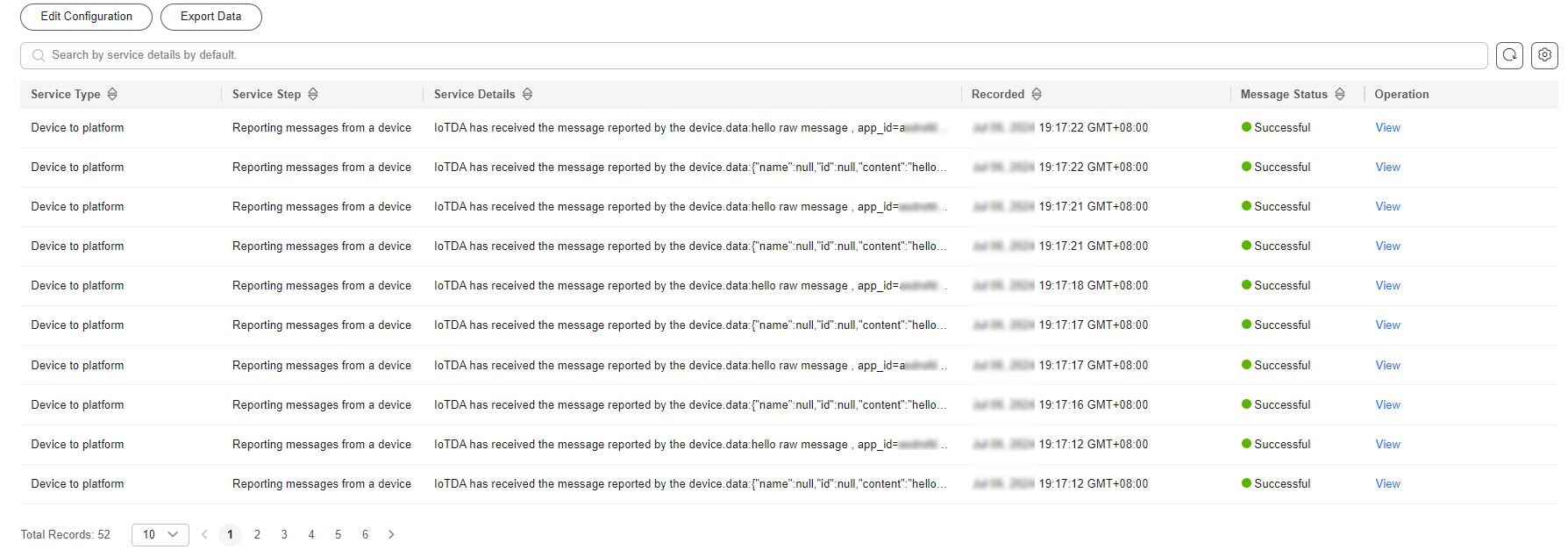
Reporting Properties
- Open the PropertySample class. In this example, the alarm, temperature, humidity, and smokeConcentration properties are periodically reported to the platform.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
// Report properties periodically. while (true) { Map<String ,Object> json = new HashMap<>(); Random rand = new Random(); // Set properties based on the product model. json.put("alarm", 1); json.put("temperature", rand.nextFloat()*100.0f); json.put("humidity", rand.nextFloat()*100.0f); json.put("smokeConcentration", rand.nextFloat() * 100.0f); ServiceProperty serviceProperty = new ServiceProperty(); serviceProperty.setProperties(json); serviceProperty.setServiceId("smokeDetector");// The serviceId must the consistent with that defined in the product model. device.getClient().reportProperties(Arrays.asList(serviceProperty), new ActionListener() { @Override public void onSuccess(Object context) { log.info("pubMessage success" ); } @Override public void onFailure(Object context, Throwable var2) { log.error("reportProperties failed" + var2.toString()); } }); Thread.sleep(10000); } }
- Modify the main function of the PropertySample class and run the PropertySample class. If the following information is displayed in the log, the property is successfully reported:
2024-04-17 15:38:38 INFO PropertySample:144 - pubMessage success
- Check the latest property values on the device details page.
