Using Event Triggers to Implement the DDL Recycle Bin, Firewalls, and Incremental Synchronization
Function Description
RDS for PostgreSQL allows you to use event triggers to implement features like the DDL recycle bin, firewalls, and incremental synchronization. Event triggers help you lower maintenance expenses. For strong database security needs, use PostgreSQL event triggers to implement the DDL recycle bin and firewalls to enhance data security.
This topic describes how to use PostgreSQL event triggers to implement the DDL recycle bin, firewalls, and incremental synchronization.
|
Function Type |
Effect |
Implementation |
|---|---|---|
|
Pre-event defense |
Blocking risky DDL operations, such as DROP TABLE, DROP INDEX, and DROP DATABASE |
Use the ddl_command_start event trigger to block unauthorized operations. |
|
Post-event backtracking |
Restoring tables from the recycle bin after they are deleted by mistake |
Use the ddl_command_end and sql_drop event triggers to record DDL operations. |
DDL Recycle Bin
Use the event triggers, pg_get_ddl_command and pg_get_ddl_drop, to collect DDL statements and save them to the ddl_recycle.ddl_log table. The triggers help you track DDL operations performed on your databases.
- Create a dedicated schema and a table.
CREATE SCHEMA ddl_recycle; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ddl_recycle.ddl_log ( id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, event_time TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT NOW(), username TEXT, database TEXT, client_addr INET, event TEXT, tag TEXT, object_type TEXT, schema_name TEXT, object_identity TEXT, command TEXT, is_dropped BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE ); - Create an event trigger function.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION ddl_recycle.log_ddl_command() RETURNS event_trigger AS $$ DECLARE cmd TEXT; obj RECORD; BEGIN SELECT query INTO cmd FROM pg_stat_activity WHERE pid = pg_backend_pid(); IF TG_EVENT = 'ddl_command_end' THEN FOR obj IN SELECT * FROM pg_event_trigger_ddl_commands() LOOP INSERT INTO ddl_recycle.ddl_log ( username, database, client_addr, event, tag, object_type, schema_name, object_identity, command ) VALUES ( current_user, current_database(), inet_client_addr(), TG_EVENT, TG_TAG, obj.object_type, obj.schema_name, obj.object_identity, cmd ); END LOOP; ELSIF TG_EVENT = 'sql_drop' THEN FOR obj IN SELECT * FROM pg_event_trigger_dropped_objects() LOOP --The original record is marked as deleted. UPDATE ddl_recycle.ddl_log SET is_dropped = TRUE WHERE object_identity = obj.object_identity AND is_dropped = FALSE; --Insert a new record to record the deletion operation. INSERT INTO ddl_recycle.ddl_log ( username, database, client_addr, event, tag, object_type, schema_name, object_identity, command, is_dropped ) VALUES ( current_user, current_database(), inet_client_addr(), TG_EVENT, TG_TAG, obj.object_type, obj.schema_name, obj.object_identity, cmd, TRUE ); END LOOP; END IF; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql; - Register an event trigger.
CREATE EVENT TRIGGER ddl_recycle_trigger ON ddl_command_end EXECUTE FUNCTION ddl_recycle.log_ddl_command(); CREATE EVENT TRIGGER ddl_drop_trigger ON sql_drop EXECUTE FUNCTION ddl_recycle.log_ddl_command();
After the execution is complete, the DDL statements are recorded in the test_ddl.tb_ddl_command table.
- Run a DDL statement and check whether changes can be recorded.
create table ddl_recycle.a(id int); select * from ddl_recycle.ddl_log;
Figure 1 Checking the execution result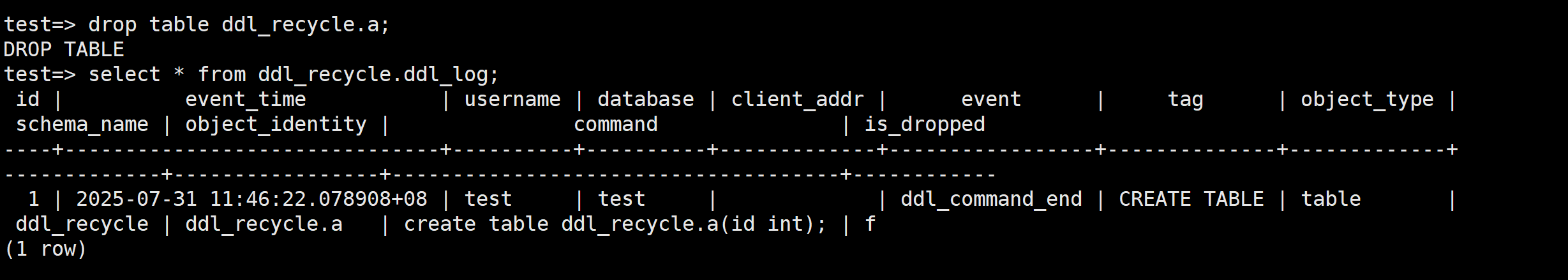
DDL Firewall
You can create event triggers as needed and use the ddl_command_start event to block the execution of specific DDL statements.