Figure 8 Product model - Property reporting
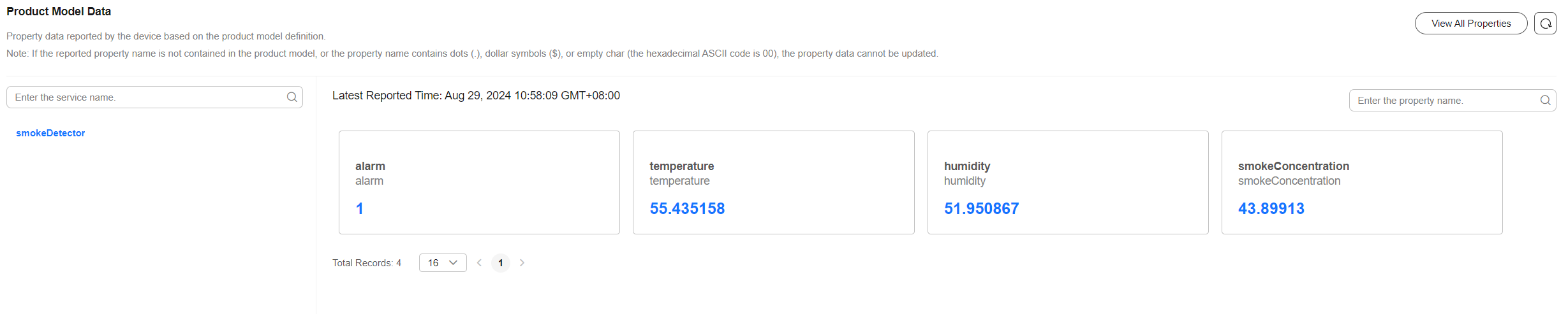
Reading and Writing Properties
- Call the setPropertyListener method of the client to set the property callback API. In PropertySample, the property reading/writing API is implemented.
- Property writing: Only the alarm property can be written.
- Property reading: Assemble the local property value based on the API format.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
device.getClient().setPropertyListener(new PropertyListener() { // Process property writing. @Override public void onPropertiesSet(String requestId, List<ServiceProperty> services) { // Traverse services. for (ServiceProperty serviceProperty : services) { log.info("OnPropertiesSet, serviceId is {}", serviceProperty.getServiceId()); // Traverse properties. for (String name : serviceProperty.getProperties().keySet()) { log.info("property name is {}", name); log.info("set property value is {}", serviceProperty.getProperties().get(name)); } } // Change the local property value. device.getClient().respondPropsSet(requestId, IotResult.SUCCESS); } /** * Process property reading. In most scenarios, you can directly read the device shadow on the platform, so this interface does not need to be implemented. * To read device properties in real time, implement this interface. */ @Override public void onPropertiesGet(String requestId, String serviceId) { log.info("OnPropertiesGet, the serviceId is {}", serviceId); Map<String, Object> json = new HashMap<>(); Random rand = new SecureRandom(); json.put("alarm", 1); json.put("temperature", rand.nextFloat() * 100.0f); json.put("humidity", rand.nextFloat() * 100.0f); json.put("smokeConcentration", rand.nextFloat() * 100.0f); ServiceProperty serviceProperty = new ServiceProperty(); serviceProperty.setProperties(json); serviceProperty.setServiceId("smokeDetector"); device.getClient().respondPropsGet(requestId, Arrays.asList(serviceProperty)); } });
- The property reading/writing API must call respondPropsGet and respondPropsSet to report the operation result.
- If the device does not allow the platform to proactively read data from the device, onPropertiesGet can be left not implemented.
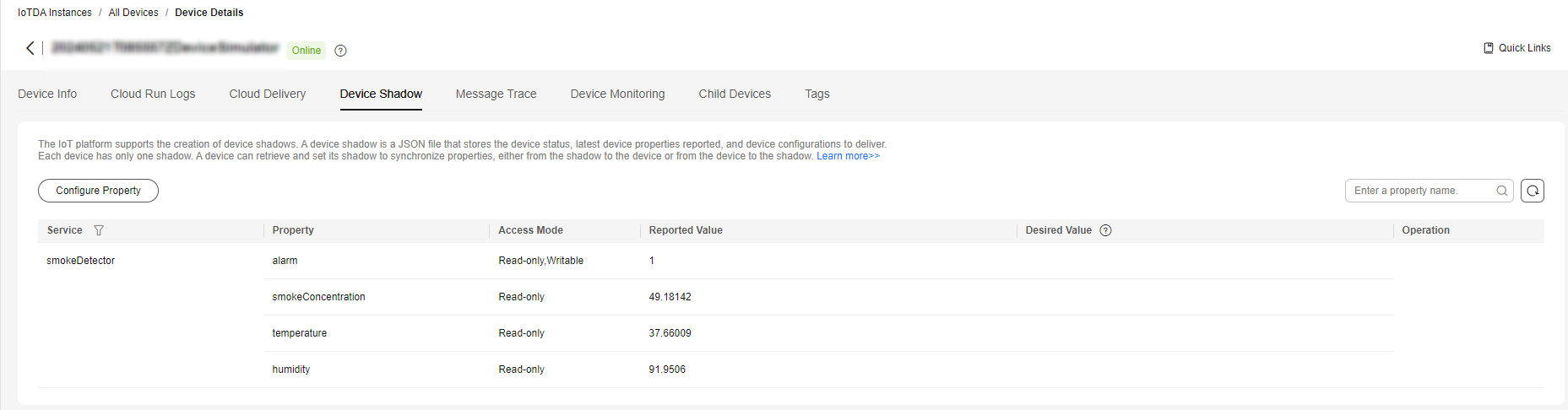
- Run the PropertySample class and check whether the value of the alarm property is 1 on the Device Shadow tab page.