- Create a table containing firewall rules.
CREATE SCHEMA IF NOT EXISTS ddl_firewall; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ddl_firewall.rules ( id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, username TEXT, tag TEXT, pattern TEXT, action TEXT CHECK (action IN ('BLOCK', 'LOG')), created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT NOW() ); - Create a firewall trigger function.
RETURNS event_trigger AS $$ DECLARE cmd TEXT; rule RECORD; is_blocked BOOLEAN := FALSE; BEGIN SELECT query INTO cmd FROM pg_stat_activity WHERE pid = pg_backend_pid(); FOR rule IN SELECT * FROM ddl_firewall.rules WHERE (username = current_user OR username = '*') AND (tag = TG_TAG OR tag = '*') ORDER BY id LOOP IF cmd ~ rule.pattern THEN IF rule.action = 'BLOCK' THEN RAISE EXCEPTION 'DDL operation blocked by rule: %', rule.id; ELSIF rule.action = 'LOG' THEN INSERT INTO ddl_recycle.ddl_log ( username, database, client_addr, event, tag, command ) VALUES ( current_user, current_database(), inet_client_addr(), 'FIREWALL_LOG', TG_TAG, cmd ); END IF; END IF; END LOOP; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql; - Register an event trigger.
CREATE EVENT TRIGGER ddl_firewall_trigger ON ddl_command_start EXECUTE FUNCTION ddl_firewall.check_ddl();
- Add firewall rules.
insert into ddl_firewall.rules values(1,'test', 'DROP TABLE', '', 'BLOCK');
- When you try to delete the table as the user test, the deletion is blocked.
create table ddl_firewall.a(id int); drop table ddl_firewall.a;
Figure 2 Checking the execution result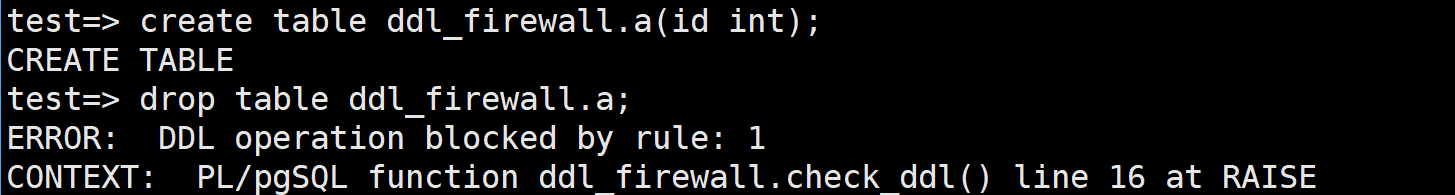
DDL Incremental Synchronization
The publisher stores executed DDL statements in the ddl_recycle.ddl_log table. The subscriber can read the records to synchronize data.
- Create a publication on the publisher.
CREATE PUBLICATION my_ddl_publication FOR TABLE ONLY ddl_recycle.ddl_log;
- Create the same table on the subscriber.
CREATE SCHEMA ddl_recycle; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ddl_recycle.ddl_log ( id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, event_time TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT NOW(), username TEXT, database TEXT, client_addr INET, event TEXT, tag TEXT, object_type TEXT, schema_name TEXT, object_identity TEXT, command TEXT, is_dropped BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE ); - Create a subscription on the subscriber.
CREATE SUBSCRIPTION my_ddl_subscriptin CONNECTION 'host=*** port=*** user=*** password=*** dbname=**' PUBLICATION my_ddl_publication;
- Create a trigger for the ddl_recycle.ddl_log table on the subscriber to implement incremental synchronization of DDL statements.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