Figure 9 Device shadow - Viewing property (Alarm)
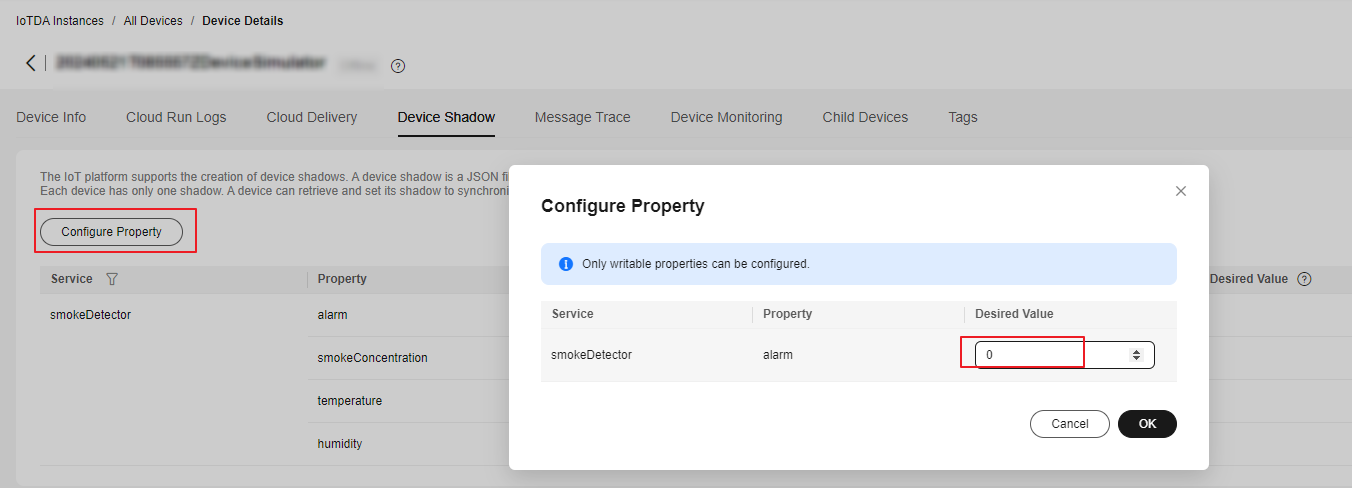
- Change the alarm property value to 0.
Figure 10 Device shadow - Configuring property (alarm)
- Check the device logs, which indicates that the device receives the property setting and the value of alarm is changed to 0.
Figure 11 Checking property settings

Delivering Commands
You can set a command listener to receive commands delivered by the platform. The callback API needs to process the commands and report responses.
- In CommandSample, the command is processed by first printing its details, and then a response is sent via respondCommand.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
device.getClient().setCommandListener(new CommandListener() { @Override public void onCommand(String requestId, String serviceId, String commandName, Map<String, Object> paras) { log.info("onCommand, serviceId = {}", serviceId); log.info("onCommand , name = {}", commandName); log.info("onCommand, paras = {}", paras.toString()); // Process the command. // Send a command response. device.getClient().respondCommand(requestId, new CommandRsp(0)); } });
- Run the CommandSample class and deliver a command on the platform. In the command, set serviceId to smokeDetector, name to ringAlarm, and paras to duration=20.
- Check logs, which indicates that the device receives the command and reports a response.
Figure 12 Checking logs

Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





